In a meaningful stride towards public health innovation and disease eradication, three Central African nations have pledged thier commitment to the global fight against Guinea worm disease, a debilitating illness that has plagued communities for decades. In a joint proclamation facilitated by the World health Institution (WHO), officials from these countries highlighted their strategic plans to eliminate the transmission of the parasitic infection, which is primarily found in rural and impoverished areas. This united effort not only underscores a renewed dedication to improving health outcomes but also aims to galvanize international support and resources to eradicate this preventable disease once and for all.as Guinea worm disease edges closer to extinction, the collaborative framework established by these countries could serve as a model for similar public health initiatives around the globe.
Commitment of Central African countries to combat Guinea-worm Disease
In a landmark agreement facilitated by the World Health Organization, three nations in Central Africa have pledged to intensify their efforts in the global fight against Guinea-worm disease.This parasitic infection,once prevalent in the region,has seen considerable decline thanks to ongoing health initiatives. The commitment marks a significant step forward, as these countries aim to build on past successes and implement more rigorous surveillance and education programs. Key strategies include:
- Community Awareness Campaigns: Educating local populations about disease transmission and prevention.
- Enhanced Surveillance: Strengthening data collection and monitoring mechanisms to track cases and outbreaks.
- Collaboration with Local Health Authorities: Engaging local governments to ensure sustained efforts against the disease.
The agreement signifies a collective recognition of the public health threat posed by Guinea-worm disease and underscores the importance of regional cooperation. Through joint initiatives, the countries are expected to share resources and best practices, which can lead to innovative solutions tailored to local contexts. A strategic framework has been developed, focusing on immediate and long-term goals, as summarized in the table below:
| Goals | Timeline | Expected Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
| Increase awareness among vulnerable communities | 2024 | Reduction in new infections |
| Improve detection and reporting mechanisms | 2025 | Higher reporting rates |
| Enhance collaboration between countries | Ongoing | Shared resources and strategies |

Understanding the Impact of Guinea-worm Disease on Public Health
The resurgence of Guinea-worm disease poses a significant threat to public health, particularly in regions with limited access to clean water and healthcare resources.Characterized by painful lesions caused by the emergence of the Guinea worm from the body, this neglected tropical disease significantly hinders daily activities, affecting individuals’ ability to work and care for their families. The consequences extend beyond physical suffering; communities face economic challenges as productivity declines and healthcare costs increase. Confronting this disease necessitates a comprehensive approach that engages local populations and emphasizes sustainable water and sanitation practices.
In a groundbreaking commitment, three Central African countries have pledged to eradicate Guinea-worm disease through concerted efforts supported by the World Health Organization. This initiative emphasizes the importance of community education and awareness programs about the disease’s transmission, prevention, and management.The collaboration aims to establish strong surveillance systems and healthcare infrastructures while integrating customary practices. The following table highlights the crucial components of tackling Guinea-worm disease:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Community Engagement | involving local leaders and health workers to educate populations. |
| Water Safety | Implementing filtration systems and improving access to clean water sources. |
| Surveillance | Monitoring cases and potential outbreaks for effective response. |
| Healthcare Access | Strengthening healthcare facilities to support treatment and prevention. |

Collaborative Strategies for Disease Eradication in Central Africa
The commitment of three Central African nations to eradicate Guinea-worm disease highlights a pivotal approach in combating infectious diseases through collaborative strategies.By leveraging resources and expertise across borders, these countries aim to implement a comprehensive plan that addresses the social and environmental factors contributing to the disease’s persistence. Key strategies include:
- Joint Surveillance: Establishing unified systems for tracking and monitoring the disease’s spread.
- Community Engagement: Mobilizing community health workers to educate populations on prevention techniques, such as filtering drinking water.
- Resource Sharing: Pooling financial and logistical resources to enhance access to healthcare and sanitation facilities.
Moreover, the collaborative framework fosters stronger relationships between governmental health bodies and NGOs, creating a robust network of support and innovation. By integrating traditional knowledge and modern scientific approaches,stakeholders can develop tailored interventions that resonate with local communities. Addressing the root causes through:
| Root Cause | Intervention |
|---|---|
| Poor Water Supply | Installation of safe water sources and filtration systems |
| Inadequate Health Education | Community-led health workshops and training |
| Neglected Tropical Diseases | Integrated disease control programs |

The Role of the World Health Organization in Supporting National Efforts
The World Health Organization (WHO) plays a pivotal role in galvanizing international support and resources for countries striving to eliminate Guinea-worm disease. By providing technical assistance, strategic guidance, and robust surveillance systems, the WHO enables nations to strengthen their health systems and effectively mobilize communities in the fight against this debilitating illness. Among its many initiatives, the organization fosters collaboration between governments, NGOs, and local organizations to ensure a unified approach toward disease eradication.
In particular, WHO’s funding and logistical expertise help facilitate:
- Capacity Building: Training healthcare workers and local communities on disease prevention strategies.
- Data Sharing: Establishing a framework for real-time disease tracking and analysis.
- resource allocation: Assisting in the procurement and distribution of disease management tools.
This concerted effort aligns with the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals, channeling global attention towards eliminating Guinea-worm disease and fostering a healthier future for affected populations.

Recommendations for Strengthening Local Health Systems
To effectively combat Guinea-worm disease and strengthen local health systems, it is indeed essential for the governments of the Central African nations to adopt a multi-faceted approach. Key recommendations include focusing on community engagement to raise awareness about disease transmission and prevention. Local stakeholders, including tribal leaders and health workers, should be mobilized to educate populations on the importance of sanitation and hygiene practices.Moreover, enhancing surveillance systems will allow for timely reporting of cases and better resource allocation, which is crucial for implementing targeted interventions.
Investing in infrastructure development, particularly in rural areas, is vital for improving access to health services. This can be achieved by:
- Establishing health posts that offer diagnostic services and treatment for Guinea-worm disease.
- Training healthcare personnel to recognize symptoms and manage cases effectively.
- Ensuring the supply of clean water to prevent the disease’s transmission.
To facilitate resource management, a framework can be established to track progress, allocate funds efficiently, and ensure communities are resilient in the face of public health challenges. Below is a simplified overview of necessary infrastructure improvements:
| Infrastructure Component | Action Required |
|---|---|
| Health Posts | Construct and staff with trained personnel |
| Water Supply Systems | Develop clean water sources and storage solutions |
| Community Sanitation Facilities | Build latrines and promote waste management |
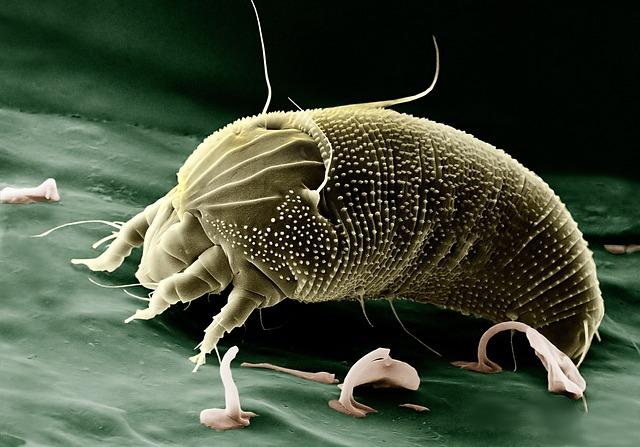
Future Prospects and Challenges in Achieving Disease Eradication Goals
The commitment of the three Central African countries to eradicate Guinea-worm disease represents a significant milestone in global health initiatives. However, achieving these ambitious eradication goals will not be without its hurdles. One of the primary challenges lies in the need for sustained funding and international support, which are crucial in ensuring the continuity of public health programs. Additionally, the following factors will play a critical role:
- Community Engagement: Local populations must be actively involved in prevention efforts to ensure adherence to health directives.
- Health Infrastructure: Strengthening health systems to improve surveillance and treatment capabilities will be vital.
- Environmental Factors: Addressing barriers such as water safety where the disease is prevalent can pose logistical challenges.
Moreover, overcoming misinformation and cultural beliefs can hinder progress. Public awareness campaigns must be tailored to counteract misconceptions about Guinea-worm disease and emphasize the importance of preventive measures. Besides, assessing the impact of climate change on disease spread could further complicate the eradication process. To encapsulate the multifaceted approach needed, the following table outlines some of the critical aspects affecting disease eradication efforts:
| Aspect | impact |
|---|---|
| Funding Availability | Directly influences program implementation and sustainability |
| community Education | Enhances understanding and cooperation in local prevention strategies |
| Health System Capacity | Determines effectiveness in managing cases and outbreaks |
| Environmental Management | Affects disease transmission rates and control measures |
In Retrospect
the commitment of three Central African countries to eradicate Guinea-worm disease marks a significant step forward in global health efforts. By partnering with the World Health Organization and leveraging resources and expertise, these nations are actively participating in a monumental public health initiative aimed at eliminating a disease that has long plagued vulnerable populations. This collaborative effort serves as a beacon of hope, not only for the residents of these affected regions but also for the global community in its fight against neglected tropical diseases. As these countries mobilize their resources and engage their communities, the potential for a Guinea-worm-free future becomes increasingly attainable. Continued support and collaboration from international health agencies, governments, and non-governmental organizations will be crucial in sustaining momentum and achieving this critical goal. The road ahead might potentially be challenging, but with shared dedication and commitment, the eradication of Guinea-worm disease could soon become a reality.







