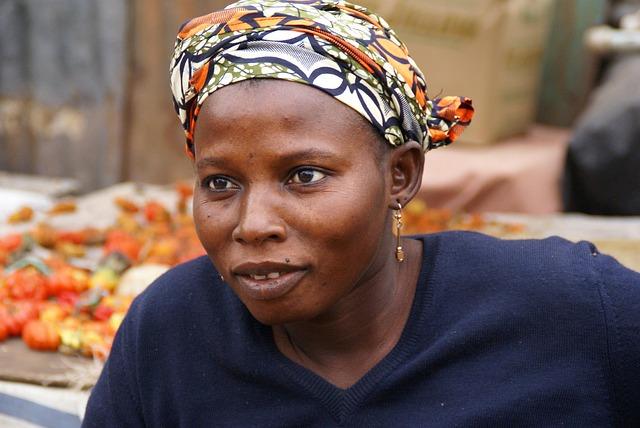
In the ‚Äćsmall West ‚ÄčAfrican‚Ā§ nation of Gambia, ‚Äća vibrant youth population is reshaping the social landscape, as the median age‚ĀĘ hovers‚Ā§ around 18 years. While the‚Ā£ energy and ‚Äćpotential of its young‚Ā§ people herald ‚Äća bright ‚ÄĆfuture, ‚ÄĆthe country ‚Ā£faces ‚Äčcritical challenges in addressing the needs and care of its aging population. The elders,who possess‚ĀĘ invaluable‚Ā§ wisdom ‚ÄĆand a wealth of‚Ā§ cultural‚ĀĘ knowledge,are increasingly at‚Äć risk of ‚Äćbeing ‚ÄĆoverlooked in a society ‚Äčthat‚Äč prioritizes the aspirations ‚Ā£of the‚ĀĘ young. This demographic shift poses pressing questions ‚Äćabout duty, respect, ‚Äćand ‚Ā£the‚ĀĘ sustainability‚Äč of‚Ā£ customary family‚Äč structures. In ‚Ā§this article, we explore how Gambia navigates‚Äč the ‚Äčdelicate balance between ‚ÄĆhonoring its elders and harnessing‚Äć the ambitions of its youth in a rapidly changing socio-economic environment. Thru the lens of community leaders, healthcare providers, and families, we delve into‚Äč the emerging strategies ‚Äčand cultural tensions that define elder care in a‚ĀĘ youthful country on the ‚Äčmove.
Generational Challenges in Gambia’s Rapidly Growing Youth Population
The demographic landscape of Gambia presents‚Ā£ a striking juxtaposition: a vibrant and ‚Äčdynamic‚Ā§ youth population ‚Ā§that ‚ÄĆis rapidly expanding, while an ‚ÄĆaging ‚Äćdemographic‚Ā§ faces increasing challenges. As youthful energy surges, the responsibilities of caring for elders are often relegated to ‚ĀĘthe fringes of societal priorities. this generational gap prompts vital questions regarding the sustainability of ‚Äčtraditional‚Äč family ‚ĀĘstructures ‚Ā§and community support ‚Äčsystems. Key‚Ā£ challenges include:
- Economic Strain: Wiht a growing youth‚Äč population, ‚ÄĆlimited‚ĀĘ job opportunities can‚Äć compel ‚ĀĘyounger generations to ‚Ā§prioritize their economic survival over elder care.
- Cultural Shifts: Modern influences ‚ÄĆand urban migration alter the traditional‚Äć norms of communal living, affecting intergenerational bonds.
- Healthcare Accessibility: A‚Äč strained ‚Ā§healthcare system,facing a shortage of resources,frequently ‚Ā§enough ‚Äćleaves ‚ĀĘthe elderly ‚ĀĘwithout ‚Äčadequate support.
While many young Gambians ‚Äčdeeply value their cultural heritage, they ‚Ā£frequently enough find themselves navigating a complex landscape of expectations and pressures. The disconnect ‚Ā§between‚Ā£ generations can lead to ‚Ā§feelings of isolation among the elderly, who may struggle with adapting to the changing social fabric. To address these‚ĀĘ issues,‚ÄĆ collaborative initiatives are essential. Consider the following approaches ‚ĀĘthat may strengthen intergenerational relationships:
| Initiative | Description |
|---|---|
| Mentorship Programs | Encouraging‚ÄĆ youths to engage with ‚Ā§elders‚ĀĘ for shared knowledge and experience. |
| Community Workshops | Creating platforms ‚Äćfor dialog around caregiving roles‚ÄĆ and responsibilities. |
| Sustainable Health Services | Developing accessible healthcare‚ÄĆ solutions tailored for the elderly population. |
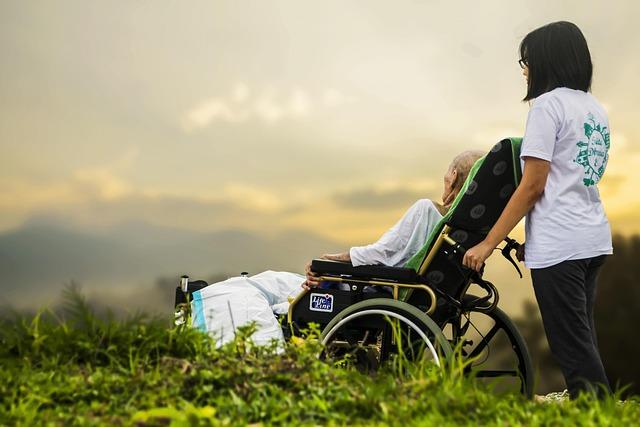

Cultural Perspectives on ‚ÄćElder ‚ĀĘCare and Traditional Practices
The ‚ĀĘcultural fabric of Gambia, rich ‚Äčin traditions, plays a pivotal role in defining‚Ā£ how elder care is perceived and practiced. In‚Äć a nation ‚Ā§where the median age ‚Ā§is ‚Ā§below 20, the‚Ā£ pressure to balance communal expectations with‚Ā£ the needs of‚Äć the elderly is ever-present. Traditionally, families have been the primary caregivers, reflecting a societal‚Ā£ belief that ‚Äćcaring‚ÄĆ for elders is a duty rather than an obligation. This intergenerational‚ĀĘ bond emphasizes respect ‚Äćand ‚ÄĆreverence‚Äč for elders,‚Äć frequently enough manifested ‚Äćthrough:
- Family ‚Ā§Involvement: Extended families, including aunts, uncles, and cousins, ‚Äčshare‚ĀĘ the responsibility of‚Ā§ caring for aging relatives.
- Community Support: neighbors ‚Äčoften‚ÄĆ lend a hand, ‚ÄĆreinforcing the collective ‚Ā£responsibility for the‚Äć elderly.
- rituals and Traditions: Cultural ceremonies‚ÄĆ that honor elders,such‚Ā§ as storytelling sessions and communal feasts,affirm their value within‚Ā£ society.
However, ‚ÄĆthe ‚Ā£rapid urbanization and a shift toward nuclear family structures are challenging these‚ĀĘ traditional‚ÄĆ practices. Young Gambians, often moving to‚Äč cities for education and employment opportunities, grapple with maintaining‚Äć the same level ‚Ā£of‚ÄĆ care for their aging relatives who ‚Äćmay remain in‚Ā£ rural areas. consequently, new methodologies of elder care are emerging,‚ÄĆ reflecting a blend of modernity and tradition:
| Modern Approaches | Traditional ‚ĀĘPractices |
|---|---|
| Home health‚Ā£ care services | family ‚Ā£caregiving |
| Senior living‚Ā£ facilities | Living‚ÄĆ with extended family |
| Digital dialogue ‚Äčtools for support | Face-to-face ‚Ā£community gatherings |
This tension‚Äć between tradition and modernity presents both challenges and opportunities for Gambians. As the country navigates this‚Äć shift,‚Ā£ it is indeed essential to consider how to ‚Äćintegrate respectful care for the elderly ‚Ā£with evolving societal ‚Äčnorms, ensuring that‚Ā§ the wisdom and‚Ā£ contributions of‚Äć the elder generation continue to be honored in a rapidly changing world.

The Role of Government and Policy in‚Ā£ Supporting Aging Citizens
The Gambian government faces a critical challenge in transitioning from a predominantly youthful demographic to one that respects and‚ÄĆ supports its aging citizens. Effective‚ÄĆ policies are essential to address the unique needs of the elderly, who have‚Äć contributed‚Äč significantly ‚ĀĘto the nation‚Äôs ‚ĀĘcultural wealth and workforce.‚Ā§ Some ‚Äčkey areas where government intervention can make ‚Ā£a difference include:
- Healthcare Accessibility: Enhancing healthcare services‚Äč tailored for older adults‚Ā§ to‚ĀĘ ensure they‚Äć receive adequate medical‚Äć attention.
- Social Programs: Introducing social support structures that provide financial assistance and community ‚Ā§engagement ‚Ā£opportunities for seniors.
- Education and Awareness: Promoting campaigns that educate‚Ā£ the‚ÄĆ younger population ‚ĀĘabout the ‚Äćvalue of older generations, encouraging respect and intergenerational bonds.
Furthermore, a extensive policy framework is necessary ‚ÄĆto‚Äč unify various aspects of elder care. Establishing partnerships with non-governmental organizations can bolster ‚Ā£resources dedicated to ‚Ā£aged care.One potential model involves ‚Ā£creating local councils focused on specific communities, which can assess the‚ÄĆ needs ‚Ā§of the‚Äč elderly in their jurisdiction and implement‚ÄĆ targeted initiatives. To‚ÄĆ visualize this framework, the following table outlines potential policy measures and their‚Äć expected‚Äć outcomes:
| Policy Measure | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|
| Increased healthcare funding | Improved health services for‚ĀĘ the elderly |
| Subsidized ‚Ā§transportation services | Better ‚Ā£access ‚ĀĘto healthcare and social activities |
| Community engagement programs | Strengthened intergenerational relationships |

Innovative‚ĀĘ Community Solutions for elderly Care
The challenge of elderly care in Gambia highlights the need ‚Äčfor ‚ÄĆinnovative community solutions that respect ‚ĀĘthe cultural values and social dynamics of a ‚Ā£nation predominantly composed of youth. Traditional ‚Äčfamily structures are strained under the pressure of urbanization and economic‚ÄĆ hardships, leading to a growing disconnect between generations.‚ÄĆ To address this issue, community-driven‚Ā§ initiatives are emerging to support the‚Ā§ elderly, ‚ÄĆintegrating‚ĀĘ technology and‚Äć traditional caregiving practices.‚Äć These initiatives‚Ā§ are not only fostering intergenerational bonds but also‚Ā£ providing the necessary resources‚ÄĆ to ensure the dignity and‚Ā§ well-being‚Äć of the elderly population.
promising models include:
- Community Care‚ĀĘ Groups: Local volunteers are trained to assist elderly members in their neighborhoods, providing companionship and essential‚ÄĆ services.
- Telehealth Services: leveraging mobile technology, health professionals can offer consultations and health monitoring‚Äč for seniors who may face mobility challenges.
- Skill Exchange‚Ā§ Programs: Younger generations can learn valuable wisdom and traditional practices from elders, while sharing their ‚ÄĆtechnical skills in return.
| Initiative | description |
|---|---|
| Home Visits | Regular visits by trained volunteers to provide support ‚Ā§and companionship. |
| Health ‚ÄčWorkshops | Educational sessions ‚Ā£on health management tailored ‚Ā£to ‚ÄĆseniors’ ‚ÄĆneeds. |
| Intergenerational Events | Community ‚Ā£gatherings‚Äć that‚Ā§ promote sharing stories‚Ā§ and experiences. |

The Impact of‚Äć Economic pressures on‚ÄĆ Family-Based Care‚ĀĘ Systems
The‚Ā£ growing economic pressures ‚Ā§in‚ÄĆ Gambia‚Äč pose‚Äć meaningful challenges ‚ĀĘto ‚Äćtraditional family-based care systems for the elderly. as the‚Äć youth population expands, ‚Ā£the burden of caregiving frequently enough falls on ‚Ā§a shrinking number of adults who are themselves ‚ÄĆgrappling‚ÄĆ with economic ‚ÄĆinstability. Families are finding it increasingly difficult to balance the ‚Äčdemands of modern work ‚Ā§life with the responsibility‚ÄĆ of caring for aging relatives. This ‚ÄĆparadigm‚Ā£ shift can ‚ÄĆlead to fragmented familial structures‚Äć where the support that elderly members once received at home is becoming‚ÄĆ less reliable.
Key factors contributing to this transformation include:
- Urbanization: Many young people‚Äć migrate to urban areas for better economic opportunities,‚Ā£ often leaving their elders behind.
- Financial Strain:‚ÄĆ Heightened living costs ‚ĀĘand job scarcity compel families to prioritize immediate financial ‚Äčneeds over caregiving.
- Cultural Shifts: Western influences are ‚ÄĆchanging family dynamics, leading to‚Ā£ a ‚Äčgradual ‚Äćerosion of traditional caregiving roles.
| factor | Impact on Elder‚ÄĆ Care |
|---|---|
| Urban Migration | Increased isolation for elders‚Äč left‚ÄĆ in ‚ÄĆrural areas. |
| Economic Instability | Reduction in resources available ‚Äčfor ‚ĀĘcare. |
| Cultural‚Äč Changes | Shift towards institutional care solutions. |

Future Directions: balancing Tradition and Modernity in Elder Support Services
As Gambia‚Äč navigates the complexities of‚ÄĆ a‚ÄĆ rapidly changing demographic landscape, the ‚Ā£challenge lies‚Ā£ in sustaining‚Ā§ the cultural practices that ‚Ā§honor‚Ā£ elders while‚ĀĘ integrating modern support systems. This‚ÄĆ balancing act can manifest through various initiatives that leverage both traditional and contemporary‚Ā£ approaches. For instance, community programs can‚Ā§ foster ‚Ā£intergenerational ‚ÄĆconnections by encouraging youths ‚Ā§to participate in ‚Äčcaretaking roles, thereby reinforcing the value of elders. Such‚ĀĘ participation not only honors longstanding customs but‚Äč also empowers younger ‚ĀĘgenerations, creating a synergistic relationship ‚ĀĘbetween age groups.
The adoption of technology in elder support services presents another pathway for innovation.Implementing digital platforms that facilitate ‚Ā§communication and‚Ā£ healthcare management can enhance‚ĀĘ the quality of life‚Äč for seniors while ‚Äčmaintaining ‚ĀĘtheir cultural values. ‚ĀĘThe‚Ā§ following table outlines potential strategies that Gambia‚Äć can explore for this dual approach:
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Community Engagement | programs that connect youths with elders ‚Ā§through‚ÄĆ shared activities, fostering respect and continuity of tradition. |
| Telehealth Services | Utilize technology to provide ‚Ā§remote ‚Äćconsultations and‚Äć support, ensuring ‚ĀĘaccessibility for seniors. |
| Cultural‚Äč Education | Workshops ‚Ā§focused on traditional knowledge ‚Ā£for the younger generation, promoting appreciation for elder contributions. |
| Resource Networking | Collaboration between local‚Äč NGOs and government for holistic elder ‚ĀĘcare solutions‚Ā§ that incorporate ‚Äčboth tradition and ‚Ā§modern ‚ÄĆpractices. |
In Retrospect
as Gambia navigates the complexities of caring for its aging ‚Äčpopulation, the interplay between tradition and‚ĀĘ modernity will be crucial in shaping the country‚Äôs approach to elder care. With a youthful demographic making up the majority, the challenge lies in fostering respect and support for‚Äć the elders who have ‚ÄĆshaped the‚Äč nation‚Äôs past. adapting‚Äć to changing social dynamics while maintaining cultural ‚Äčvalues‚Äč will require innovative solutions ‚ÄĆand ‚Äćcommunity engagement. As ‚ĀĘgambians‚ÄĆ strive‚ĀĘ to‚ÄĆ balance these needs, the outcome will not only reflect their commitment ‚Äćto their elders but also define the societal fabric of this vibrant nation. The journey ahead is one ‚ĀĘof opportunity and responsibility, where‚Äć honoring‚Ā£ the past is ‚Äčessential for a ‚ÄĆharmonious future.