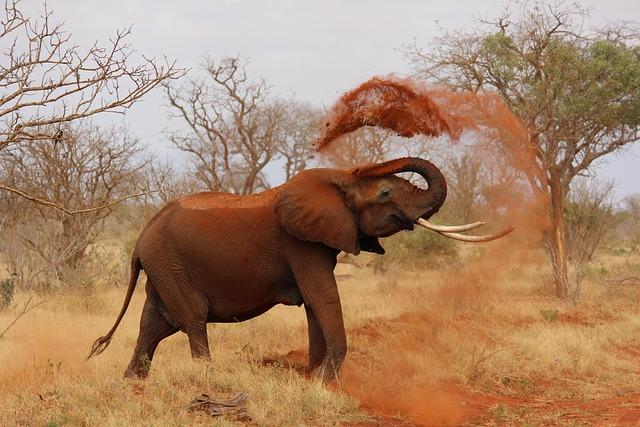
Title: how ŌĆŗTourism Could Actually Help AfricanŌüŻ Wildlife in One of KenyaŌĆÖs Important National Reserves
As global awareness of environmental conservation grows, theŌĆī intricate relationship between tourism Ōüóand wildlifeŌüŻ preservation has emerged as a focal point in discussions ŌĆīsurrounding sustainable development. in kenya, homeŌüŻ to some of Africa’s ŌüŻmost iconic national reserves, this ŌĆŗdynamic is especially pronounced. ŌĆīDespite the challenges posed by poaching and habitat loss,ŌĆī tourism offers a beaconŌĆŹ of hope for safeguarding the continent’s rich biodiversity. This article explores the potential of responsible tourism in one of kenyaŌĆÖs vital national reserves, examining ŌĆŗhow a carefully ŌüŻmanaged influx of visitors can not only bolster local economies but also play a crucial role in wildlife conservation.Ōüż By Ōüżpromoting awareness and funding protective measures, tourism can become a powerful ally in the fight to preserve KenyaŌĆÖs unique ecosystems for futureŌĆŗ generations.
The Economic Benefits of Sustainable Tourism for Wildlife Conservation
The intertwining of sustainable tourism andŌüó wildlife conservation presents a promising landscape for economic growth while together protecting KenyaŌĆÖs rich biodiversity. By prioritizingŌüż eco-pleasant travel options and responsible visitor behavior, national reserves can tap into significant financial resources. These funds can be reinvested into conservation efforts, ensuring habitats are preserved and the ecosystems remain ŌĆīvibrant. Moreover, the increased influx of tourists often prompts local communities to participate actively in conservation,Ōüż thereby fostering a sense of stewardship. The benefits can include:
- Job Creation: Sustainable tourism generates employment opportunities in hospitality, guiding, and conservation roles.
- Increased Funding: Entrance fees and park-related revenues can be directed towardsŌüó vital ŌĆīconservation programs.
- Community Development: Local businesses benefit from tourism, leading to improved infrastructure and services.
Additionally, engaging tourists in wildlife conservation education can enhance thankfulness for the natural environment, encouraging Ōüżthem to contribute ŌĆŗmore effectively through donations or volunteer efforts. This heightened awareness and involvement can transform visitors ŌĆŗinto advocates for wildlife protectionŌüó long after their departure. As tourism generates revenue, it canŌĆŹ create a Ōüżcycle of prosperity were local economiesŌüż thrive while ŌĆītheŌüż natural habitats sustain their ecological integrity. ŌüŻThe potential outcomes of responsible tourism are encapsulated in the table below:
| Economic Benefits | Conservation Impact |
|---|---|
| Revenue from Tourism | Funding for Anti-Poaching ŌüżInitiatives |
| Local Business Growth | Enhancement in Habitat Restoration Projects |
| employmentŌĆŗ Opportunities | Community Engagement in Conservation ŌüżEfforts |

Community Engagement: Empowering Locals to Protect Their Natural Heritage
In an era where wildlife conservation faces increasing challenges,Ōüó engaging local communities has emerged as a powerful Ōüóstrategy for protecting Africa’s natural heritage. By *actively involving residents* in conservation efforts, national reserves can bolster their effectiveness and sustainability. ThisŌüŻ approach not only empowers locals ŌĆŗbut also fosters ŌĆŗa deep-rooted sense of ownership over their environment, ensuring that wildlife protection becomes a shared responsibility rather than an external imposition. Some key benefits of community engagement include:
- Building Trust: Establishing strong relationships between conservationists and Ōüżlocal populations encourages cooperation and Ōüżmutual respect.
- enhancing ŌüżAwareness: Education initiatives increase knowledge about the ecological importance of wildlife, Ōüófostering a culture of conservation.
- Economic Incentives: Eco-tourism initiatives can ŌĆŹprovide locals with sustainable income opportunities while incentivizing wildlife protection.
Moreover, successful models from various regions demonstrate that tourism can serve as a financial lifeline for local communities while simultaneously preserving wildlife habitats. ByŌüŻ creating *beneficiary programs* where theŌüó revenues generated from tourism are reinvested into ŌĆīlocal initiatives, communities can see Ōüódirect returns on their commitment to conservation. Below is a simple comparison of how tourism revenues can be allocated for maximum community impact:
| Revenue Category | Allocation Percentage | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Wildlife Conservation | 40% | Direct investment ŌĆŹin anti-poaching measures and habitat restoration |
| Community Development | 30% | Education, healthcare, and infrastructure improvement |
| Employment Opportunities | 20% | Creating jobs in eco-tourism and related services |
| administrative Costs | 10% | Operational costs for managing tourism initiatives |

Balancing Ecosystems: HowŌüó Responsible Tourism Supports Biodiversity
ResponsibleŌĆŹ tourism acts as a powerful catalyst ŌĆŗfor preserving biodiversity, particularly in regions like KenyaŌĆÖsŌüż national reserves. ŌüżBy ŌĆŹembracing sustainable practices, tourists can contribute to the ŌĆŹconservation of wildlife while enjoying an immersive experience in nature. Sustainable initiatives, such as community-led conservation programs, offer economic incentivesŌĆŹ forŌĆī local populations to protect their natural resources. This form of tourism not only protects endangered species Ōüżbut ŌĆŗalso enhances ŌĆŹhabitat restoration efforts. Key strategies include:
- CommunityŌĆŹ Engagement: Involving local communities ŌĆīin conservation enables them to become Ōüżstewards of their environment.
- Wildlife ŌĆŗMonitoring: Tourists can participate in wildlife tracking and monitoring projects that provide valuable data for research.
- Eco-FriendlyŌüó Accommodations: Staying in eco-lodges supports green practices that have aŌĆŹ low impact on the ecosystem.
Investing in responsible tourism not only Ōüóboosts ŌĆīthe local ŌĆŗeconomy but alsoŌĆŗ fosters aŌĆī deeper understanding ŌĆīofŌĆī wildlife conservation challenges. By aligning tourist interests withŌĆŹ conservation goals, national reserves can thrive as both ecological sanctuaries andŌüó sustainable business ventures. Consideration ofŌüó the following impact areas demonstrates how tourism can effectively support biodiversity:
| Impact Area | TourismŌĆī contribution |
|---|---|
| WildlifeŌüó Conservation | Funding for anti-poaching patrols and habitatŌĆŹ preservation. |
| Education | Raising awareness about biodiversity and the importance Ōüżof ecosystems. |
| Research | Supporting scientific studies aimedŌüż at understanding ecological balance. |

Innovation in Conservation: TechnologyŌĆÖs ŌüóRole in Advancing Wildlife Protection
In recent years, technology has ŌüŻemerged as aŌĆŹ pivotal ally in the fight for wildlife conservation, particularly in Kenya’s national reserves. the integration of drones, remote ŌĆīsensing, and artificial intelligence has revolutionized traditionalŌĆŗ conservation methodologies. ŌüŻDrones equipped with high-resolution cameras allow for expansive aerial monitoring of wildlife populations and habitats, enabling conservationistsŌüó to quicklyŌĆŹ identify threats such as poaching orŌüŻ habitat encroachment. Alongside this, satellite imaging Ōüógrants researchersŌĆŗ the ability to assess land-use changes over time, providing crucialŌüż data ŌüŻfor effective management strategies.
Moreover,the application ofŌĆŹ machine learning algorithms toŌĆī analyze patterns in animal behavior enhances understanding and ŌĆīprediction of wildlife movements,which can be instrumental in safeguarding endangered species. ŌüŻThe real-time dataŌĆŗ collected through mobile applications empowers ŌĆŹpark rangersŌĆī with data at their fingertips, improving the speed and efficacy of their responses to emerging threats. The synergy of these technological advancements not only fosters a ŌüŻproactive approach to wildlife protection but also offers sustainable tourismŌüż solutions that benefit local communities and wildlife alike. Some key technological innovations in ŌĆīthe field include:
- Remote Camera Traps: Monitor animal activities and population metrics.
- Ecological Tagging: Track movements andŌĆŹ health of specific species.
- Data Analytics Platforms: Aggregate data for strategic decision-making.

Challenges and Solutions: AddressingŌüó the Downsides of Tourism in National Reserves
Tourism, while often celebrated for its economic advantages, can introduce significant challenges to national reserves, particularly those aimedŌĆŗ at protecting wildlife. Overcrowding, oneŌüó of the ŌĆīmost pressing issues, can lead toŌüż habitat degradation, increased litter, and disturbancesŌĆŗ to wildlife. Additionally, the influx of visitors can strain local resources, such as water and food supplies, making it toughŌüó for both wildlife andŌüó local communities to thrive. Wildlife poaching and illegal trade can also be exacerbated by tourism, as the presence of tourists might inadvertentlyŌüŻ create ŌĆŹopportunities forŌĆŗ poachers toŌĆŹ capitalize on the situation. Addressing these challenges requires a multi-faceted approach thatŌĆŗ prioritizes the Ōüódelicate ŌüŻbalance between tourism andŌĆŗ conservation.
To transform these challenges into opportunities, several solutions should be implemented.ŌĆŗ Enhanced management practices are essential, including visitor caps to limit overcrowding and designated pathways to minimize habitat disruption.Engaging local communities through eco-tourism initiatives can empower them to takeŌüŻ an active roleŌüż in conservation ŌüŻand provide choice livelihoods that reduce reliance on poaching. education programs that informŌüż tourists about responsible behaviorŌĆī in national reserves can ŌĆŹfoster a culture of respect forŌüż wildlife and the environment. Moreover, investing in infrastructure improvements,Ōüó such as waste management ŌĆīsystems and renewable energy solutions, can mitigate the negativeŌĆŗ impacts ofŌĆŹ tourism while ensuring that the ŌüŻbenefits Ōüżare equitably shared among all stakeholders involved.

Future ŌĆīProspects:Ōüż Creating a Sustainable Model for Wildlife Tourism in Kenya
As Kenya grapples with theŌüó dual challenges of wildlife conservation and economic growth,the future of wildlife tourism can be ŌüŻanchored inŌüż sustainable practices that prioritize both ecological balance and the communities that rely on these resources. Implementing robust strategies can enhance the positive impacts of tourism on wildlife. Key initiatives may include:
- Community Involvement: Engaging local populations in tourism management ensures ŌĆŹthey benefit directly from preserving wildlife.
- Responsible WildlifeŌĆī Encounters: Establishing guidelines that promote ethical interactions between Ōüżtourists and animals helps maintain natural behaviors and habitat integrity.
- Eco-friendlyŌĆŗ Infrastructure: Developing accommodations and amenities that minimize environmental footprints reduces the Ōüósector’s overall impact on fragile ecosystems.
- Conservation Education: Educating tourists about Ōüóthe ecological importance of theŌüŻ regions they visit fosters long-term advocacy and support for wildlife initiatives.
Furthermore,Ōüó data-driven monitoring systems can facilitate adaptive management strategies thatŌĆŗ bolster wildlife populationsŌĆŹ and habitat quality. Consider the following tableŌüŻ thatŌüó outlines potential key performance indicators (KPIs) for measuringŌĆī the success of sustainable tourism practices in national reserves:
| indicator | Target | Measurement Method |
|---|---|---|
| Wildlife PopulationŌĆī Growth | 10% increase/year | Aerial surveys,Ōüż camera traps |
| Local Employment Rate in Tourism | 30% of jobs filled by locals | Annual workforce audits |
| Visitor Satisfaction Rate | 90%ŌĆŗ positive reviews | Post-visit surveys |
| Decrease in Poaching Incidents | 50% reduction | Report analysis from conservation bodies |
By integrating these approaches, Kenya can pave the way toward a wildlife tourism ŌüŻmodel that not only preserves its natural heritage but also empowers local communities and stimulates economic Ōüógrowth, ensuring the survival of its iconic species for generationsŌüż to come.
Insights ŌüŻand Conclusions
the delicate balance betweenŌüż tourism and conservation in KenyaŌĆÖs national reserves exemplifies a complex ŌĆŗyet promising approach to wildlife preservation.ŌĆŗ By harnessing the economic potential of eco-tourism, local communities ŌĆŗcan play a pivotal ŌĆīrole in safeguarding their naturalŌüó heritage. Sustainable tourism not only generates vital revenue but also fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility among local populations towards their environment.As we ŌüŻhave explored, with strategic planning and a commitment to preserving biodiversity, Ōüżtourism can act as a powerful ally ŌĆŗfor wildlife conservation in Africa. Moving forward,it is imperative Ōüżfor stakeholdersŌĆögovernments,NGOs,and the tourism industryŌĆöto collaborate and innovate,ensuring that the ŌĆŗmajestic landscapes and diverse ŌĆīfauna of Kenya ŌĆŹcontinue to thrive for generations to come. By investing in conservation-minded tourism,we can pave the way for a harmonious coexistence between people and wildlife,turning a potential threat into aŌüż celebrated opportunity Ōüżfor both nature and communities ŌĆŹalike.