exploring the Cabo Verde Archipelago: A Geographic Overview
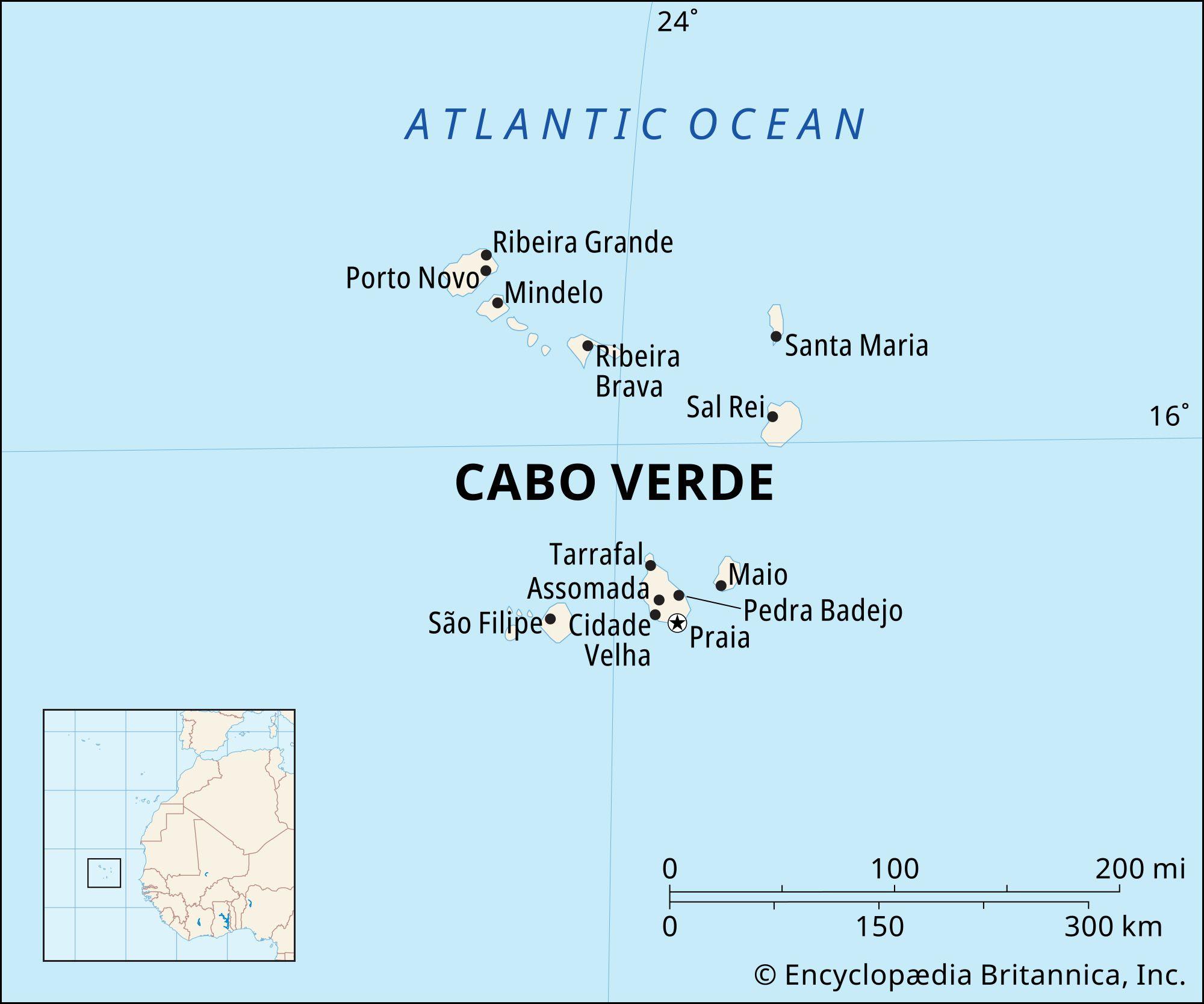
The Cabo Verde archipelago, nestled in the central Atlantic Ocean, holds a strategically notable position off the northwest coast of Africa. Consisting of ten volcanic islands, this vibrant archipelago is not only a unique blend of cultural influences but also a focal point for geological and ecological studies. The study area map presented in the article serves as a crucial tool for researchers and policymakers alike, aiding in the understanding of Cabo Verde’s diverse environments and their implications for local development and conservation.By examining the geographical context of these islands, we can unravel the complexities of their natural resources, climate patterns, and human interactions, all of which play a pivotal role in shaping the future of this island nation and it’s surrounding marine ecosystems. This article aims to provide an informative overview of the Cabo Verde archipelago, highlighting its geographical meaning and the importance of rigorous research in promoting sustainable practices in the region.
Location and Geography of the Cabo Verde archipelago
The Cabo Verde Archipelago, an exquisite set of volcanic islands, is located in the central Atlantic Ocean, approximately 570 kilometers off the coast of North Africa. This unique geographic positioning places it within the “Sahel” region, characterized by a semi-arid climate. The archipelago consists of ten main islands and several islets scattered across an area of roughly 4,033 square kilometers. Among these islands, the largest and most populous are Santiago, SĂŁo Vicente, and Sal. the complex geography is marked by both mountainous terrains and extensive coastal areas, contributing to a diverse range of ecosystems.
Each island offers a distinct landscape and cultural identity, owing to the variations in elevation and climate. for a clear understanding of the geographic diversity,consider the following features:
- Elevation Variation: Some islands,like Fogo,boast peaks over 2,800 meters,while others,such as Sal,are relatively flat.
- Climate Diversity: From the arid conditions of Maio to the lush vegetation found on Santiago, the climatic range enriches local biodiversity.
- Marine Ecosystem: The surrounding waters are teeming with diverse marine life, making the archipelago a hotspot for fishing and aquatic exploration.

Ecological Significance of Cabo Verde’s Diverse Landscapes
Cabo Verde’s unique geographical position and varied topography create a wealth of ecological niches,contributing to a remarkable diversity of flora and fauna. The archipelago boasts a range of environments, from arid landscapes to lush mountainous regions, which are home to endemic species adapted to these distinct habitats. This ecological variety supports complex ecosystems that play crucial roles in maintaining biodiversity both locally and regionally. For instance,the island of SĂŁo Nicolau showcases endemic bird populations that are vital for seed dispersal,while the volcanic soils of Fogo cultivate a rich array of plant species,some of which are used in conventional medicine.
Furthermore, the coastal ecosystems surrounding Cabo Verde, including coral reefs and mangroves, serve as critical habitats for marine life. These areas are not only essential for the ecological balance but also contribute considerably to local fisheries, which sustain the livelihoods of island residents. The interaction between terrestrial and marine ecosystems enhances resilience against climate change impacts,demonstrating the interconnectedness of Cabo Verde’s landscapes. Effective conservation efforts are imperative to preserve these habitats and the unique species that inhabit them, ensuring that future generations benefit from the ecological richness of this dynamic archipelago.

Cultural Heritage and Historical Overview of cabo Verde
The Cabo Verde archipelago, an UNESCO World Heritage site, boasts a rich tapestry woven from African, Portuguese, and Brazilian influences. This unique blend is evident in the islands’ vibrant music and dance traditions, notably the morna and coladeira, which express themes of love, hardship, and nostalgia. The islands’ language, Kriolu, further reflects this fusion, incorporating elements from both African languages and Portuguese. Cabo Verdean culture is celebrated annually through various festivals, such as the Festa de SĂŁo JoĂŁo and the Carnaval, where locals engage in elaborate dances and colorful parades, showcasing their cultural pride and historical depth.
Cabo Verde’s historical narrative is deeply entwined with its role as a center for the Atlantic slave trade during the 15th to the 19th centuries. Beyond its dark history,the islands also emerged as a crossroads for maritime trade,allowing for a melting pot of ideas and traditions.The architectural heritage found in cities like Praia and Mindelo reveals influences from colonial styles, with structures adorned with intricate tile work and vibrant colors. As a nation,Cabo Verde continues to honor its past while embracing modernity,making it a dynamic study area for scholars and cultural enthusiasts alike.

Challenges and Opportunities for Sustainable Development
The Cabo Verde archipelago, located off the northwest coast of Africa, faces a myriad of challenges in its pursuit of sustainable development. As a small island developing state, the region is especially vulnerable to the impacts of climate change, including rising sea levels and extreme weather events.Moreover, limited natural resources and dependence on external imports further complicate efforts toward self-sustaining economic growth. key challenges include:
- Environmental degradation: Overfishing and deforestation threaten biodiversity and marine ecosystems.
- Water scarcity: The arid climate limits freshwater resources, essential for both consumption and agriculture.
- Energy reliance: The archipelago’s heavy reliance on imported fossil fuels hampers efforts to transition to renewable energy sources.
Despite these challenges, Cabo Verde presents several opportunities for advancing sustainable development. The nation has made significant strides in adopting renewable energy technologies, particularly wind and solar power, which have the potential to transform its energy landscape.Furthermore, the growing emphasis on eco-tourism can promote both economic growth and environmental conservation. Opportunities for sustainable development include:
- Investment in green technologies: Harnessing wind and solar energy can reduce dependency on imports and lower carbon emissions.
- Community-driven initiatives: Engaging local populations in conservation efforts can enhance community resilience and sustainable livelihoods.
- international collaboration: Partnerships with global organizations can facilitate access to funding and expertise for sustainable projects.
| opportunity | Potential Impact |
|---|---|
| Investment in Renewable Energy | Reduction of carbon footprint and energy independence |
| Eco-tourism Development | Boost to local economies and promotion of conservation |
| Education & Awareness Campaigns | Empowered communities advocating for sustainable practices |
Recommendations for Future Research and Conservation Efforts
to enhance the understanding and preservation of the Cabo Verde archipelago’s unique ecosystems, future research should prioritize a multi-disciplinary approach that encompasses both ecological and socio-economic dimensions.This may include:
- Long-term ecological monitoring: Implementing systematic studies to track changes in biodiversity and habitat conditions.
- Community engagement: Involving local populations in conservation efforts to ensure sustainable practices align with their cultural and economic needs.
- Climate change impact assessments: Investigating how rising sea levels and temperature fluctuations affect marine and terrestrial habitats.
- Invasive species research: Identifying and managing threats posed by non-native flora and fauna.
Conservation initiatives should be coupled with targeted funding and policy advocacy to support sustainable practices throughout the archipelago. Key areas to address include:
| Conservation Focus | Action Items |
|---|---|
| Marine protected Areas | Expand and enforce regulations to protect critical habitats. |
| Biodiversity corridor development | Create ecological corridors to enhance species migration. |
| Research Funding | Secure grants for cross-disciplinary collaborative studies. |
| Education & Outreach | Raise awareness of conservation principles among youth and local communities. |

Mapping Technology’s Role in Understanding Cabo Verde’s Environment
The Cabo Verde archipelago, nestled off the northwest coast of Africa, is a striking example of how mapping technology can deepen our understanding of environmental dynamics. Utilizing advanced geographic information systems (GIS) and remote sensing, researchers can create detailed visualizations that reveal the intricate interplay between natural ecosystems and human activities. these tools facilitate the identification of critical habitats, habitat fragmentation, and land use changes, which are paramount in assessing biodiversity and guiding conservation efforts.
Furthermore, mapping technology aids in monitoring climate change impacts, enabling scientists to visualize phenomena such as sea-level rise, desertification, and temperature variations across the islands. the integration of real-time data with historical records through interactive maps empowers policymakers and stakeholders to make informed decisions that positively influence environmental sustainability. Below is a simple overview of significant environmental factors influencing Cabo verde’s landscape:
| environmental Factors | impact on Cabo Verde |
|---|---|
| Climate Change | Increased temperatures and irregular rainfall patterns |
| Deforestation | Loss of biodiversity and increased soil erosion |
| Urbanization | Pressure on natural resources and habitat alteration |
| Coastal Erosion | threat to communities and ecosystems along coastlines |
In Conclusion
the study area map highlighting the Cabo Verde archipelago serves as a vital resource for researchers and policymakers alike, encapsulating the geographical significance of this unique region in northwest Africa. The strategic location,diversity of ecosystems,and cultural richness underscore the need for targeted studies to address various environmental and socio-economic challenges facing the islands.As interest in Cabo Verde continues to grow, this map will undoubtedly play a crucial role in guiding future research initiatives and fostering sustainable development efforts. By understanding the intricate layers of this archipelago’s geography, we can better appreciate its contributions to global biodiversity and heritage, all while working to preserve its natural beauty for generations to come.