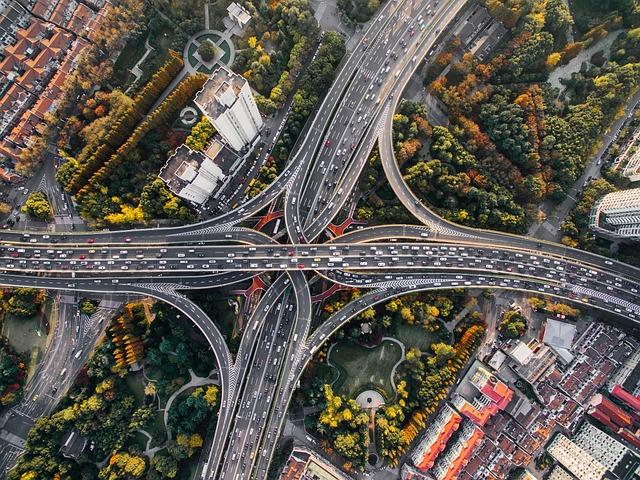
In recent years, Uganda has emerged as one of Africa’s focal points for infrastructure development, with a meaningful influx of Chinese investment transforming the nation’s landscape. As roads, bridges, adn energy facilities sprout across the country, the influence of Chinese firms and financing has become increasingly palpable.Though, this aspiring undertaking is not without its challenges. While many Ugandans celebrate the improvements in connectivity and energy accessibility, concerns loom over issues such as debt sustainability, labor practices, and environmental impact. This article delves into the complexities of Chinese infrastructure development in Uganda,examining both the triumphs that promise greater economic opportunities and the trials that pose critical questions about the long-term implications for the east African nation. Join us as we explore how Uganda navigates this intricate web of progress and pitfalls in its pursuit of a modernized infrastructure.
Chinese Investments in Uganda’s Infrastructure Landscape

The collaboration between China and Uganda in infrastructure development has been marked by significant investments aimed at modernizing the nation’s transport, energy, and telecommunications sectors. Major projects include the construction of roads, bridges, and railways that are expected to enhance connectivity and stimulate economic growth. Notable investments include:
- Kampala-Entebbe Expressway: This toll road has dramatically reduced travel time between the capital and the international airport, boosting tourism and business accessibility.
- Hydro-electric projects: Initiatives like the Karuma and Isimba hydroelectric plants have augmented Uganda’s energy supply, supporting both domestic needs and future industrial growth.
- Standard Gauge Railway (SGR): The ongoing SGR project aims to connect Uganda with neighboring countries, improving regional trade and transport efficiency.
However, these developments have not come without challenges. Concerns regarding debt sustainability,environmental impact,and local workforce involvement remain prominent. Critics highlight that while Chinese companies bring expertise and resources, there is often insufficient engagement with local contractors, which limits domestic capacity building. Moreover, issues related to transparency and governance have been raised, suggesting a need for regulatory frameworks that safeguard uganda’s interests. Addressing these hurdles is crucial for ensuring that the benefits of investment translate into sustainable development for all Ugandans.
Assessing the Impact of Chinese Development Projects on Local Communities

As Uganda continues to experience a surge in Chinese development projects, the effects on local communities are becoming increasingly nuanced. On one hand, these initiatives have led to significant improvements in infrastructure, such as roads, bridges, and hospitals, which have catalyzed economic growth and enhanced access to essential services. For example, the construction of the Entebbe International Airport expansion has boosted tourism and trade, leading to job creation and local business opportunities. However, these projects also bring challenges, particularly regarding environmental degradation and displacement of communities. Residents often face the dilemma of immediate economic benefits against the backdrop of losing their land and cultural heritage.
Moreover, the sustainability of these development projects is a pressing issue. While the influx of Chinese investment has introduced advanced technology and methods, the implementation of these projects often lacks a robust framework for community engagement or local participation. This gap can lead to a disconnect between development goals and the actual needs of the community. To illustrate the varied impacts, consider the following table highlighting key aspects of the development projects:
| Aspect | Positive Impact | Negative Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Job Creation | Increased employment opportunities for local workers | Job availability often favors skilled, external workers |
| Infrastructure Development | Enhanced transportation and communication networks | Potential for environmental disruption |
| Community Engagement | Local businesses can thrive from increased activity | Insufficient involvement in decision-making processes |
Challenges Faced by Chinese Firms in Uganda’s Infrastructure Sector

The landscape of Uganda’s infrastructure sector presents several hurdles for Chinese firms, hampering their operational efficiency and overall project success. Notably, political instability remains a pressing concern, as evolving government policies can drastically affect project timelines and investment security. Additionally, bureaucratic challenges often lead to delays in project approvals and permit acquisition, stifling the otherwise necesary momentum to foster infrastructure development. Chinese companies must also navigate the complexities of local workforce management, which includes cultural differences and varying work ethics that may hinder collaboration and productivity.
Furthermore, the sustainability of projects initiated by Chinese firms is regularly questioned, leading to potential social and environmental resistance. Communities may oppose the projects due to perceived negative impacts on local economies and ecosystems. This is compounded by a lack of transparency in operational practices, which may foster mistrust among local stakeholders. To mitigate these challenges, companies are increasingly recognizing the importance of engaging with local communities and enhancing their corporate social obligation initiatives, aiming to create a more favorable surroundings for infrastructure collaboration.
building Capacity: Training and Development Opportunities through Sino-Ugandan Cooperation

Capacity-building initiatives are crucial for ensuring that local communities benefit from the vast infrastructure projects being undertaken by Chinese firms in Uganda. These initiatives have been considerably bolstered through Sino-Ugandan cooperation, particularly in areas such as engineering, project management, and technical skills.collaborative training programs implemented by Chinese companies not only enhance the skills of Ugandan workers but also foster a sense of ownership and participation in development projects. Key training areas include:
- Construction Techniques: Providing hands-on experience with modern construction machinery and methods.
- Project Management: Equipping Ugandans with skills to manage large-scale projects effectively.
- Quality Assurance: Ensuring that local workers understand international standards and practices in construction.
- Technical Training: Focusing on the maintenance and repair of infrastructure.
A notable aspect of this collaboration is the establishment of training centers that serve as hubs for knowledge sharing and skill development. The training programs not only cater to new entrants in the workforce but also aim to upgrade the existing skills of current workers. A recently launched initiative has been structured around a dual approach,combining classroom learning with practical submission in the field. this method is not only efficient but also encourages a collaborative spirit among Ugandan workers and their Chinese counterparts. The following table highlights some current training initiatives:
| program | Duration | Participants |
|---|---|---|
| Heavy Machinery Operation | 3 months | 50 Ugandan workers |
| Project Management Basics | 6 weeks | 30 mid-level managers |
| Quality Control Procedures | 2 weeks | 20 quality assurance officers |
Strategies for Ensuring Sustainable and Inclusive Infrastructure Development

to achieve infrastructure development that benefits all segments of the Ugandan population, it is essential to adopt an approach that prioritizes local engagement and capacity building. Before launching major projects, stakeholders must conduct comprehensive community consultations to identify the specific needs and concerns of affected populations. Involving local communities in decision-making processes can lead to projects that not only address infrastructural gaps but also enhance local ownership and economic participation. Additionally, investing in training programs for local workers ensures that the skills and benefits resulting from major infrastructure projects remain within the community, fostering long-term employment prospects.
Furthermore, sustainability should be at the forefront of all infrastructure initiatives. This can be achieved through the integration of eco-friendly technologies and materials that minimize environmental impact. Governments and developers should consider adopting strategies such as:
- Utilizing renewable energy sources for construction and operation
- Implementing green building standards to enhance energy efficiency
- Investing in public transportation systems to reduce carbon footprints
- Conducting environmental impact assessments prior to project approval
Establishing collaborative frameworks that bring together public and private sectors can streamline the financing of such initiatives while ensuring that projects are both economically viable and environmentally responsible.
| Key Focus Areas | Actions Required | Expected Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
| Community Engagement | Conduct consultations and workshops | Projects that reflect community needs |
| Local Capacity Building | Implement training programs for workers | Enhanced skills and local employment |
| Sustainability Practices | adopt eco-friendly construction methods | reduced environmental impact |
| Public-Private Partnerships | Collaborate on financing solutions | Efficient resource allocation |
Future Prospects: Navigating the path Ahead for chinese-Ugandan Partnerships

The path ahead for Chinese-Ugandan partnerships is marked by a unique blend of promise and challenges. As both nations continue to explore avenues for collaboration, several key areas are poised for development, including:
- Infrastructure Expansion: With ongoing projects in roads, railways, and energy, Uganda stands to gain significant economic momentum.
- Technology Transfer: Increased emphasis on technology sharing can empower Ugandan industries and facilitate sustainable practices.
- Cultural Exchange: Strengthening cultural ties will not only enhance mutual understanding but also support tourism and educational initiatives.
However, to successfully navigate future cooperation, stakeholders must address several pressing concerns. Critical among these are:
- Debt Sustainability: Ensuring that Uganda does not fall into excessive debt while financing projects is vital for long-term stability.
- Local Workforce Development: Fostering local labor participation in Chinese projects can enhance skill development and reduce dependency.
- Environmental Impact Assessment: Prioritizing ecological considerations in all infrastructure projects will safeguard Uganda’s rich biodiversity.
Wrapping up
the landscape of Chinese infrastructure development in Uganda serves as a complex tapestry woven with both significant achievements and notable challenges. As the Ugandan government seeks to propel the nation toward economic growth and improved living standards, partnerships with Chinese firms have undeniably provided much-needed financial resources and technical expertise. Projects such as the Kampala-Entebbe Expressway and the Standard gauge Railway exemplify the potential for transformative infrastructure that can foster connectivity and stimulate trade.
However, these advances are not without their pitfalls. Issues related to debt sustainability, environmental concerns, and local community displacement underscore the necessity for a more nuanced approach. As Uganda navigates the intricate dynamics of these partnerships, the need for transparency, accountability, and sustainable practices becomes increasingly imperative.
Ultimately, the experience of Chinese investment in Uganda’s infrastructure not only highlights the triumphs of development but also serves as a cautionary tale of the trials that accompany such ambitious endeavors. Moving forward, striking a balance between rapid development and long-term sustainability will be crucial for ensuring that the benefits of infrastructure projects are equitably shared among all Ugandans. The lessons learned from this evolving narrative will be vital for shaping future collaborations between developing nations and global partners.