As teh impacts of climate change continue to manifestŌüó across the globe, fewŌüż regions are feelingŌĆī the heat more acutely than AfricaŌĆÖs Sahel region, ŌĆīparticularly in BurkinaŌĆī Faso and Mali. Stretching alongŌüŻ the ŌĆŹsouthern edge of the Sahara Desert,ŌĆŗ the Sahel has long been characterized by its challenging climate, but ŌĆŗrecent findings highlight how human-causedŌüŻ climate change is exacerbatingŌüż already extreme Ōüóheat conditions. According to a recent report by ClimateŌĆŗ Central,ŌĆŗ rising temperatures linked toŌüŻ greenhouse gas emissions are ŌĆīintensifyingŌüŻ droughtsŌĆŗ and heatwaves, ŌüŻthreatening agricultural yields, water supplies, and ŌüŻthe livelihoodsŌüó of millions.Ōüó As communities grapple with ŌüótheseŌĆŗ escalating climatic challenges, understanding the connection between human activity Ōüżand the environmental ŌĆŹcrisis becomes crucial for developing effective adaptation and mitigation strategies. ThisŌüó article ŌĆŗdelves into the interplay of climate change and extremeŌĆī heat in ŌüżBurkina Faso Ōüżand Mali, exploring the implications for both local populations Ōüżand the broader fight ŌĆŗagainst global warming.
ImpactŌĆī of Climate Change on Temperature Trends in the Sahel Region
The Sahel region, particularly in ŌĆīcountries like Burkina Faso Ōüżand ŌĆŹMali, hasŌüż been ŌĆŗexperiencing Ōüóalarming shifts ŌĆŹin temperature due to climate change.The average temperatures haveŌĆŗ been steadily rising, and the frequency ofŌĆŗ extreme heat events has increasedŌüó significantly. ŌüóAccording to climate models, the region isŌüŻ poised to witnessŌĆŗ an escalationŌüż in temperature trends, which poses grave challenges for local populations, economies, andŌĆŹ ecosystems. ThisŌĆī warming trend canŌüż be attributed primarily to human-driven factors,including greenhouseŌĆī gas emissions,deforestation,and land use changes,exacerbating the already arduous living ŌĆŹconditions ŌĆŹin these arid areas.
As temperatures climb,the implicationsŌĆŹ for ŌüŻagriculture and waterŌüŻ resources Ōüżare ŌüŻprofound. LocalŌĆŗ communities, heavily reliant on customary Ōüófarming ŌĆŗand pastoral practices, are facing a dualŌĆŗ crisis of drought and declining ŌĆīyields. AdaptiveŌüŻ measures are becoming essential, as Ōüótraditional resilience strategies Ōüżare frequentlyŌüż enough insufficient ŌĆīagainstŌĆŹ the Ōüónew climate realities. ŌĆŗKey impacts include:
- Increased drought frequency Ōüżaffecting crop production.
- Heat stress impacting livestockŌüż health and productivity.
- Reduced ŌĆŗwater availability from dwindling surfaceŌĆŗ and ŌĆŗgroundwaterŌĆŹ sources.
To illustrate the situation, the following table summarizes the average temperature increase over the last few decades in Burkina ŌĆīFaso ŌĆŗand Mali:
| year | Average ŌüóTemperatureŌĆŹ (┬░C) | Increase Compared to 1980s (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 1980 | 25.1 | – |
| 1990 | 25.6 | 2.0% |
| 2000 | 26.2 | 4.4% |
| 2010 | 27.0 | 7.6% |
| 2020 | 27.8 | 10.8% |

The SocioeconomicŌüŻ Consequences of Extreme Heat in Burkina Faso and Mali
Extreme heat in ŌĆīBurkina Faso and Mali presents a myriad of socioeconomic challengesŌüŻ that grip communities in the sahelŌĆŹ region. AsŌüŻ temperatures rise, ŌüŻagricultural productivityŌĆŗ suffers due toŌĆŗ heat stress, leading toŌüó diminished crop yields and food insecurity.Ōüż Traditional farming methods, heavily reliant Ōüóon seasonal rain, are rendered less effective Ōüóas ŌĆīrainfall patterns become ŌĆīunpredictable.Ōüó ThisŌüó has profound Ōüóimplications for the livelihoods of millions, particularly smallholderŌüż farmersŌĆŹ who are already vulnerable.
The increasing heat alsoŌĆī exacerbates health issues, leading to higher mortality rates associated with heat-relatedŌüŻ illnesses. Vulnerable populations, includingŌĆŗ childrenŌüó and the elderly, are particularly at risk. As health systems struggle to Ōüócope, economic productivity declines, further entrenching poverty. The following factors illustrate the interconnected challenges faced:
- Food Insecurity: Reduced agricultural output affects food ŌĆīavailability and prices.
- Health Crisis: Climate-induced illnesses Ōüżplace additionalŌĆŹ strain on healthcare ŌĆŗservices.
- Migration: heat-driven resource scarcity can lead ŌüŻto displacement and increased urbanŌüŻ migration.
- Economic ŌüŻInstability: Rising costs andŌüó declining productivity hinder economic Ōüógrowth.

Adaptation Strategies for Communities Facing Rising Temperatures
As communities in Burkina Faso and Mali grapple with ŌĆŗthe impactsŌĆŹ of ŌüŻextreme ŌĆŹheat due to climate change, innovative adaptation strategies are becoming increasingly essential. Local governments and organizations are taking proactive measures to enhance resilience against rising temperatures. Water conservation techniques suchŌüŻ as rainwater harvesting and the construction ŌĆŹof small-scale dams can definitely help ensure ŌĆŗa stable water supply during dry spells. Additionally, ŌĆŗimproving agricultural practices byŌüż introducingŌüŻ drought-resistant crop varieties and ŌüŻagroforestry systems allows ŌüŻfarmers to sustainŌĆŹ their livelihoods while adapting to hotter conditions. ŌüżThe widespread implementation of community-basedŌüŻ educationŌüŻ programs fosters ŌüŻawareness around heat-related ŌĆīhealthŌüż risks,ŌĆŹ empowering residents to ŌĆīmake informed decisions regardingŌüŻ theirŌĆī well-being Ōüżand to protect vulnerable populations, particularly young childrenŌüż and theŌĆī elderly.
Collaboration plays a vitalŌüż role inŌĆŹ the triumphant adaptation of ŌüótheseŌüż communities.Ōüż Establishing partnerships with localŌĆŗ NGOs and internationalŌĆŗ organizations can facilitate resource sharing,ŌĆŗ technical assistance, and funding for climate resilience projects. A focus on sustainable energyŌüó innovations, such as solar-poweredŌĆī irrigation systems, not only addresses immediateŌüŻ agricultural challengesŌĆŹ but also contributes to long-term economic ŌĆŗstability. Moreover, local governments are ŌüŻstarting to Ōüódevelop heat action plans ŌĆŹthat Ōüóinvolve monitoring Ōüżtemperature trends and issuingŌüŻ heat alerts, Ōüżthereby preparing ŌĆŗcitizens for extreme weatherŌĆī events. These thorough strategies form a blueprint ŌĆīfor communities toŌĆŗ not only endureŌĆī the harsh realities Ōüóof ŌĆīclimate change Ōüóbut thrive in theŌĆŗ face ŌĆŹof adversity.
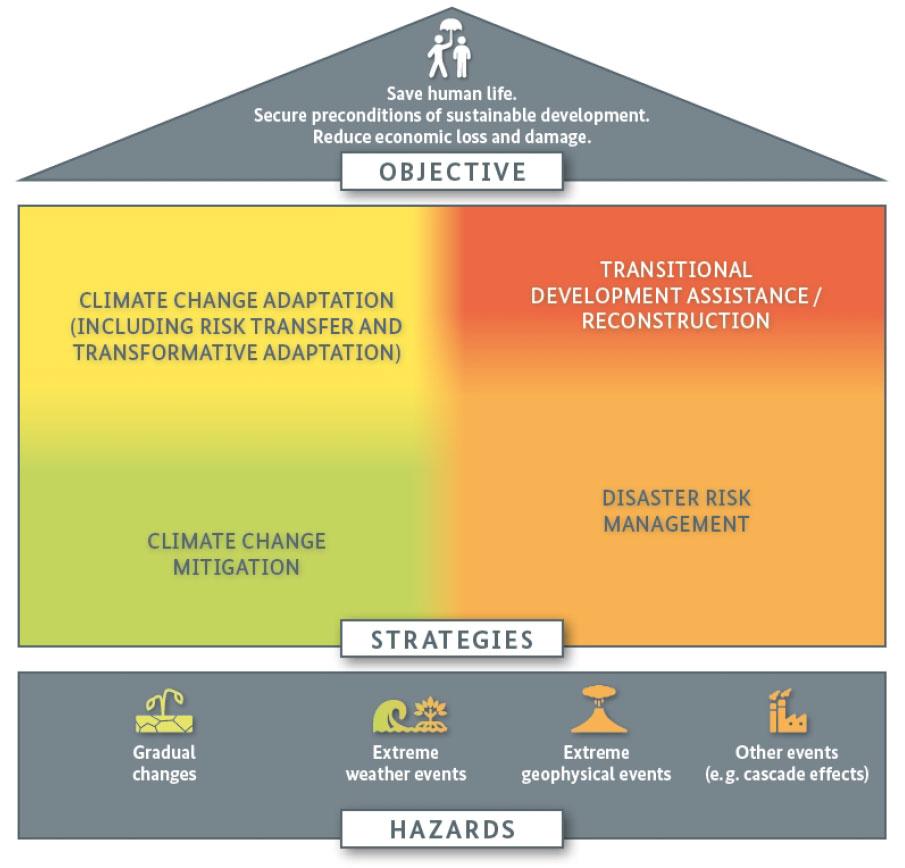
Policy Recommendations Ōüżfor Mitigating Climate ŌüżChange ŌĆīEffects
To ŌüŻcombat the dire effects ŌĆŗof climate change in the ŌĆŹSahel region,particularly Ōüóin Burkina ŌüżFaso and Mali,a ŌüóseriesŌüż of multifaceted policyŌĆŗ recommendations are ŌüŻessential. Governments and local ŌüŻauthorities must prioritize the implementation of effective climate adaptation strategies that bolster community resilience.This includes investing ŌĆŹin sustainable agricultural practices, ŌüŻsuch ŌüżasŌüó agroforestry and drought-resistant Ōüócrops, which can help communitiesŌĆŹ mitigate food insecurity exacerbated by risingŌüó temperatures. Additionally, enhancing water managementŌĆŹ systems ŌĆŹ through ŌĆŹrainwater harvesting ŌüŻand ŌĆŗefficient irrigation techniques canŌĆī significantly support local farmers ŌĆīin sustaining ŌĆŹtheir ŌĆŗlivelihoods amidstŌüó increasingly ŌĆŗerratic rainfall patterns.
Furthermore,ŌĆŹ international collaborationŌĆŹ is crucial in ŌĆŗaddressing the cross-border ŌĆŗnatureŌĆŗ of climate impacts in the Sahel. Policy frameworks should beŌĆī establishedŌĆŗ thatŌĆī encourage multi-national partnerships, focusing on shared resources and facts exchange regarding climate scientists’ŌüŻ findings. Increased financing for climate ŌĆŗadaptation initiatives, alongside educationŌĆī and training Ōüżprograms ŌĆŗ aimed atŌĆŹ building local ŌĆīcapacity, will empower communities toŌĆī adapt ŌĆŗtoŌĆŹ changing climatic conditions effectively. By fostering local engagementŌĆī andŌüŻ integrating traditional knowledge with modern ŌüŻclimate science, stakeholders canŌĆī develop innovative solutions tailored to the unique challenges faced in this vulnerable region.

The Role of International Cooperation in Sahel Climate Resilience
International collaboration is critical in enhancing climate resilience within the Sahel region, where the impacts of climate change, ŌüŻsuch as persistent ŌĆŗdroughts and Ōüżextreme Ōüóheat, are exacerbated. Regional ŌĆŹorganizations ŌĆīlike the African Union and Community of Sahel-Saharan States (CEN-SAD) play vital ŌüŻroles in uniting member countries to share resources andŌĆī knowledge. Through joint initiatives, nationsŌüż can develop Ōüócomprehensive strategies ŌĆīto combat ŌĆīthe adverse effectsŌüż of climate change, leveraging together:
- Research and ŌüżDevelopment: Collaborative scientific research can lead ŌĆŹtoŌüŻ innovative ŌĆŗtechnologiesŌĆŗ for climate Ōüóadaptation.
- Capacity Building: Supporting local communities ŌĆīwith training programs enhancesŌĆī theirŌüó ability to respond to climate-related ŌĆŗchallenges.
- Resource ŌüóSharing: Equitable distribution of water and agricultural resources can alleviate pressureŌĆŗ in areas most Ōüżaffected by climateŌĆŹ extremes.
Moreover, partnerships with international ŌüŻorganizations such as the UnitedŌĆŗ Nations ŌĆŗand World Bank ŌĆŹ can provide critical funding and ŌĆŹexpertise. These collaborations can catalyze the implementation of sustainable agricultural practices and bolster the development of ŌĆŗinfrastructure resilient to climate shocks. AŌĆŗ table summarizing successfulŌĆŹ international interventions in the Sahel Ōüóhighlights ŌĆīkey projects:
| Project Name | Lead Organization | FocusŌüó Area | year Initiated |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sustainable Agriculture Program | FAO | food security | 2018 |
| Water Resource Management | UNDP | Water Conservation | 2020 |
| Climate ResilienceŌĆŹ Project | World ŌüŻBank | Infrastructure | 2019 |
In essence, ŌĆŹproactive international cooperation serves not only to address ŌĆŗimmediateŌüŻ challenges posed by climate change in the Sahel but also to create sustainable practices that enhance the long-term resilience of communities in burkinaŌüó Faso,ŌüŻ Mali, and beyond.

Innovative SolutionsŌĆŗ for sustainable agriculture Amidst Extreme Heat
As temperatures soar Ōüżin the Sahel Ōüóregion, innovative agricultural practices are crucial to Ōüósafeguard foodŌĆŹ security and sustain ŌĆīrural Ōüżlivelihoods. Farmers are increasingly adopting ŌĆŹ climate-smart agriculture ŌĆī techniques, ŌüŻwhichŌüŻ emphasize ŌĆīresilience and adaptation to extreme heat conditions. Strategies include:
- Improved crop varieties: Utilizing drought-resistant seed varieties thatŌüó can thrive in high ŌüŻtemperatures.
- Agroforestry: Integrating trees with crops toŌüó enhance biodiversity, Ōüóreduce ŌüŻsoil erosion, and improve microclimates.
- waterŌüż management: Implementing effective irrigation Ōüżsystems and rainwater harvesting to optimize water usage.
Education and community collaboration play ŌĆŹvital roles ŌüŻin facilitating theseŌüŻ transformations. Farmers are participating in ŌĆīworkshops to share knowledge about sustainable ŌüŻpractices and access to resources.ŌüŻ Additionally, ŌüŻlocal governments and NGOs are creating networks to distribute ŌĆīvital information and technologies effectively.ŌĆī AŌĆī significant focus is on:
- Training programs: Offering ŌĆŹhands-on experiencesŌĆī for farmers in adaptive agricultural techniques.
- Seed banks: ŌĆŹ Establishing community seed banks to preserveŌĆŗ native and resilient crop varieties Ōüófor future planting.
- Market access: Connecting farmers to markets for their diverse produce,enhancing economic resilience.
| Innovative Solutions | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Drought-resistant crops | Higher Ōüżyield ŌĆŹeven ŌĆīin extreme heat |
| Agroforestry practices | Improved soil quality and biodiversity |
| Efficient water management | Reduced water wastage and enhancedŌüó availability |

In ŌĆŹConclusion
the escalating extreme heat experienced ŌĆīin Burkina Faso and Mali is a stark reminder ofŌüŻ the dire impacts of human-caused climate ŌĆŗchange on vulnerable regions. As the Sahel grapples withŌüŻ rising temperatures and severe weather patterns, the need for urgent action becomes ever more critical. The findings highlighted inŌĆŹ this report serve as ŌĆŗa call ŌüŻtoŌĆŗ both localŌĆŗ governments and theŌüŻ global community ŌüŻto prioritize climate resilience strategies and sustainable practices. While the challenges are daunting, addressing ŌĆīclimateŌüż change is not onlyŌĆŹ a matter of environmental necessity butŌĆŗ also of human rights and dignity for millions living in the Sahel.As we look to the future,collaborative efforts to mitigate the effects of climate ŌĆŹchange can pave the ŌĆīway for a more sustainable ŌüŻand equitableŌüż world. Addressing these challenges head-on willŌĆī be crucial ŌĆīin safeguarding livelihoods and ensuringŌĆī a brighter future for the Ōüżpeople of Ōüóburkina Faso, Mali, and beyond.







