West and Central Africa: Flooding ‚ÄćSituation ‚Ā§Overview – As of 5 October 2024 – Chad – ReliefWeb
As of October 5, 2024, West ‚Äćand Central Africa continues ‚Ā£to grapple with the‚Ā§ devastating impacts of ‚Äčwidespread flooding exacerbated by a combination of heavy rainfall and environmental factors. Chad, a landlocked country in the ‚ÄĆheart of ‚Äćthe‚Äć Sahel region,‚ÄĆ has ‚ĀĘemerged ‚ÄĆas one of ‚Äćthe hardest-hit areas, experiencing significant humanitarian challenges as a result of‚ÄĆ the flooding. With‚ĀĘ thousands displaced from their homes, ‚ÄĆcritical‚ĀĘ infrastructure compromised, and agricultural activities severely disrupted, the need for immediate relief and long-term ‚Ā£strategies has never been ‚Äčmore urgent.‚ÄĆ This article provides an overview of‚Ā£ the current‚ĀĘ flooding‚ÄĆ situation in‚Äč Chad,‚ÄĆ highlighting the ‚Ā£key developments, the response efforts underway, and the ongoing challenges‚ĀĘ facing affected communities. As the ‚Äćregion‚Äć contends with this environmental ‚Äćcrisis, ‚ÄĆthe implications for food security,‚Ā£ public health, and socioeconomic stability‚Äč remain profound, underscoring the necessity for ‚ÄĆconcerted action from national and international ‚Ā£stakeholders ‚Ā§alike.
Impact of‚Äč Recent Flooding on Communities in Chad

The recent flooding ‚Ā£in Chad has had a devastating impact on local communities, affecting both infrastructure and livelihoods across the ‚ÄĆregion. Thousands of ‚ĀĘfamilies have been displaced, prompting urgent humanitarian responses. The floods have overwhelmed essential services, ‚Ā£leading ‚Ā§to significant disruptions in access to‚Ā£ clean water and sanitation facilities. ‚ÄćConsequently, the‚Ā£ risk of waterborne diseases has surged, with‚ĀĘ health officials warning‚Ā£ of‚ÄĆ potential outbreaks if immediate action is not taken. local ‚ÄĆauthorities, alongside international aid organizations, ‚Äčare mobilizing resources to assist these communities by providing temporary housing, food, and medical supplies.
The economic repercussions of the flooding are equally alarming. Many agricultural areas have been submerged, destroying ‚Ā£crops ‚ĀĘand threatening ‚Ā§food security for countless households. The loss of livestock ‚ÄĆdue to flooding further exacerbates ‚ĀĘthe situation,severely affecting the‚Ā§ livelihoods of pastoralist communities. Key challenges‚ĀĘ include:
- Access to Markets: With roads ‚Äćdamaged or impassable, farmers find it tough to‚Äć reach markets ‚Ā§to‚ĀĘ sell‚ÄĆ whatever produce‚Äć remains.
- Food Prices: ‚ĀĘ As supplies dwindle, prices for‚Äć basic commodities are skyrocketing, placing‚Ā§ additional financial strain ‚ÄĆon vulnerable families.
- Long-term Recovery: Rehabilitation of affected areas will require‚Äć significant‚Äč investment‚ÄĆ and support, complicating the path to normalcy‚Äč for‚Ā£ many.
| Impact‚Äč Area | Current Status |
|---|---|
| Displacement | Over 20,000 families‚ĀĘ displaced |
| Agricultural Damage | Estimated loss ‚Äćof‚Äć 50% of crops |
| Health risks | Increased risk of cholera and malaria outbreaks |
Assessment of humanitarian Needs and ‚Ā§Vulnerabilities
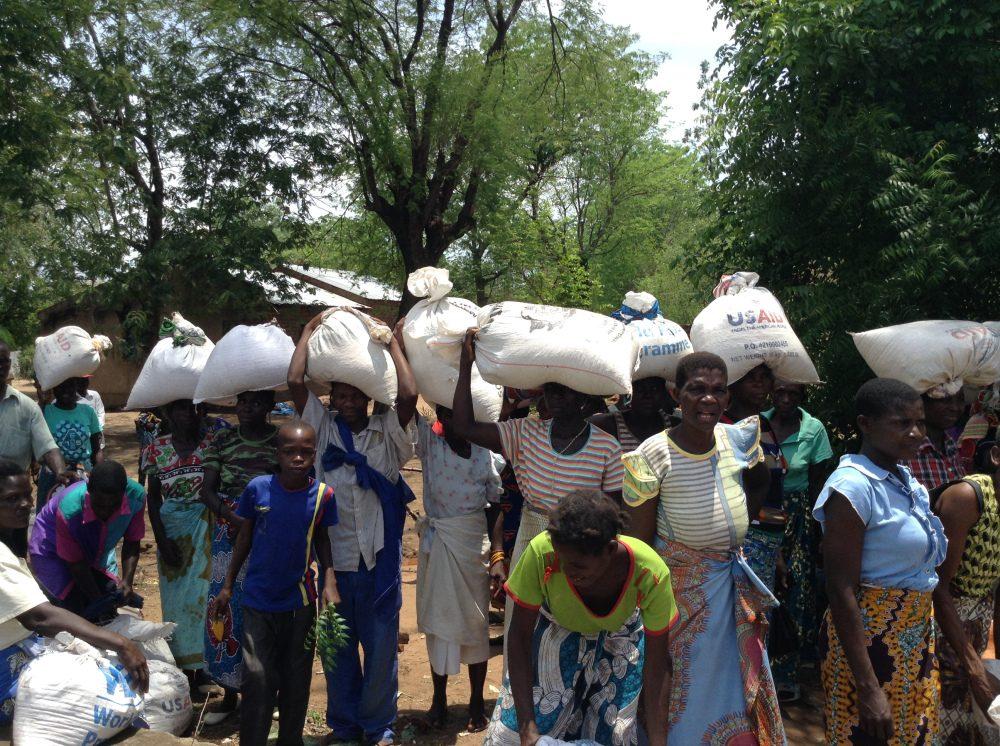

in ‚ĀĘthe wake of the‚Äč recent flooding across ‚Ā§Chad, a complete assessment‚Äč of humanitarian needs highlights the critical vulnerabilities faced by affected‚Äć populations.Many ‚Äčcommunities, particularly in rural areas, ‚ĀĘhave suffered extensive damage to‚Ā£ their homes ‚Äčand infrastructure, exacerbating existing challenges. Key‚Äć factors contributing to the severity‚Ā§ of the ‚Äčsituation ‚ĀĘinclude:
- Displacement ‚Äčof Families: ‚Ā§Thousands‚ĀĘ have been forced to‚Ā§ flee their homes, ‚Ā§leading to overcrowding in temporary shelters.
- Food Insecurity: disruption of agricultural activities has resulted‚Ā£ in diminished food supplies, ‚Ā§increasing malnutrition rates.
- Health Risks: Flooding has led to the proliferation‚Äč of waterborne diseases, further complicating access‚ĀĘ to healthcare‚Äć services.
Considering these challenges, a targeted response‚Ā§ plan is urgently needed to ‚Äćaddress the immediate and long-term needs of‚ĀĘ the affected‚Ā£ communities. Humanitarian organizations are preparing to implement multi-sectoral interventions, emphasizing:
- emergency Relief Supplies: Distribution of food, clean water, and sanitation kits ‚Äćto‚ĀĘ vulnerable populations.
- Healthcare‚Ā§ Support: ‚Äć Mobile clinics and vaccination‚Ā£ campaigns to combat disease outbreaks.
- psychosocial Support: Counseling services to assist ‚Ā§families traumatized by loss and ‚Ā£displacement.
| Area Affected | Population Impacted | Immediate ‚ÄćNeeds |
|---|---|---|
| Chad Central‚Äč Region | 100,000+ | food,Shelter,Hygiene Kits |
| Logone Occidentale | 50,000+ | Water,Health services |
| Kanem Region | 75,000+ | Psychosocial Support,Nutrition |
Response efforts by Local and International Organizations

‚Äć In response‚Ā£ to the‚ĀĘ devastating floods‚Äć affecting‚ÄĆ Chad‚ĀĘ and surrounding ‚Äćregions, both local and international‚ĀĘ organizations have‚Ā§ mobilized swiftly to provide immediate aid and assist in ‚Ā£recovery efforts. ‚Ā£ Local NGOs such as the Chadian Red Cross ‚Äćhave been at the forefront, delivering essential supplies including food, clean‚Äč water, and medical assistance to affected ‚ĀĘcommunities. Their volunteers are actively engaged ‚Ā£in both rescue ‚ĀĘoperations and long-term rehabilitation‚Ā£ initiatives to ‚Ā§help families rebuild their lives after the disaster.Meanwhile, international bodies like UNICEF and the World Food Program ‚ĀĘare collaborating ‚ĀĘclosely with government‚Ā§ agencies to‚Äč coordinate ‚Äčrelief ‚Ā£efforts, ensuring that resources are effectively distributed to ‚Ā£those‚ĀĘ in need. ‚ĀĘ
‚ĀĘ
‚Ā£ ‚Ā£ The collective efforts are essential to address both the immediate crisis ‚Ā§and the‚ĀĘ long-standing vulnerabilities‚Äć exacerbated by the flooding. Some of the key activities being undertaken include:
- Provision of Emergency Shelter: Temporary housing solutions‚Ā£ are ‚Ā§being deployed to ensure that displaced families have a‚Äč safe place to stay.
- Health Services: Mobile clinics are‚ĀĘ being established to‚Äć provide critical healthcare, including vaccinations and treatment for waterborne diseases.
- Community Engagement: Workshops ‚ĀĘand informational sessions are being‚Äć organized to educate communities on disaster preparedness and resilience-building strategies.
efforts are also being documented for ‚ÄĆfuture‚Äč analysis, with organizations establishing frameworks to‚ÄĆ assess the efficacy and reach‚Ā£ of their ‚Äčoperations.‚Äč Below is a summary of the ongoing ‚ÄĆresponse efforts by various ‚ĀĘorganizations:
‚Äč
| Organization | Type of Assistance | Status |
|---|---|---|
| Chadian Red ‚ÄčCross | Food‚Äć and Water Distribution | Ongoing |
| UNICEF | Healthcare and Child Support | Active |
| World Food Programme | Nutritional Aid | Deployment |
Recommendations for Enhanced Preparedness and Mitigation Strategies

To improve the response to flooding incidents‚ÄĆ in West‚Ā§ and ‚ĀĘCentral‚Äć Africa, it is essential to enhance local‚Ā£ capacity by implementing community-driven preparedness initiatives. These initiatives‚Äč can be ‚Ā£supported ‚ÄĆthrough tailored training programs aimed‚Ā§ at building skills in flood risk assessment‚Ā£ and management. Key ‚ĀĘstrategies to consider‚Ā§ include:
- establishing‚Ā§ early warning ‚Äčsystems: ‚ÄčUtilize local knowledge‚Äč and technology to develop robust systems that provide timely alerts to ‚Ā£communities.
- strengthening infrastructure: invest in‚Äč flood-resistant infrastructure, such as levees and drainage systems,‚Äć particularly‚Ā§ in ‚Äćvulnerable areas.
- Promoting ‚Ā§sustainable land ‚Ā§use: Implement zoning laws that discourage settlement in ‚Ā£high-risk flood zones‚Äč and encourage ‚ÄĆreforestation to ‚ÄĆenhance ‚Ā£natural‚Äć barriers.
In ‚Äćaddition,‚Ā§ cross-border collaboration is vital for ‚Äćeffective flood management. Regional organizations‚Ā£ should pursue ‚ĀĘjoint initiatives that address shared‚Äć challenges‚ĀĘ posed by frequent flooding events. This cooperation can be further‚ÄĆ facilitated ‚ĀĘthrough:
- data sharing: Create a regional database ‚Äčto monitor rainfall‚Ā§ and flooding patterns to improve predictive capabilities.
- Coordinated response teams: Establish multi-national response teams that can‚Ā§ quickly deploy‚Ā£ to ‚Äčthe‚Äč most affected regions during severe flooding ‚Ā£events.
- Public awareness campaigns: ‚ĀĘLaunch educational programs that engage‚Ā£ communities ‚Ā£in understanding flooding risks ‚Ā£and preparedness measures.
Long-term Strategies for ‚Ā§Building Resilience in ‚ÄĆFlood-Prone Areas

Developing effective long-term strategies for enhancing resilience in flood-prone areas requires a multifaceted approach that incorporates community engagement, infrastructure progress, and sustainable environmental ‚Ā£practices. Local communities should be at the forefront of disaster risk management initiatives, fostering a sense of ownership ‚ÄĆand accountability. Key ‚Äćstrategies include:
- community-Based Training: Implement regular workshops focused on ‚Ā£emergency preparedness ‚Äčand response‚Ā§ planning.
- Infrastructure ‚Ā§Investment: Invest in flood-resistant structures and drainage systems to ‚Ā£manage water flow better and mitigate flooding effects.
- Land Use Planning: Enforce regulations‚ÄĆ that limit construction ‚ĀĘin ‚Äćhigh-risk flood zones and encourage‚ĀĘ the rehabilitation of wetlands ‚Ā§and natural barriers.
- Environmental ‚ÄĆRestoration: Promote the restoration of‚Ā§ natural habitats that can absorb excess water, such‚Äč as mangroves and wetlands.
Additionally,ongoing monitoring and evaluation of climate‚ĀĘ data are crucial for developing adaptive strategies tailored to changing weather patterns. This can involve ‚Äčthe creation of‚Ā£ a centralized database ‚ÄĆto track flooding trends‚Äć and allow for predictive modeling. Collaborative efforts among local governments, NGOs, and international organizations can ‚Ā§enhance resource allocation and streamline‚Äč dialog. A‚Äć table ‚Äčsummarizing‚Äć these strategies ‚ĀĘcould look like ‚ĀĘthis:
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Community Engagement | involve ‚ÄĆlocal‚Äć populations in risk assessment and planning |
| Infrastructure Development | Build flood-resistant facilities and improve drainage |
| Sustainable Practices | Restore natural barriers to manage excess ‚Äćwater |
| Data Monitoring | Establish systems for tracking flood risks and patterns |
The Role of Climate Change‚ĀĘ in Increasing Flood Risks ‚Ā£in West and Central Africa

Climate change is‚ĀĘ significantly ‚Ā£influencing‚Äč the pattern and intensity of ‚Äćrainfall in West and Central‚Äć Africa, contributing to‚Äč an‚Äč alarming increase in flood risks across the ‚Äčregion. ‚ÄĆAs temperatures rise and‚Ā§ weather patterns become more erratic,local communities are witnessing ‚ÄĆunprecedented levels of precipitation,often leading to severe flooding. Key factors include:
- Intensified Rainfall: Studies indicate that the frequency and‚Ā§ intensity of heavy rainfall events‚Ā§ have increased, resulting in more significant runoff and water ‚Äčaccumulation.
- Inadequate Infrastructure: Many‚ĀĘ areas‚Ā£ lack sufficient drainage systems to cope with sudden deluges,exacerbating the impact of floods.
- Deforestation and Land Use Changes: Loss of vegetation cover reduces the land‚Äôs ‚Äčcapacity to absorb water, resulting in faster runoff and higher‚Ā§ flood risks.
The ‚Äćcompounding effects of‚Ā£ these climate-related factors are particularly pronounced in low-lying regions ‚Ā£and urban areas‚Äć where population density is high. Local governments and international organizations ‚Äćface ample challenges in addressing these issues, as floods disrupt livelihoods,‚ĀĘ displace communities,‚Ā£ and‚Ā£ strain already limited resources. To quantify the situation, a breakdown of recent flood ‚ĀĘevents illustrates the gravity of the threat:
| Location | Flood Event ‚ĀĘDate | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Chad | September 2024 | Displacement‚Äč of over 50,000 residents |
| Niger | August 2024 | Destruction of crops on 10,000 hectares |
| Cameroon | July 2024 | loss of‚ÄĆ infrastructure costing millions |
In Summary
the flooding situation in West and Central Africa, particularly ‚Ā£in Chad, remains a pressing humanitarian concern‚Ā§ as‚Äć of October 5, ‚Äč2024. The region continues ‚Äčto grapple ‚Äčwith the devastating impacts‚Ā£ of extreme ‚Ā§weather patterns exacerbated by climate change and ongoing socio-economic challenges.As communities ‚Äčface displacement, food insecurity, and‚Ā§ health risks, the‚Ā§ international‚Ā£ response must be‚Äč both immediate ‚Ā£and sustained to provide the necessary support. Humanitarian organizations are ‚Äčon the ground,‚Ā£ working‚Äć tirelessly ‚ÄĆto deliver assistance and implement long-term strategies for resilience.The ‚Äćsituation demands continued attention and action‚Ā£ from stakeholders, ‚Ā£governments, and ‚ÄĆthe global ‚Ā§community to‚Äč alleviate the ‚Ā§suffering of those affected and to‚Ā§ bolster efforts aimed at disaster preparedness and response. The road to recovery will undoubtedly ‚ÄĆbe challenging, but with coordinated efforts and sustained commitment, there is hope for the affected‚Ā§ populations to rebuild and thrive in the face of adversity.