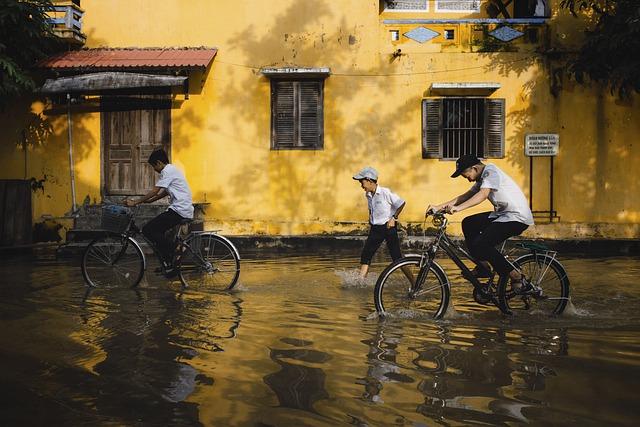in recent days, Botswana has been grappling with severe flooding triggered by relentless and torrential rains, leading to the emergency closure of schools and major roads across the nation. The unprecedented deluge has not only disrupted daily life but also raised concerns about the potential long-term implications for infrastructure and public safety. As communities navigate the challenges posed by rising waters, government officials and local agencies are mobilizing resources to address the immediate needs of those affected. This article will delve into the current state of the flooding crisis, its impact on education and transportation, and the broader environmental factors contributing to this extreme weather event.
Impact of Unprecedented Rainfall on Botswana’s infrastructure
The recent torrential rainfall in Botswana has had a devastating effect on the country’s infrastructure,leading to notable closures and disruptions. Key roads, especially those linking major urban centers, have been rendered impassable due to flooding, causing severe delays in transportation and logistics. The closures have further strained the supply chain, affecting the delivery of essential goods such as food and medical supplies. in urban areas, the accumulation of water has overwhelmed drainage systems, resulting in property damage and hazardous conditions for residents.
Moreover, educational facilities have not been spared, with many schools forced to close their doors to ensure the safety of students and staff. The implications of these disruptions are profound, as prolonged school closures can affect educational attainment and increase the strain on local communities. The government has outlined their response plan, which includes:
- Assessment of damage: Thorough checks to evaluate the extent of the destruction.
- Infrastructure repairs: Prioritization of critical repairs on public transport routes and schools.
- Emergency aid: Provision of food and essentials to displaced families.
To address these challenges effectively,a coordinated response is essential. The following table outlines the key infrastructures affected by the flooding:
| Infrastructure | Status | estimated Recovery Time |
|---|---|---|
| Major Highways | Closed | 2-3 weeks |
| Primary Schools | Closed | 1 month |
| Hospitals | Operational but limited | Immediate |
Consequences for Education: School Closures and Scheduled Disruptions
The unprecedented flooding in Botswana due to relentless rain has not only posed a direct threat to the safety of its residents but has also led to significant disruptions in the education sector. With schools shut down across various regions, students are facing an interrupted academic year, which could have long-term implications on their learning outcomes. The closures prevent students from engaging in crucial learning activities and accessing essential resources, exacerbating existing educational inequalities. The following points highlight the impact of such disruptions:
- Delayed Academic Curricula: With schools closed, educators are struggling to keep up with the prescribed syllabus timelines.
- Increased Dropout Rates: Prolonged periods of inactivity may lead some students to abandon their studies altogether.
- Emotional and Psychological Effects: The ongoing uncertainty and instability may affect students’ mental well-being and motivation.
As authorities assess the situation, they are also considering potential remedial measures to mitigate the educational impact of these closures. For instance, both physical and digital learning alternatives are being discussed to help students stay engaged.In light of these challenges, the following measures could be beneficial:
| Proposed Measures | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote Learning platforms | Implementation of online classes to ensure continuity of education. |
| Flexible Learning Schedules | Adjusting academic calendars to allow for catch-up sessions later in the year. |
| Community Support Initiatives | Engaging local organizations to provide learning materials and emotional support. |
emergency Response Strategies: Government and Community Actions
The ongoing floods in Botswana have prompted immediate actions from both government and community leaders, highlighting the need for a coordinated response. Authorities have mobilized resources to assess the damage and provide assistance to affected areas. Key actions include:
- Rapid Damage Assessment: Teams are dispatched to evaluate the extent of flooding and its impact on infrastructure.
- Evacuation Plans: Emergency services are implementing evacuation protocols for communities at the highest risk.
- Resource Allocation: Essential supplies such as food, water, and medical aid are being distributed to those in need.
Community participation is also significant in the face of this disaster, fostering resilience among local populations. Initiatives have been established to assist neighbors and support recovery efforts, with a focus on:
- Volunteer Mobilization: Local organizations are rallying volunteers to aid in relief efforts and clean-up operations.
- Awareness Campaigns: Communities are organizing details drives to educate residents on safety measures and evacuation procedures.
- Community Coordination: Meetings are held to streamline local resources and response strategies, enhancing cooperation among various groups.
Long-Term Solutions: Building Resilience Against Future Flooding
As Botswana grapples with the aftermath of severe flooding, it becomes increasingly clear that short-term responses will not suffice. To build lasting resilience against future flooding, stakeholders must prioritize active community engagement in disaster preparedness and risk management.Educational programs focusing on flood awareness can empower citizens to respond effectively during emergencies. Furthermore, establishing robust communication channels ensures that real-time information is disseminated efficiently, minimizing chaos during crises.
Investment in infrastructure is equally critical in mitigating the impacts of flooding. Local governments should consider adopting a multi-pronged approach that includes:
- Enhancing drainage systems: Improving the capacity and functionality to handle heavy rainfall,thereby reducing urban flooding.
- Restoration of natural barriers: Protecting wetlands and riverbanks to absorb excess water naturally.
- Updating land-use policies: Implementing zoning laws that restrict development in flood-prone areas.
| Action | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|
| Community Education Programs | Increased awareness and preparedness |
| Infrastructure Investment | Improved flood resilience |
| Natural Barrier Restoration | Enhanced ecological protection |
Lessons Learned: Improving Water Management and Urban Planning
In the wake of the recent floods in Botswana, a critical reevaluation of water management strategies and urban planning practices is essential. The relentless rain revealed significant vulnerabilities in infrastructure, highlighting the need for adaptive measures that consider climatic variability. Communities are facing unprecedented challenges as schools and roads are rendered unusable, marking a need for proactive planning to mitigate future risks. To enhance resilience, it is crucial to prioritize the following strategies:
- Integrated Water Resource Management: Adopting holistic approaches to manage water resources while considering both urban and rural needs.
- Infrastructure Upgrades: Retrofitting existing drainage systems to handle extreme weather patterns.
- community Engagement: Involving local populations in the planning process to ensure solutions are tailored to their specific needs and experiences.
- Early Warning Systems: Implementing technology to predict severe weather events and communicate risks effectively.
Urban planning must evolve to incorporate sustainable practices and comprehensive land-use policies. Existing urban spaces should be assessed to identify flood-prone areas, thereby guiding future development away from high-risk zones. Implementing green infrastructure, such as parks and permeable surfaces, can substantially improve water absorption and reduce runoff. To facilitate this transition, a collaborative effort among government agencies, private stakeholders, and local communities will be necessary. The table below outlines recommended actions and their projected impact:
| Action | Projected Impact |
|---|---|
| Develop early warning systems | Improved response times and reduced damage |
| Create new flood management zones | Enhanced protection of critical infrastructure |
| Promote sustainable land practices | Better environmental stewardship and reduced runoff |
| Invest in community training programs | Increased preparedness and resilience |
Community Support: Resources Available for Affected Residents
In the aftermath of the recent floods in Botswana, numerous resources have been made available to assist affected residents. Local government and non-profit organizations have mobilized support services to ensure that individuals and families can access essential aid. Key resources include:
- Emergency Shelters: Temporary accommodations set up at community centers and schools.
- Food and Water Distribution: Daily distributions of non-perishable foods and clean drinking water.
- Medical Assistance: Mobile health clinics deployed to provide immediate healthcare services.
- Mental Health Support: Counseling services available to help residents cope with the emotional impact of the floods.
Residents can connect with local support networks for additional assistance. Local authorities have established hotlines and information centers to facilitate communication and ensure that everyone receives the help they need. Below is a table summarizing some of the contact points for these services:
| Service | Contact Number | Availability |
|---|---|---|
| Emergency Shelters | 0800 123 456 | 24/7 |
| food Distribution | 0800 654 321 | 10 AM - 4 PM |
| Medical Assistance | 0800 987 654 | Daily 8 AM – 6 PM |
| Mental Health Support | 0800 111 222 | 9 AM – 5 PM |
Closing Remarks
the recent floods in Botswana serve as a reminder of the unpredictable severity of climate events and their cascading effects on infrastructure and daily life. With schools shut down and key transportation routes rendered impassable, the immediate challenges for affected communities are stark. Authorities are mobilizing resources to address the situation and provide assistance to those in need, but the lasting implications on education, mobility, and local economies are yet to be fully realized. As the country grapples with the impact of relentless rains, the resilience of the affected populations will be crucial in navigating the recovery process. Continued monitoring and reporting will be essential as the situation evolves, underscoring the importance of preparedness in the face of climate-related challenges.