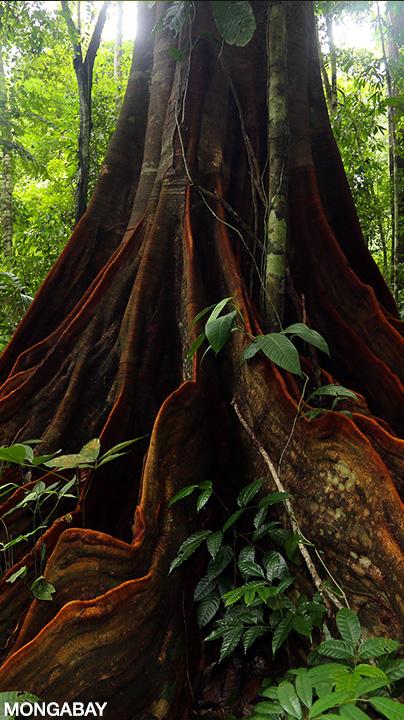
Exploring the Biodiversity of Gabon’s Rainforest ‚Ā£floor:‚ÄĆ A closer‚Äć Look at Fig. 4.1(a)
In the heart of Central Africa lies Gabon,a country renowned for its lush rainforests teeming ‚Äćwith‚Ā§ unparalleled biodiversity. Among the most intriguing aspects of these ‚Äćecosystems ‚Ā£is the rainforest ‚Ā£floor, a vibrant yet often ‚Äćoverlooked layer that plays‚ÄĆ a ‚Ā£crucial role in the ecological balance‚Ā£ of the region. Fig. 4.1(a) serves as a window ‚Ā£into this verdant world,‚ÄĆ showcasing‚ÄĆ the ‚Äčintricate life ‚Äčforms ‚Äćand dynamic interactions that characterize the forest floor. This article ‚ÄĆdelves into the significance of Gabon’s rainforest floor, comparing it to‚Äć other tropical rainforests across ‚Äćthe globe, and‚Äč highlights how its unique flora and‚Ā£ fauna ‚Ā£contribute to the health‚ÄĆ of the ecosystem. As‚ÄĆ we ‚Äčunravel‚ĀĘ the ‚Äčcomplexities of ‚Äćthis vital habitat, we also‚Äč aim to‚Ā£ raise awareness about ‚ĀĘthe ‚Äćpressing conservation‚Ā£ challenges‚ĀĘ facing ‚Äčthese irreplaceable environments, underscoring the need for ‚ÄĆongoing research and preservation efforts.
Exploring Biodiversity‚Ā§ in Gabon’s Rainforest Floor
The rainforest floor of‚ÄĆ Gabon ‚Äćis‚Ā§ a vibrant ‚Ā£tapestry of‚Ā£ life, ‚ĀĘwhere diverse ecosystems intertwine to ‚Äčcreate a‚Ā§ habitat rich in ‚Äčflora and fauna. Visitors to this ‚ĀĘlush surroundings can expect ‚Ā§to encounter an extensive variety of species, many of which‚Äč remain undiscovered. Some key characteristics of the rainforest floor include:
- Dense Vegetation: ‚ÄćThe layer is dominated‚ÄĆ by ferns, ‚Äćshrubs, and ‚Ā£young trees, all competing for sunlight.
- Myriad‚Äč Insect Species: Thousands ‚Ā§of species, from‚Ā£ tiny ants to‚Ā£ colorful‚ÄĆ butterflies, play crucial roles ‚Äčin ‚Ā£pollination and decomposition.
- Forest Floor Dwellers: ‚Äć Creatures such as‚ĀĘ duikers, porcupines, and various reptiles thrive in the‚ÄĆ underbrush, showcasing the ‚Äčadaptability‚Ā£ of ‚Äćwildlife‚Äč in this ecosystem.
Moreover, the interconnectedness of ‚Ā§species in this habitat is essential for maintaining ecological balance. Mycorrhizal‚Ā£ fungi, as a‚Ā£ notable example, form symbiotic relationships with trees, facilitating nutrient exchange while enhancing the soil’s ‚ĀĘhealth. The forest ‚Ā£floor also acts as a filter, mitigating soil erosion‚Ā§ and facilitating water retention, which sustains the‚ÄĆ intricate web ‚Ā£of life above and below the surface. A‚ÄĆ small glimpse into the biodiversity reveals a‚Äč complex table of interactions‚Ā£ among‚Äć species:
| Species Type | Role in ‚ÄčEcosystem | Notable ‚ĀĘSpecies |
|---|---|---|
| Flora | Produce oxygen, ‚ĀĘprovide habitat | Palms, Epiphytes |
| Insects | Pollinators, decomposers | Beetles, ants |
| Fauna | Seed dispersers, predators | duikers, ‚Ā£Panthers |
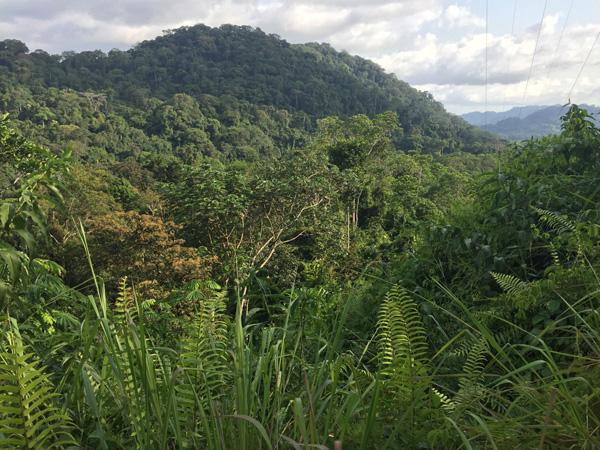

The‚Äč Unique ‚Ā§Ecosystem of Gabon: A Closer Look
The ‚Äčrainforest floor ‚Ā§in ‚ÄĆGabon serves as ‚Ā§an intriguing layer of ‚Ā£the ‚ÄĆdiverse ecosystem, playing a‚Ā£ critical role in sustaining the‚Äč region‚Äôs‚ÄĆ rich biodiversity. ‚ú® Home‚Äć to‚Äć an‚Äč array of flora and fauna,‚ÄĆ this vibrant area is characterized by a‚Ā§ tantalizing‚Äć mix ‚Äćof species, ‚ÄĆmany of‚ÄĆ which are endemic and thrive in the ‚Ā£unique climatic conditions.‚ÄĆ Some of the‚Äć notable features of this ‚Äčecosystem include:
- Diverse ‚Ā§Plant Life: ‚Ā£ The rainforest floor hosts an intricate network of ferns, ‚Ā§shrubs, ‚Äčand‚Ā§ young trees‚Ā§ that create ‚Äća lush understory.
- Wildlife ‚Ā§Interactions: ‚Ā§Numerous animals, including various primates‚ĀĘ and birds, contribute to the ‚Äčecological ‚Äčbalance by dispersing seeds and ‚ĀĘpollinating flowers.
- Fungal Networks: ‚ÄĆMycorrhizal fungi play a crucial ‚Ā£role in nutrient‚Äč recycling, forming symbiotic relationships with plant‚ÄĆ roots.
Furthermore,human activity poses meaningful challenges‚ÄĆ to the integrity ‚Äćof Gabon‚Äôs rainforest ecosystem. ‚ĀĘDeforestation, driven predominantly by agriculture and logging,‚Ā£ threatens ‚Äćnot ‚Ā§only the ‚Äčbiodiversity but ‚ĀĘalso‚Ā§ the delicate balance of carbon storage ‚Ā§and‚Äč global climate regulation. To address these‚ĀĘ challenges,‚Äč Gabon has implemented various conservation ‚Äčstrategies aimed at ‚ĀĘprotecting‚ĀĘ its natural heritage, such as:
- Protected ‚ÄćAreas: A significant portion‚Äć of Gabon‚Äôs land is designated as national parks, ‚Äćwhich help safeguard critical ‚ĀĘhabitats and ‚ÄĆspecies.
- Community Involvement: Engaging local communities in conservation‚Ā£ efforts fosters sustainable ‚ÄĆpractices that benefit both the environment and ‚ĀĘthe economy.
- Research Initiatives: Ongoing scientific research is ‚Äčcrucial for understanding the complexities of this ecosystem and developing‚ĀĘ effective conservation ‚ĀĘmethods.
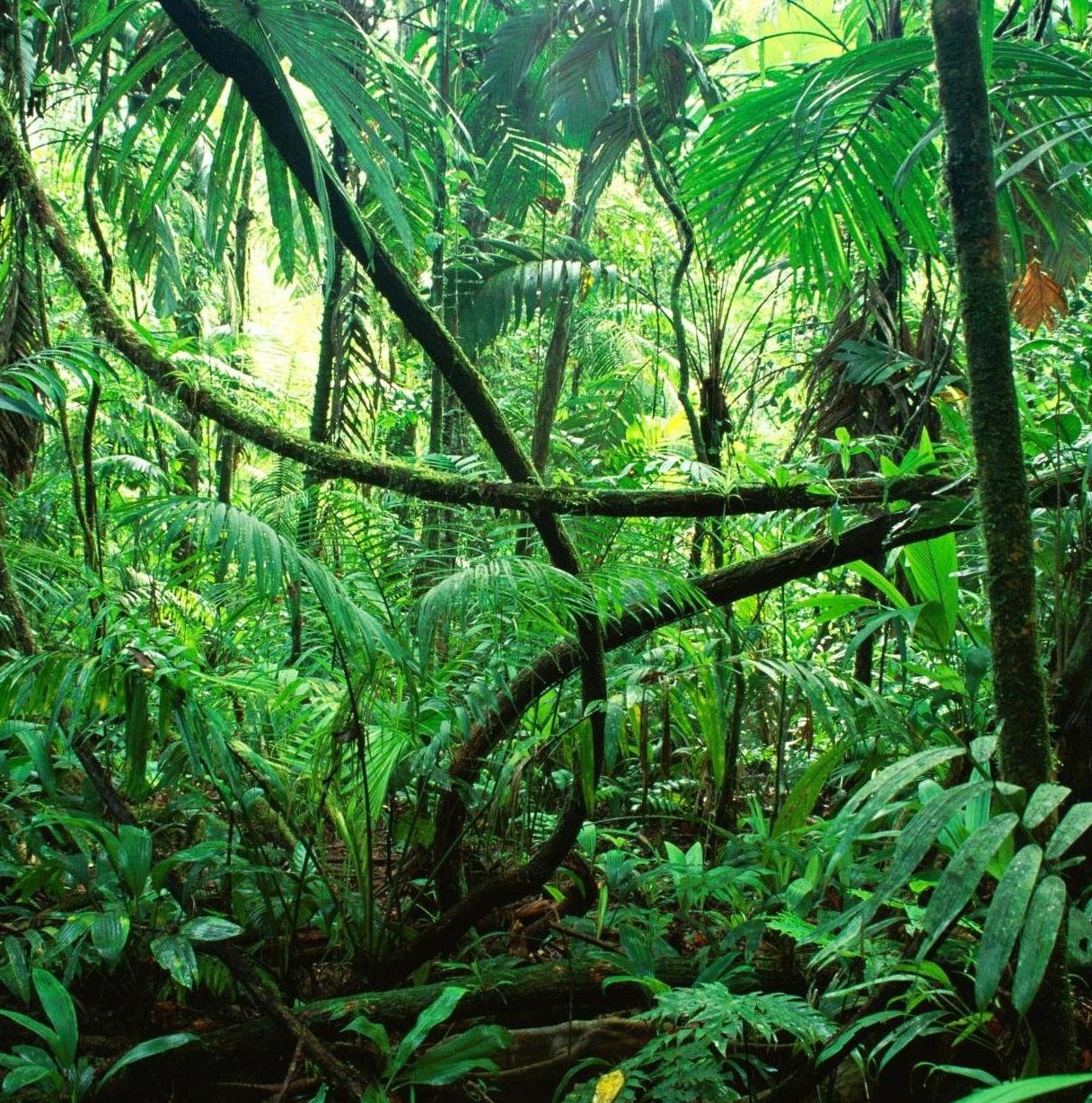

Threats‚Ā§ to the Rainforest Floor and conservation Efforts
The rainforest floor, often overshadowed‚Äč by‚Äć the towering canopy ‚ĀĘabove, is ‚Ā£a biologically ‚ĀĘrich ‚ÄĆenvironment teeming with life. However,‚ÄĆ this crucial layer is ‚Äćunder‚ĀĘ threat‚Äć from numerous‚ÄĆ human activities. Deforestation for agriculture and logging‚Äč has emerged ‚Äčas ‚Äča ‚Ā£primary risk, ‚ĀĘfragmenting habitats and endangering ‚ÄĆthe myriad ‚ÄĆspecies that inhabit ‚Äćthis layer.‚Ā£ Additionally, mining ‚ĀĘoperations wreak‚Ā£ havoc on subterranean ecosystems, raising ‚ĀĘconcerns ‚Äćabout soil degradation and water‚ÄĆ contamination. ‚ÄčFurthermore,the unchecked spread ‚Äćof invasive ‚Ā§species poses a ‚ĀĘsignificant challenge,as they ‚Ā£outcompete ‚Ā£native flora and fauna,destabilizing the ‚ÄĆdelicate balance‚ÄĆ essential for maintaining biodiversity.
In response to these threats, various conservation‚Ā£ efforts are being mobilized. Local communities, NGOs, ‚ÄĆand governmental bodies ‚Äćare collaborating‚Ā§ to‚Ā§ implement sustainable land-use practices, focusing on agroforestry‚Ā§ methods that enhance both biodiversity and crop‚Äć yields.‚Äč Education initiatives ‚Äćhave also ‚Äčemerged, aimed at raising awareness‚Äć about the ecological importance of the rainforest floor. Additionally, protected areas and reserves are being established, providing‚Ā§ safe havens‚ĀĘ for threatened species. The table below highlights some of these key conservation strategies and ‚ÄĆtheir objectives:
| Conservation Strategy | Objective |
|---|---|
| Sustainable Agriculture | reduce deforestation while ‚Äćmaintaining food security |
| Protected ‚ÄćAreas | Safeguard habitats and‚Ā§ promote biodiversity |
| Community Education | Inspire local stewardship and awareness |
| Research Initiatives | Understand ecological impacts‚Ā£ and ‚Äćimprove conservation ‚Ā§methods |

Impact of Climate Change‚Äč on Gabon’s Forest Habitats
Climate change‚Ā£ is exerting ‚Ā£significant ‚Ā£pressure on ‚ÄčGabon’s lush forest habitats,‚ĀĘ which‚ÄĆ are among the most ‚ĀĘbiodiverse‚Ā£ ecosystems on the planet. The rising ‚Äčglobal temperatures ‚Ā§and shifting weather patterns are leading to several adverse effects, including:
- Increased temperature: Higher temperatures can stress ‚ĀĘplant species, disrupting their ‚Äćgrowth‚Ā£ and ‚ÄĆreproduction cycles.
- Altered rainfall patterns:‚ĀĘ changes in precipitation‚Äć can lead to‚Ā£ droughts or excessive ‚Äčrainfall, ‚Äčboth of which threaten the delicate balance‚Ā§ of ‚Äčforest ecosystems.
- Wildfire risks: Prolonged‚ĀĘ dry‚Äč periods increase the frequency and intensity of ‚Ā£wildfires, devastating large areas of forest.
The implications‚Äč of these changes extend beyond just flora, significantly ‚Äčaffecting the fauna that‚Äć depend on ‚ÄĆthese forests. Species such as the‚Ā£ Western Lowland gorilla and the ‚Ā§African forest elephant face threats from habitat ‚Äčloss and fragmentation as their‚Äč environments become less hospitable.Moreover, the impacts of climate change on ‚Ā§ecological ‚Ā£interactions‚ĀĘ can‚ĀĘ result ‚Ā§in:
- shifts in species ‚ÄĆdistribution: Many species ‚ĀĘmay ‚Ā£migrate to cooler areas,‚ÄĆ disrupting‚Ā£ existing‚ÄĆ ecological relationships and food chains.
- Increased ‚ĀĘcompetition: As some species move, competition for‚Äć limited resources‚Ā§ becomes heightened, putting further ‚Ā£stress on vulnerable ‚Ā§species.
- loss of biodiversity: The cumulative ‚Äčeffect of these‚Äč factors ‚ĀĘcould lead to species ‚Ā£extinction, threatening the ‚Ā§overall health of‚Äć Gabon’s forests.

Promoting Sustainable Practices for Rainforest Preservation
Rainforests are vital ecosystems, harboring biodiversity ‚Äćthat is unequaled anywhere else on the planet. To combat deforestation and degradation, it is ‚ÄĆessential to adopt a‚ÄĆ multi-faceted ‚ĀĘapproach toward ‚Äčsustainable practices that not only‚Ā£ benefit the environment ‚Ā£but‚ĀĘ also support ‚Äćlocal‚Äč communities. Some‚ĀĘ notable strategies include:
- agroforestry: Integrating trees ‚Ā£into agricultural systems can ‚Äčsafeguard biodiversity while‚Äć enhancing crop yields.
- Ecotourism: Promoting‚ĀĘ responsible ‚Ā£travel ‚Ā§can ‚ÄĆgenerate ‚ĀĘrevenue for conservation efforts and ‚Äćraise awareness about‚Äć the importance of rainforests.
- Sustainable‚Äć logging techniques:‚Ā§ Implementing selective logging and reduced-impact logging methods helps maintain forest integrity while allowing for resource ‚Äćextraction.
- Community-driven conservation: Empowering local populations ‚Ā§to manage nearby forest‚ÄĆ areas fosters‚ÄĆ stewardship and protects their ‚Ā£livelihoods.
Moreover, educational ‚Äćinitiatives play a crucial role in increasing awareness‚ÄĆ of rainforest‚ÄĆ preservation. By engaging young people in conservation‚ÄĆ programs ‚ĀĘand providing resources on sustainable practices, we can cultivate a generation that prioritizes ‚Ā§ecological balance. Introducing policies that encourage reforestation and support renewable energy ‚ÄĆprojects can significantly minimize ‚Äčhuman impact on these critical ‚Äćareas.‚Äć Consider the following planned actions‚Ā£ to reinforce these efforts:
| Action | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|
| Community‚Ā§ workshops on‚ĀĘ sustainable agriculture | Enhanced ‚Äčunderstanding and practice of eco-friendly farming |
| Funding for reforestation ‚Ā£projects | increased forest area and ‚ÄĆbiodiversity |
| Partnerships with conservation NGOs | Stronger resources and expertise ‚Äčin protection efforts |

Engaging Local Communities in Conservation Initiatives
Local communities ‚ÄĆare often the first line of‚Ā§ defense ‚Äćagainst threats to ‚ĀĘnatural ecosystems,making their involvement crucial in conservation ‚Äćefforts. Engaging these communities requires a multifaceted approach that ‚Äčvalues their conventional knowledge and strengthens their‚Ā§ roles as stewards of the environment. By fostering partnerships, conservationists can‚Ā§ create initiatives that ‚Ā£resonate‚ÄĆ with local cultures and lifestyles. This can include:
- educational ‚Ā£Workshops: Conducting workshops to raise‚Ā£ awareness about the importance of biodiversity and sustainable practices.
- Community-Led ‚ĀĘProjects: Supporting initiatives ‚Ā£that allow locals to manage ‚Äćnatural resources, ensuring they have a stake‚Ā£ in preserving‚ÄĆ their environment.
- Eco-Tourism: ‚ĀĘPromoting eco-friendly tourism experiences that provide ‚Ā£financial incentives‚Äć for communities‚ĀĘ to protect‚Ā£ their ‚Ā£natural surroundings.
Furthermore, utilizing technology can enhance community engagement by linking local efforts with broader conservation networks. This integration can be achieved through:
| Technology‚ÄĆ Use | Description |
|---|---|
| Mobile Apps | apps that allow‚Äć locals ‚Äčto report wildlife sightings or illegal activities in real-time. |
| Social Media Campaigns | Using platforms to showcase ‚ĀĘlocal ‚ĀĘconservation ‚Äćsuccesses, attracting support ‚Äčand funding. |
| Geographic Information‚Äč systems‚Äč (GIS) | Leveraging ‚ĀĘGIS ‚Äćfor mapping biodiversity hotspots and areas needing protection. |
Final Thoughts
the examination of‚ĀĘ fig. 4.1 (a), which captures the lush and vibrant rainforest ‚Ā§floor of ‚ÄĆGabon, Africa, serves as a‚Ā£ poignant‚Äč reminder ‚ĀĘof the intricate biodiversity and‚Ā£ ecological significance of ‚ÄĆthese habitats. the image not only illustrates the unique flora‚Äč and fauna that ‚Ā§thrive in‚ÄĆ this‚Ā£ environment but also‚ÄĆ highlights‚Ā§ the pressing conservation challenges ‚Äćthat rainforests face ‚Äćtoday.As we ‚Äčcontinue to ‚ĀĘexplore and document these vital ecosystems, it becomes ‚Ā§increasingly clear that ‚ÄĆprotecting ‚Äčthem‚Äč is ‚Ā§not just a local concern but ‚ÄĆa ‚Äčglobal imperative. With ongoing human‚Äč activities threatening‚Ā§ their existence, it‚ĀĘ is ‚ÄĆindeed‚Ā£ crucial to advocate for sustainable practices and conservation efforts that ensure the survival of ‚Ā§these irreplaceable natural wonders for future generations. As ‚Ā§researchers‚Äć and‚ĀĘ environmentalists work ‚Äčtirelessly to uncover the‚Äć complexities ‚Ā§of rainforest ecosystems, the‚ÄĆ insights gained from images‚ĀĘ like Fig. 4.1 (a) will play‚Äć an‚ĀĘ essential role‚Äć in fostering a deeper understanding and appreciation of our‚Ā§ planet’s‚Ā§ delicate balance.