Exploring Ancient Egypt: A Journey Thru Time and Civilization
Ancient Egypt stands as one of the most fascinating and enduring civilizations in human history, captivating the imaginations of historians, archaeologists, and enthusiasts alike. Encompassing a rich tapestry of culture,government,and religion,this ancient land along the banks of the Nile River was home to a remarkable array of rulers and innovations that shaped the course of human progress. From the enigmatic pyramids and majestic temples to the intricate hieroglyphs that narrate tales of gods and mortals, Ancient Egypt offers a window into a world where art, spirituality, and governance intertwined seamlessly. This article delves into the multifaceted aspects of Ancient Egypt, examining its history, societal structure, belief systems, and artistic achievements while also providing insights into the geography that shaped this iconic civilization.Join us as we unravel the captivating story of Ancient Egypt, a society that continues to influence and inspire the modern world.
Exploring the Rich Tapestry of Ancient Egyptian History
The ancient civilization of egypt, with its remarkable achievements and mystique, represents one of the most influential cultures in human history. Characterized by the iconic pyramids, intricate hieroglyphics, and the powerful pharaohs, this society thrived along the banks of the Nile River for thousands of years. Political structure played a crucial role in its longevity, with a centralized government led by pharaohs who were deemed both rulers and deities. The ancient Egyptians made remarkable advances in various fields, including medicine, astronomy, and engineering, contributing to their reputation as skilled architects and thinkers.
The cultural legacy of ancient Egypt continues to captivate the modern world through its art,religious beliefs,and social organization. Key aspects of their culture included:
- Religion: Polytheism was prevalent, with gods and goddesses representing natural and social phenomena.
- Art: Renowned for its distinctive style, art was often used for religious and commemorative purposes, serving to depict the afterlife.
- Writing: Hieroglyphics emerged as a meaningful form of communication, combining both ideographs and phonetics.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Government | centralized, ruled by pharaohs |
| Religion | Polytheistic; worship of numerous gods |
| Writing | Hieroglyphics and papyrus scrolls |
| Art | Symbolic and spiritual, focused on the afterlife |
Understanding the Structure and Function of Ancient Egyptian Government
The government of ancient Egypt was a complex structure that blended religion, politics, and social hierarchy, making it unique in the ancient world. At its apex stood the pharaoh, a divine ruler who was believed to be the intermediary between the gods and the people. The pharaoh’s authority was supported by a cadre of officials, including viziers, who managed day-to-day operations, and various local governors known as nomarchs.This hierarchical system allowed for effective management of resources, agricultural production, and labor—essential elements in sustaining the vast civilization. The government not only operated on a political level but also reinforced religious beliefs, as pharaohs were deified after death, influencing the spiritual and cultural landscape of ancient Egyptian society.
Furthermore, the ancient Egyptian legal system was heavily influenced by the concept of Ma’at, wich represented truth, balance, and order. Laws were derived from religious doctrines, and judges, often priests, were tasked with upholding these divine principles. The importance of record-keeping is noteworthy, as it played a crucial role in governance. Scribes, skilled in writing and administration, documented everything from tax collections to court proceedings, ensuring accountability and structured governance. Below is a simple overview of key governmental roles and their primary functions:
| Title | Primary Function |
|---|---|
| Pharaoh | Supreme ruler and divine authority |
| Vizier | Chief advisor and overseer of administration |
| Nomarch | Governor of a province or region |
| Scribe | Keeper of records and legal documentation |
| Priest | Religious leader and law enforcer |
Cultural Practices and Daily Life in Ancient Egypt
In ancient Egypt, daily life was deeply intertwined with cultural practices that both reflected and reinforced their beliefs and social structures. The Egyptians were keen observers of the natural world, and their agricultural calendar was largely dictated by the annual flooding of the Nile River. Key practices included:
- farming: The fertile banks of the Nile allowed for the cultivation of essential crops such as wheat and barley.
- Festivals: Celebrations and rituals played a significant role in reinforcing community bonds, with numerous religious festivals honoring gods and pharaohs.
- Artisan Work: Skilled artisans crafted jewelry, pottery, and intricate textiles, contributing to a vibrant local economy.
The social fabric of ancient Egypt was hierarchical, yet the daily experiences of individuals varied widely across this spectrum.The majority of the population, comprised of farmers and laborers, engaged in communal activities such as:
- construction Projects: Many citizens participated in the construction of temples and monuments, which were vital to the nation’s identity and pride.
- Family Life: Family played a central role, with most households comprising several generations, fostering strong support systems.
- Trade: Local and long-distance trade networks facilitated the exchange of goods, which was crucial for sustaining daily life.
| Cultural Element | Significance |
|---|---|
| Agriculture | Foundation of economy and sustenance |
| Festivals | Reinforcement of religious beliefs and community |
| Artistry | Expression of cultural identity and legacy |
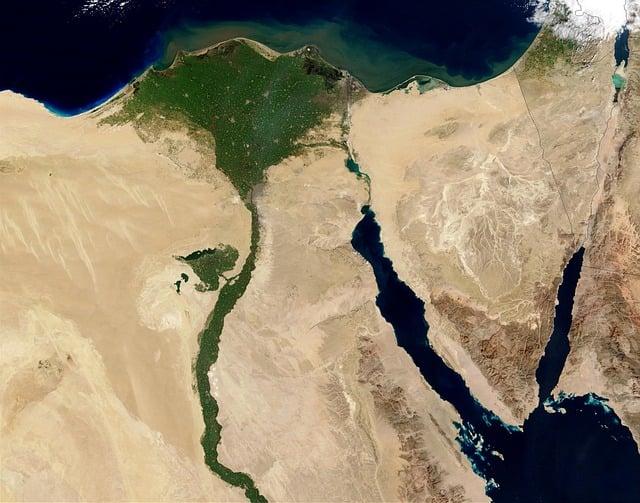
Mapping the Geographic Extent of the Ancient Egyptian Civilization
The ancient Egyptian civilization extended across a diverse and fertile landscape, primarily centered around the banks of the Nile river. this river served as the lifeblood of the civilization, enabling agriculture and trade while also inspiring cultural developments. The geographic reach of ancient Egypt can be categorized into several key regions, including:
- Lower Egypt: Characterized by the delta region where the Nile spreads into numerous branches before emptying into the Mediterranean Sea, it was a crucial area for trade and agriculture.
- Upper Egypt: Located upstream from the delta, this narrow strip of land was known for its majestic temples and rich agricultural production.
- Desert Regions: surrounding the Nile, the vast deserts served as natural boundaries, protecting the civilization and influencing trade routes with neighboring cultures.
| Region | significance |
|---|---|
| Lower egypt | Hub of trade and agriculture due to fertile delta |
| Upper Egypt | Site of significant temples and agricultural wealth |
| Western desert | Resource-rich area influencing trade |
| Eastern Desert | Key route for connecting Upper Egypt to the Red Sea |
moreover, interactions with adjacent regions expanded the empire’s influence through trade and conquest. This interaction was instrumental in the exchange of ideas,materials,and technologies with neighboring civilizations such as Nubia to the south and the Levant to the northeast. As a result, ancient Egypt not only defined its own identity through a strong central governance and rich culture but also played a vital role in a broader regional context that enhanced its legacy in art, science, and architecture.
The Pantheon of Ancient Egyptian Gods and the Role of Religion
The landscape of ancient Egyptian religion was rich and complex, characterized by a plethora of deities that personified various aspects of life, nature, and the cosmos. The pantheon included notable gods such as Ra, the sun god revered as the creator, and Osiris, the god of the afterlife, symbolizing resurrection and fertility. Additionally, Isis, the goddess of magic and motherhood, played a critical role in both mythology and the everyday lives of the Egyptians. These divine figures were not mere symbols; they were deeply integrated into the cultural and social fabric, influencing everything from growth and harvest to the pharaoh’s divine right to rule.
The religious practices of ancient Egypt encompassed both ritualistic and daily activities,underscoring the gods’ omnipresence in all facets of life. Temples served as the centers of worship, where priests conducted elaborate ceremonies and offerings to appease the gods. The beliefs in the afterlife were profound, leading to elaborate burial customs and monumental architecture, such as the pyramids that served as final resting places for pharaohs. The Egyptians’ reverence for their gods was reflected in various forms of art, including sculptures and hieroglyphics that depicted divine mythologies, reinforcing the profound connection between religion, governance, and culture.
| God/Goddess | Domain | Symbol |
|---|---|---|
| Ra | Sun, Creation | Sun Disk |
| Osiris | Afterlife, Resurrection | Crook and Flail |
| Isis | Magic, Motherhood | Throne |
| Horus | Sky, Kingship | Eye of Horus |
Artistic Achievements and the Evolution of Writing in Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt stands as a beacon of artistic excellence, where the interplay between art and writing reflects a profound cultural narrative. The hieroglyphic system, consisting of logographic and alphabetic elements, was not merely a means of communication but an intricate art form itself. The vibrant depictions found in tombs and temples served a dual purpose: they conveyed messages to the gods and immortalized the individuals whose legacies they sought to preserve. The evolution of writing, from the early pictographs to the more stylized hieroglyphs, showcases a civilization that valued both aesthetic beauty and functional utility. Over centuries, the sophistication of their writing system also increased, leading to the development of hieratic and demotic scripts that catered to different societal needs and contexts.
Moreover, the artistic achievements of ancient Egyptians were not confined to their writing. They mastered various mediums, including sculpture, painting, and pottery, which all reflected their religious beliefs and social hierarchy. Key elements of Egyptian art included:
- Symbolism: Colors and symbols were employed purposefully to convey spiritual meanings.
- Proportion and Scale: Figures were depicted according to their social rank rather than realism.
- Thematic Consistency: Art served to reinforce societal norms, often showcasing scenes of daily life, religious rituals, and funerary practices.
| Medium | notable Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Sculpture | Stones like granite and limestone; lifelike representations of gods and pharaohs. |
| Painting | Vivid colors; religious themes frequently enough depicted in a strict, flat style. |
| Pottery | Utilitarian and decorative, often bearing intricate designs and motifs. |
To Wrap It Up
the rich tapestry of Ancient Egypt continues to captivate historians, archaeologists, and the general public alike. From its complex social structure and innovative governance to its profound religious beliefs and artistic achievements, the influence of this ancient civilization reverberates through time, shaping our understanding of human development. With remarkable advancements in writing and architecture,along with a pantheon of gods that reflects the values and ideals of Egyptian society,the legacy of Ancient Egypt serves as a critical chapter in the broader narrative of human history. As ongoing archaeological discoveries unearth new insights and deepen our appreciation for this remarkable civilization, Ancient Egypt remains a testament to the enduring power of culture, innovation, and belief.For those eager to delve further into this fascinating world, resources like Britannica provide a wealth of information to explore and understand the myriad facets of Ancient Egyptian life.