In recent years, U.S.foreign aid has played a crucial role in supporting some of the world’s most vulnerable populations, particularly in Africa. however, with notable funding cuts emerging from Washington, the repercussions are being felt acutely across the continent.This article delves into the alarming consequences of these reductions,highlighting the intertwining narratives of fear,pain,and hunger that characterize the daily lives of millions. As humanitarian organizations grapple with dwindling resources, communities are facing heightened instability, worsening health crises, and a deepening food insecurity. Through a detailed exploration of the cascading effects of these policy shifts,we aim to shed light on how U.S. funding cuts not only undermine years of progress but also threaten the very stability of nations striving to overcome adversity.
Impact of Funding Cuts on Health services in Africa
The recent funding cuts from the U.S. have precipitated a crisis that ripples through the health services sector in Africa. With essential resources dwindling,healthcare facilities are grappling with numerous challenges. Public health programs that were once robust are now faltering, leading to increased mortality rates and a resurgence of preventable diseases. Some of the critical impacts include:
- Increased Out-of-Pocket Expenses: Patients are forced to pay more for services,which many cannot afford.
- Staff Layoffs: Hospitals and clinics are terminating staff, leaving fewer healthcare workers to support growing populations.
- Resource Shortages: Life-saving medications and equipment are becoming scarce, threatening treatment for chronic illnesses.
- Diminished Outreach Programs: Initiatives aimed at maternal and child health, vaccination drives, and HIV/AIDS prevention are suffering significant cuts.
To illustrate the severity of this situation, a recent analysis reveals significant declines in various health metrics across several countries:
| Country | Healthcare Access Change | Child Mortality Rate | Vaccination Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nigeria | Decreased by 30% | 124 per 1,000 live births | 62% |
| Kenya | Decreased by 25% | 52 per 1,000 live births | 73% |
| Uganda | Decreased by 20% | 43 per 1,000 live births | 68% |
These statistics underscore not only the immediate harm caused by funding cuts but also the long-term consequences for future generations. Programs designed to foster health equity are now facing unprecedented hurdles, ultimately threatening the very fabric of community health and stability in the region.

The Rising Tide of Food Insecurity and Its consequences
The recent cuts in U.S. funding for food assistance in Africa have exacerbated an already critical situation, revealing dire implications for millions who rely on these resources for survival. As droughts, conflict, and rising food prices continue to plague many regions, the reduction in aid not only threatens immediate hunger relief but also jeopardizes long-term nutritional stability. The ripple effects are staggering; without sufficient food support, communities face increased rates of malnutrition, especially among vulnerable populations such as children and pregnant women. Food insecurity is not merely an issue of empty stomachs but a multifaceted crisis impacting health, education, and economic productivity.
The consequences of rampant food insecurity extend into various dimensions of society, leading to decreased educational outcomes, increased healthcare costs, and ultimately, a cycle of poverty that is hard to escape. Data indicates that:
- U.S. funding reductions have resulted in a projected 30% increase in malnutrition-related diseases.
- Schools in affected regions report that up to 50% of students are too hungry to concentrate during lessons.
- Communities face a 40% decline in agricultural productivity due to weakened labor forces struggling with hunger.
| Impact Category | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|
| Healthcare | Increased malnutrition-related diseases |
| Education | Reduced student performance |
| Agriculture | Decreased productivity |
As the landscape of food aid shifts, the responsibility falls on policy-makers and global leaders to recognize the gravity of the situation and prioritize interventions. The humanitarian calls must not only address immediate relief efforts but also consider strategic investments that will build resilience against future crises. Without decisive action, the forecasts for food insecurity will only become more dire, leading to wider social and economic upheaval across the continent.
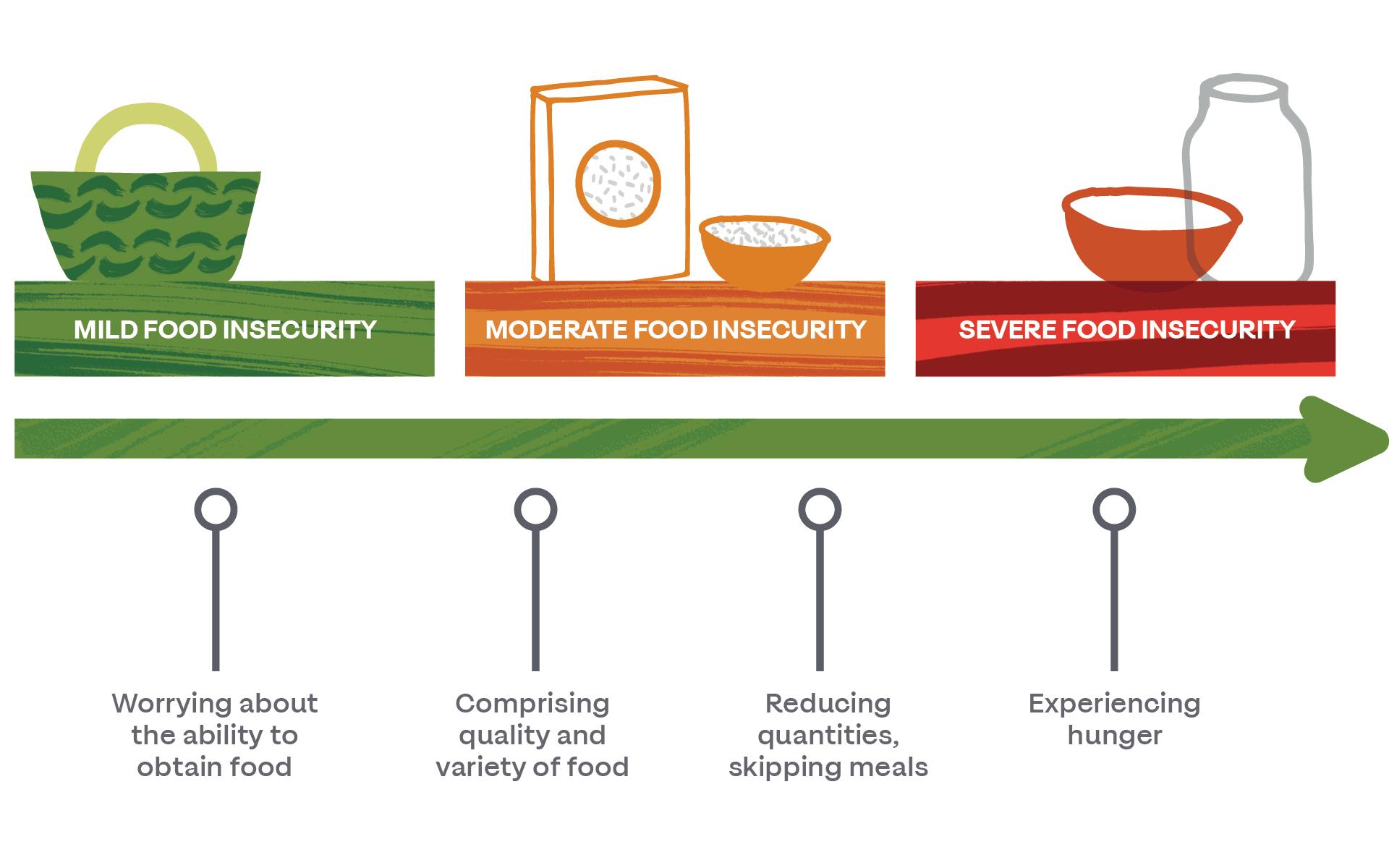
The human Cost of Reduced Humanitarian Aid
In recent years, substantial cuts to humanitarian aid have led to an alarming rise in suffering across Africa.According to numerous reports, millions are now facing severe hunger, with food insecurity exacerbated by the withdrawal of critical funding. A staggering percentage of rural communities, once resilient, are now teetering on the brink of famine. The reductions in aid have starkly translated into increased malnutrition rates,particularly among vulnerable populations such as children and pregnant women,where the lack of basic nutritional resources poses a threat to their very survival. The ripple effects are profound, as families are forced to make harrowing choices, often sacrificing education and health for the mere hope of a meal.
Moreover,the consequences extend beyond immediate hunger. Health services have been stripped down due to funding shortages, leaving many without access to essential medical care. Diseases that were once manageable are surging back, creating a public health crisis that further burdens already strained communities. Humanitarian organizations are struggling to fill the gap, frequently enough prioritizing life-saving measures that can only address symptoms rather than systemic poverty. as a result, the long-term outlook for development grows bleaker. A recent study highlights the cascading effects of these cuts:
| impact of Aid Cuts | Consequences |
|---|---|
| Food Insecurity | Increased hunger and malnutrition |
| Healthcare Access | Rise in preventable diseases |
| Education | Drop in school attendance rates |

Long-Term Effects on Education and Community Development
The repercussions of U.S. funding cuts extend far beyond immediate relief, profoundly affecting educational initiatives and community development across Africa.Crisis-driven funding has long acted as a lifeline for various educational programs, including initiatives aimed at increasing literacy rates and promoting gender equality in schools. As resources dwindle, there is a significant risk of school closures, inadequate teacher training, and a shortage of essential learning materials, which can derail years of progress. The ripple affect encompasses various facets of community life, stymieing growth and innovation just when they are most needed.
In communities where educational opportunities are severely compromised,the long-standing consequences become starkly evident. The loss of educational infrastructure and support leads to a cycle of poverty that is arduous to break. Consider the following impacts on community development:
- Increased Dropout Rates: Young people, particularly girls, are more likely to abandon their education when schools lack resources and stability.
- Economic Decline: A poorly educated workforce hampers economic growth and reduces opportunities for community advancement.
- Social Disintegration: Education frequently enough fosters community cohesion; without it, divisions can deepen, leading to conflicts.
| Impact | Short-Term Effect | Long-Term Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Educational Resources | Lack of textbooks | Reduced literacy rates |
| School Leadership | Inexperienced teachers | permanently underqualified workforce |
| Community Engagement | Decreased participation in local programs | Weak community ties and trust issues |

Potential Solutions to Mitigate the Crisis
To address the escalating crisis triggered by funding cuts, a multifaceted approach is essential. First and foremost, a reallocation of resources within existing budgets can help redirect funds towards critical sectors like healthcare and food security. Partnerships with local organizations should also be strengthened to ensure that aid reaches those who need it most. Innovative funding mechanisms, such as social impact bonds or crowdfunding initiatives, could supplement customary aid models, attracting investment in sustainable projects that provide long-term solutions to poverty.
In addition, international collaboration is crucial. Countries with more stable economies can increase their contributions to multilateral relief efforts, which woudl distribute aid more efficiently.Moreover, leveraging technology can enhance transparency and delivery of resources. As an example,mobile apps can facilitate the tracking of food distribution,while data analytics can identify areas with the greatest needs. A focus on education and skill development will also empower communities to become self-sufficient, breaking the cycle of dependency on external aid.

Call to Action for U.S.Policy Makers and Global Allies
The current humanitarian crisis in africa demands urgent attention and action from U.S. policy makers and our global allies. Complete funding for health, nutrition, and education is not just an option—it is a necessity.local economies are collapsing, and communities are suffering from increasing rates of malnutrition and disease. To mitigate further devastation, we must consider adopting the following measures:
- Restore funding levels to pre-cut amounts to support critical health programs.
- Facilitate partnerships with local governments and non-governmental organizations to ensure resources effectively reach those in need.
- Promote sustainable agricultural practices to enhance food security and resilience against climate change.
Strategic collaboration among nations is essential to confront this escalating crisis. By investing in humanitarian assistance and long-term development initiatives,the U.S. can play a pivotal role in reversing the course of hunger and suffering across the continent.It is indeed crucial that we prioritize not only immediate relief but also invest in capacity building for future resilience. Some potential policy initiatives include:
| Policy Initiative | Description |
|---|---|
| Increased Humanitarian Aid | Direct financial assistance to organizations providing relief services. |
| Food Security Programs | Investment in agricultural development and food distribution systems. |
| Health Infrastructure Support | Enhancing local health systems to combat infectious diseases. |

The Way Forward
As the repercussions of U.S. funding cuts continue to unfold across the African continent, the intertwining issues of fear, pain, and hunger present an urgent and complex humanitarian crisis. These reductions threaten not only immediate relief efforts but also the long-term stability and development of many nations already grappling with challenges ranging from health crises to food insecurity. The stories of resilience amidst despair emphasize the critical need for sustained international support and engagement. As global actors reassess their roles in aid and development, the lives of millions hang in the balance, reminding us all of the collective responsibility to address these pressing issues with urgency and compassion. The situation demands not only awareness but action,underscoring the importance of ongoing dialog and advocacy to ensure a brighter future for those affected. The journey toward recovery will be arduous, but it begins with commitment—commitment from all sectors of society to prioritize the well-being of Africa’s most vulnerable populations.