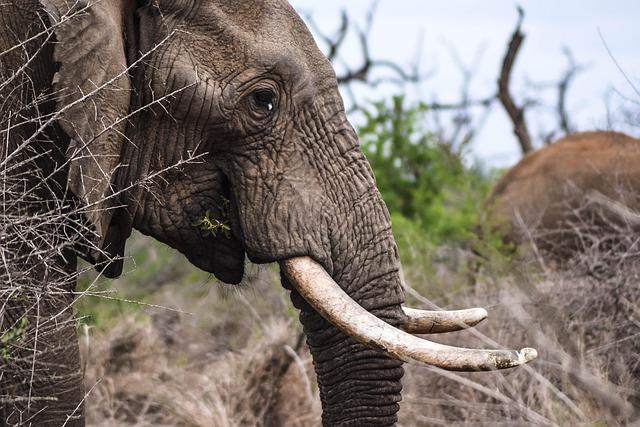
In a remarkable revelation for wildlife conservation, a new survey has solidified GabonS status as the largest stronghold for critically endangered african forest elephants. Conducted by the Wildlife Conservation Society (WCS), this extensive study underscores the vital importance of Gabon’s dense jungles as a refuge for these majestic creatures, whose populations have dwindled alarmingly due to poaching adn habitat loss. The findings, which highlight not only the number of elephants residing in Gabon but also the ecological significance of this region, are a clarion call for immediate protective measures and greater global awareness. As the plight of African forest elephants becomes increasingly dire, Gabon’s role as a bastion for their survival is more crucial than ever. This article delves into the details of the survey, its implications for conservation efforts, and the ongoing challenges faced by these elusive giants.
Gabon Emerges as the Primary Sanctuary for Critically Endangered African Forest Elephants

Recent surveys reveal that Gabon is quickly establishing itself as a bastion for the critically endangered African forest elephants, with significant populations thriving in the countryﻗs vast protected areas. The Wildlife Conservation Society (WCS) has documented a remarkable resurgence in elephant numbers, signaling success in conservation efforts and habitat protection. Gabonﻗs extraordinary body of laws and policies aimed at ecological preservation has made it a prime location for these majestic creatures to flourish. key contributing factors to this positive trend include:
- Extensive Protected Areas: Over 11 national parks cover nearly 12% of the countryﻗs land, providing safe havens for elephants.
- Community Engagement: Local communities play a crucial role in conservation efforts, participating in anti-poaching initiatives.
- Strong Legislative Framework: Rigorous wildlife protection laws help in the deterrence of illegal hunting and logging activities.
This new data underscores Gabon’s unique position as a sanctuary for the African forest elephant. The ongoing research spearheaded by WCS highlights the importance of continuous monitoring and adaptive management strategies to ensure these populations remain stable amidst environmental threats. Gabon is not only a haven for elephants but also an essential component of the global biodiversity landscape. It is crucial to maintain support for these initiatives to protect a species that plays a vital role in its ecosystem.
| Conservation Efforts | Description |
|---|---|
| Anti-Poaching Patrols | Regular patrols to prevent illegal hunting activities. |
| Habitat Restoration | Efforts to restore degraded habitats vital for elephant survival. |
| Research and Monitoring | Ongoing studies to track population health and migration patterns. |
Survey Findings Reveal Population Trends and Conservation Successes in Gabon

the latest survey results shed light on the current status of Gabon’s wildlife and underscore the country’s pivotal role in global conservation efforts. Notably, gabon has emerged as the largest stronghold for the critically endangered African forest elephants, with recent population estimates indicating a significant increase.The survey highlighted key findings that indicate triumphant conservation strategies, which include:
- Increased Anti-Poaching Patrols: Enhanced law enforcement efforts have successfully deterred illegal hunting.
- Community Engagement: Local communities are taking an active role in conservation, fostering a sense of ownership over their natural resources.
- Protected Areas Expansion: New conservation areas have been designated, providing crucial habitats for various species.
In addition to the rise in elephant populations, the survey revealed broader ecological benefits related to these conservation efforts. For instance, Gabon’s dense forests have seen improvements in biodiversity, with several species returning to habitats previously threatened by poaching and habitat destruction. The following table displays the population changes of key species in Gabon, reflecting the positive trends resulting from these conservation initiatives:
| Species | Population Estimate (2022) | Change from 2018 (%) |
|---|---|---|
| African forest Elephant | 12,000 | +25% |
| Western Lowland Gorilla | 4,500 | +18% |
| Chimpanzee | 10,000 | +30% |
The Importance of gabon’s Ecosystems for Global Biodiversity Preservation

Gabon stands as a pivotal region in the global effort to safeguard biodiversity, especially in the context of its unique ecosystems. The country is home to an extensive array of wildlife and habitats, many of which play a crucial role in the health of the planet’s ecological balance. The rich tropical rainforests, coastal mangroves, and savanna ecosystems provide sanctuary to countless species, including the critically endangered African forest elephant. This vibrant biota not only underscores the importance of ecological preservation but also highlights Gabonﻗs role as a living laboratory for conservation strategies applicable worldwide.
Preserving Gabon’s ecosystems fosters global biodiversity through several key functions:
- Carbon Sequestration: Gabonﻗs forests act as vital carbon sinks,helping mitigate climate change.
- Habitat for Endangered Species: The diversity of habitats supports not just elephants but numerous threatened species.
- Water Cycle Regulation: These ecosystems play a significant role in maintaining local and regional hydrological cycles.
To emphasize Gabon’s vital role in biodiversity, the following table outlines the critical importance of its ecosystems:
| Aspect | Importance |
|---|---|
| Forest Coverage | 70% of Gabon’s land area, supporting myriad species |
| Unique Flora | Over 8,000 plant species, many found nowhere else |
| Indigenous communities | Stewards of the land, maintaining customary ecological knowledge |
Strategies for Enhancing Protection Efforts for African Forest Elephants in Gabon

The alarming reality of declining populations of African Forest Elephants necessitates innovative strategies to bolster their protection in Gabon. Collaborative partnerships between governmental agencies, local communities, and conservation organizations can create a formidable approach. These partnerships should focus on:
- Strengthening the enforcement of anti-poaching laws to deter illegal hunting.
- Implementing community-based programs to educate residents on the importance of elephants in maintaining ecosystem balance.
- Enhancing surveillance technologies, such as drones and camera traps, to monitor elephant populations and track poaching activities.
- promoting ecotourism initiatives that provide enduring income for communities while fostering a culture of conservation.
Investing in habitat restoration is equally critical; protecting and expanding the natural habitats of these elephants will ensure their survival. Addressing factors such as deforestation and climate change is vital, as they pose significant threats to elephant habitats. A comprehensive conservation strategy should include:
- Mapping and protecting key migratory corridors that connect fragmented habitats.
- Restoring degraded ecosystems to increase biodiversity and provide adequate food sources for the elephants.
- Conducting regular population assessments to adapt management practices effectively and ensure the resilience of local elephant populations.
- Engaging local and indigenous communities in conservation efforts to foster a shared stewardship of natural resources.
Community Engagement: The Role of Local Populations in Elephant Conservation

Local populations play a pivotal role in the conservation of critically endangered African forest elephants, especially in regions like Gabon, where these majestic creatures find their largest stronghold. Community engagement fosters a deeper understanding among residents about the ecological significance of elephants and their role in maintaining healthy ecosystems. Through educational initiatives, locals are empowered to participate actively in conservation efforts, which helps to build a sense of shared responsibility.This is crucial as communities that rely on natural resources often hold the key to sustainable management practices, contributing to both conservation and economic stability.
Evidence shows that integrating local knowledge and traditions into conservation strategies leads to more effective protection measures. the following strategies exemplify how local communities can actively engage in elephant conservation:
- Community Conservation Programs: Initiatives that incentivize local stewardship over natural resources.
- Wildlife Monitoring: Training locals to participate in tracking elephant populations and recognizing their habitats.
- Conflict Mitigation: Implementing solutions that address human-elephant conflict through dialogue and resource sharing.
- Ecotourism Progress: Promoting responsible tourism that benefits both the economy and conservation efforts.
| Engagement strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Education Programs | Workshops that inform locals about elephant behavior and conservation. |
| Resource Sharing | Collaboration with NGOs to provide resources for local conservation projects. |
| Monitoring Initiatives | Local guides working with conservationists to survey elephant populations. |
International Collaboration Essential for Sustaining Gabon’s Forest Elephant Population

As new evidence reveals Gabon as the largest sanctuary for the critically endangered African forest elephants, the need for international collaboration becomes increasingly apparent. To effectively bolster conservation efforts, nations and organizations must join forces to address the multifaceted challenges faced by these majestic creatures. Sustainable management and protection of their habitat require a unified approach that encompasses:
- Research and Monitoring: Collaborative studies can provide crucial insights into the population dynamics and health of the forest elephant population.
- Anti-Poaching Initiatives: Joint operations across borders can enhance patrolling efforts and resource allocation to combat poaching.
- Community Engagement: Programs promoting local involvement can foster a sense of stewardship among communities living near elephant habitats.
- policy Development: Harmonizing wildlife protection laws across nations will facilitate consistent conservation measures.
Moreover, conservationists are urged to create platforms for knowledge exchange and resource sharing among various stakeholders. This can include:
| Collaborative Initiatives | Impact |
|---|---|
| Wildlife Protection Treaties | Strengthened legal frameworks to combat illegal trafficking. |
| Joint Research Programs | Enhanced understanding of species behavior and habitat needs. |
| Public Awareness Campaigns | Increased local and global support for elephant conservation. |
By fostering these alliances, Gabon’s efforts in conservation not only protect the remaining forest elephants but also serve as a model for wildlife management globally. Through shared knowledge and coordinated action, the future of these critical ecosystems can be secured, marking a definitive step towards sustainable coexistence. The survival of the african forest elephant hinges on how effectively the global community can unite in purpose and strategy.
Insights and Conclusions
the recent survey conducted by the wildlife Conservation Society highlights Gabon’s critical role as a sanctuary for the endangered African forest elephants. This pivotal finding not only underscores the importance of Gabon’s diverse ecosystems in sustaining biodiversity but also serves as a clarion call for ongoing conservation efforts. as we face escalating threats from habitat loss and poaching, the data from this survey reinforces the need for collaborative initiatives between governments, ngos, and local communities to protect these magnificent creatures and their habitats.The future of African forest elephants hangs in the balance, and it is indeed incumbent upon all stakeholders to ensure that Gabon remains a stronghold for these iconic species. Continued surveillance, protective legislation, and community engagement will be essential as we move forward in the fight against wildlife extinction. in safeguarding the forests of Gabon, we are not only preserving a vital ecological heritage but also ensuring the survival of a species that plays a crucial role in maintaining the health of its environment.