In a significant move ‚ÄĆagainst gender-based violence, Members of Parliament in The‚Äć Gambia‚Ā£ have voted to‚Äć uphold the ban on‚Äč female genital‚Ā£ mutilation (FGM), ‚Äća longstanding practice that has affected countless women and girls across the nation. This decisive action comes amid growing international awareness ‚Äćand condemnation of FGM, which has been recognized as ‚Ā£a violation of human‚ĀĘ rights and a serious public health issue. The Gambian legislature‚Äôs recent decision reflects a broader commitment to advancing women’s rights, safeguarding health, and promoting the empowerment of girls in the ‚Ā§country. As activists celebrate this legislative‚Äć victory, the debate ‚ĀĘsurrounding FGM continues to shape ‚Äčthe dialog on gender equality and cultural practices within The Gambia and beyond.
MPs Support Legislation to End‚Äč Female Genital Mutilation in The Gambia
the recent decision by Members of Parliament in The Gambia marks a significant step forward in ‚Äćthe fight‚ÄĆ against female genital mutilation (FGM). This legislation, now upheld, not only reinforces the existing ban but also aims to ensure stricter enforcement and greater awareness. The ‚Äćparliamentary debate highlighted the urgent need for societal change and the protection‚Äć of women’s rights, with key points including:
- Protection of women‚Äôs Health: emphasis on the physical and psychological ‚Äčimplications of FGM.
- Cultural Sensitivity: acknowledgment of the cultural practices surrounding FGM,paired with reevaluation‚Ā£ for the sake of women‚Äôs well-being.
- Community Education: Initiatives to raise awareness about the dangers and illegality of FGM.
The passing of ‚Äćthis legislation represents a unifying commitment among lawmakers to advocate‚Äć for women’s rights and safeguard future generations. With the support of various stakeholders, ‚Ā£including NGOs and international bodies, there is a hopeful outlook on the potential ‚ĀĘimpact of this legislation. The ‚ĀĘgovernment is poised to implement comprehensive strategies to monitor‚Ā£ compliance,which may include:
| Strategy | Objective |
|---|---|
| Awareness Campaigns | Educate communities about the harms of FGM |
| Law Enforcement Training | Equip law enforcement with the knowledge to enforce the ban effectively |
| Support Services | Provide psychological and medical support for survivors |
The Societal Impact of Upholding the ban on Female Genital Mutilation
The decision by Members of Parliament in The Gambia to uphold ‚ĀĘthe ban on female genital mutilation (FGM) serves as a pivotal moment ‚ÄĆin the fight for women‚Äôs rights‚ĀĘ and health.‚ÄĆ By reinforcing this legislation, the government signals a commitment to protecting the rights of women and girls, ultimately fostering a culture‚ĀĘ of empowerment and dignity. This ‚Ā§legal ‚ĀĘmove is accompanied by a‚ĀĘ broader societal shift that emphasizes the importance of education and awareness surrounding the physical and psychological dangers of FGM. As communities begin ‚ÄĆto understand the implications of ‚ĀĘthese ‚Ā§practices, they are more likely to‚ĀĘ champion the ‚Äćrights of‚Äč women, leading to a transformative approach that prioritizes health and‚Ā£ autonomy.
The implications of maintaining ‚ĀĘthis ban extend beyond ‚Äčthe legal ‚Äćframework, fostering‚Äć a ripple effect throughout gambian society. Some of the key societal benefits may‚Ā§ include:
- Improved Public Health: ‚ĀĘ Reducing FGM cases can‚ÄĆ lead‚ĀĘ to lower ‚ÄĆinstances of complications during childbirth, and also decreased mental health issues.
- community Empowerment: Encouraging dialogue about women’s ‚Äčrights cultivates a sense of solidarity among women, strengthening community ties.
- Economic Growth: Empowered women contribute significantly to the workforce, leading ‚Ā§to ‚ÄĆincreased economic development.
As the Gambia embarks on this new chapter,‚Äč it is indeed imperative for all stakeholders, including ‚ÄĆgovernment entities, NGOs, and community leaders, to collaborate in ‚Äćadvancing education and preventive measures. The collective effort to uphold the ban signifies a monumental stance ‚Äčagainst a deeply entrenched tradition and‚ĀĘ heralds a future where women’s voices are no longer silenced.

Healthcare Perspectives on Female Genital ‚ÄčMutilation and ‚ÄĆWomen’s Rights
Recent developments in The ‚Ā£Gambia highlight a‚Äć significant‚ÄĆ shift in healthcare perspectives regarding female genital mutilation (FGM) and women’s rights. The passage of a‚Äč law aimed ‚Äćat reinforcing the ‚ĀĘban on FGM demonstrates a growing recognition ‚Äćof its harmful ‚Äćeffects, not only on women’s physical ‚Ā£health but also on ‚Äčtheir psychological well-being. studies indicate that FGM can lead to a myriad of health complications, including chronic pain, infections, and even complications during childbirth. By prioritizing the health and‚ÄĆ rights of women,Gambian lawmakers‚Äć are ‚Ā§responding‚ĀĘ to‚Ā£ calls ‚Ā§from both local and international communities to take a stand against this practice.
in addressing the implications of this ‚ÄĆlegislation, it is indeed vital to consider the broader context of women’s rights in‚Ā£ The Gambia.‚Äč Upholding the ban on FGM ‚Ā£is a crucial step toward gender ‚Äčequality ‚Ā£and women’s empowerment. The following points summarize the anticipated benefits of this ruling:
- Improved Health‚Äč Outcomes: Decreasing ‚Äčthe prevalence of FGM ‚ĀĘleads to better overall health‚Ā§ for women and girls.
- Psychological‚Äć Benefits: Reducing ‚ĀĘthe‚ĀĘ incidence of FGM can alleviate trauma and promote mental health.
- Cultural Shift: Encouraging societal change that supports women’s rights and autonomy over their own bodies.
- Legal Precedent: Strengthening‚Ā£ laws‚ÄĆ supports victims and provides a‚ĀĘ framework ‚Äćfor enforcement.

Community Education and Awareness: Key‚ĀĘ Strategies for Implementation
Effective community‚ĀĘ education is ‚Ā§vital for fostering understanding and ‚Äčinitiating behavioral change regarding sensitive ‚Äčissues, such as ‚Ā£female genital mutilation (FGM). Key strategies for successful‚ĀĘ implementation include:
- Engagement of‚Äć Local Leaders: Involving community leaders fosters trust and ensures that educational messages resonate with ‚Äčcultural values.
- Interactive ‚ÄćWorkshops: Hands-on learning ‚Äćexperiences can help demystify misconceptions surrounding FGM‚ĀĘ and ‚Äćemphasize the health ‚ÄĆrisks‚ĀĘ associated with the practice.
- Utilization of Local Media: Collaborating with community radio stations and local newspapers can broaden the reach of educational campaigns.
- Tailored Educational Materials: Creating culturally‚Äć relevant content that addresses the unique needs of‚ĀĘ different demographics enhances‚Ā§ receptiveness to the‚Ā£ information presented.
Furthermore, establishing ‚ĀĘsupport networks can significantly aid in the reinforcement ‚ĀĘof anti-FGM‚Äć campaigns. Community‚Ā§ support structures may include:
| Support Network | Description |
|---|---|
| Women’s Groups | A platform for ‚Ā§sharing experiences and strategies to resist FGM. |
| Health Educators | Professionals who ‚ÄĆprovide information on‚ĀĘ the health implications of FGM. |
| Youth Advocacy Platforms | Engaging young peopel to spread awareness and promote social change. |

International Responses and Future Implications for The Gambia
The recent decision by the‚Ā£ Gambian parliament to uphold‚ÄĆ the ban on female genital mutilation (FGM) has garnered significant attention on the ‚ÄĆinternational stage, reflecting a‚Ā§ broader‚Äć commitment to protecting women’s rights and health. Global organizations, such as the United Nations and the World Health Organization, have praised this legislative ‚Ā§move, emphasizing that it aligns with international ‚Äčstandards ‚Ā£for human rights ‚ÄĆand gender equality. Analysts suggest that the decision could set a precedent in West Africa, encouraging neighboring countries‚Ā§ to adopt similar prohibitions against FGM. Such actions resonate with the Lasting Development Goals,‚Äć particularly‚Äć Goal 5, which aims to achieve gender equality and empower all women and girls by 2030.
However, while the ban is a progressive step, its implementation remains a crucial challenge. Many communities still uphold cultural practices that involve FGM,‚Äć and there is a pressing need for ‚Ā§comprehensive education and advocacy to change mindsets. Key strategies for successful enforcement include:
- Public Awareness Campaigns: ‚ÄĆCollaborating with ‚Ā£local leaders to advocate against FGM.
- Legal Support: Strengthening law enforcement ‚Ā£mechanisms to prosecute offenders.
- Community Engagement: Involving community members in ‚Ā£discussions‚Äć about the health risks and human rights implications of‚Äč FGM.
Future international ‚ÄĆresponses may ‚ÄĆinclude funding for local NGOs working towards education and prevention initiatives,as well as fostering partnerships with governments in the region to promote shared learning and best‚ÄĆ practices. ‚Ā§With sustained global interest and local commitment, the move to uphold‚Äč the ban on FGM in The Gambia‚Äć could herald a positive shift in societal norms surrounding women’s health and rights across West Africa.

Recommendations for Strengthening Enforcement of the Ban on Female Genital Mutilation
To effectively‚Ā§ strengthen ‚ÄĆthe enforcement of the ban on‚Ā£ female genital ‚Ā£mutilation (FGM) in The gambia, a multifaceted approach must be adopted.First and foremost, it is essential to establish clear‚ĀĘ lines of accountability ‚Ā£ among law enforcement agencies, ensuring that officers are trained‚Äč and resourced‚Ā§ to‚Äć act against violations.Community engagement initiatives should be launched, ‚Ā£prioritizing education and awareness campaigns that target both men and women, emphasizing the health‚Ā§ risks and human rights ‚ĀĘimplications of FGM.additionally, collaboration with local leaders and health practitioners can foster trust and facilitate open dialogues within communities.
Furthermore, implementing a robust reporting ‚Äćmechanism is crucial to enable victims and witnesses to safely report‚Ā§ incidents ‚Äćof ‚ÄćFGM without fear of ‚Ā£reprisal. This system could include anonymous hotlines and support services that cater to ‚Äčthe needs of affected individuals. To ensure the sustainability of these measures, it is vital to monitor and evaluate the impact of enforcement actions ‚ĀĘregularly.Setting up a dedicated task force to oversee these initiatives could enhance coordination and ‚Äčimprove overall strategies against ‚ÄćFGM.Below is a table summarizing key recommendations for enforcement:
| Recommendation | Description |
|---|---|
| Accountability | Establish clear accountability within law enforcement agencies. |
| Education | Launch awareness campaigns‚Ā§ focusing on health risks and‚ÄĆ human‚Ā£ rights. |
| Support Mechanisms | Implement anonymous reporting hotlines and victim‚Äć support services. |
| Task Force | Create a dedicated task‚ĀĘ force to oversee FGM enforcement measures. |
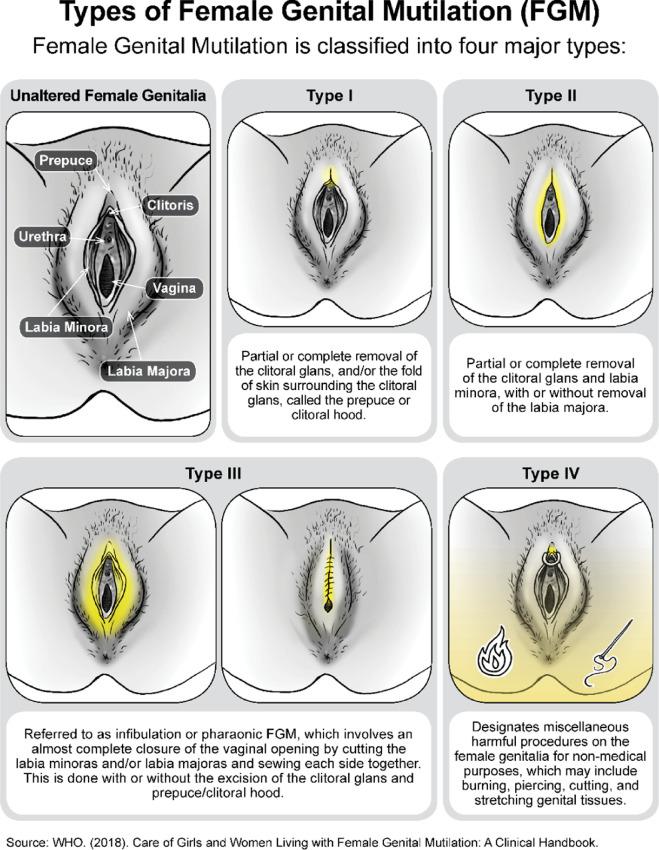
To Conclude
the recent ‚ĀĘdecision‚ÄĆ by Members of Parliament ‚Ā£in The Gambia to uphold the‚Äć ban on female genital mutilation (FGM) marks a significant step ‚Äćforward in the country’s efforts to protect women’s rights and health. This legislative move not only reinforces the government’s commitment to eradicating FGM but also aligns with international human rights standards. As awareness around the dangers and ethical implications of FGM continues to grow, the Gambia’s stance reflects a broader cultural shift towards valuing and safeguarding the‚Äć rights of women and girls.‚Ā§ However, challenges remain in the implementation and enforcement of ‚Äčthis ban, necessitating ‚Ā§collaborative efforts‚Äč between authorities, civil society, and communities to foster a sustained commitment to ending this practice. The decision signals hope for a future where Gambian women can live free from the harmful effects ‚ÄĆof FGM, paving the way for improved health outcomes and greater gender equality in the region.