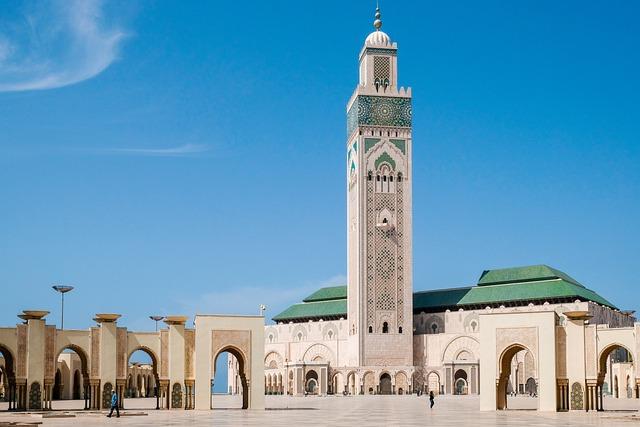
Introduction to Morocco’s country Profile
Morocco, a North African nation distinguished by its rich cultural heritage and diverse landscapes, serves as a captivating crossroads between Europe and Africa. This vibrant country, known for its bustling markets, ancient medinas, and stunning geographical contrasts—from the windswept Sahara Desert to the snow-capped Atlas Mountains—offers a unique blend of tradition and modernity. In this comprehensive profile, we delve into Morocco’s past context, economic landscape, political framework, and social dynamics, drawing upon insights and data from BBC.com to provide a nuanced understanding of this remarkable nation. As Morocco continues to navigate the complexities of globalization while maintaining its distinct identity, we explore the challenges and opportunities that shape its future on the world stage.
Key Geographical Features and Their Impact on Morocco’s Culture

Morocco’s landscape is a tapestry woven from a variety of geographical features that shape both its environment and the cultural practices of its inhabitants. The country is framed by the rugged Atlas Mountains, which stretch across the center, influencing everything from climate to agriculture. The mountains not only provide essential water resources through their snowmelt but also serve as a cultural barrier, resulting in diverse traditions among the Berber communities residing within. Additionally, the Sahara Desert to the southeast offers a stark contrast with its vast expanses of sand dunes, influencing the nomadic lifestyle of desert dwellers who maintain age-old customs and trades.
The mediterranean Sea and Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, respectively, not only contribute to Morocco’s mild climate but also play a significant role in cultural exchanges. Coastal cities like Casablanca and Tangier have long been melting pots where European, African, and Middle Eastern influences converge. This coastal geography has fostered vibrant fishing industries and artistic traditions, with seafood and spices becoming staples in Moroccan cuisine. Furthermore, the proximity to Europe has led to a unique blend of cultures, evident in moroccan arts, music, and architecture, highlighting a rich historical narrative shaped by both land and sea.
Historical Landmarks Reflecting Morocco’s Rich Heritage

Morocco is a tapestry woven with history,architecture,and diverse cultures,reflected in its remarkable historical landmarks. Among these, the Kasbah of Ait Benhaddou stands out as a UNESCO World Heritage Site, showcasing the stunning earthen clay architecture that has adorned the region for centuries. This ancient fortress offers an authentic glimpse into traditional Moroccan life and has served as a backdrop for numerous films, earning it a place in popular culture. Another significant site is the Hassan II Mosque in Casablanca, renowned for its striking minaret and intricate artistry, which epitomizes moroccan craftsmanship and spirituality.
When exploring such landmarks, visitors will encounter various styles that highlight the country’s rich cultural intersections. The following locations exemplify the beauty and importance of Morocco’s heritage:
- Medina of fez: Known as one of the world’s oldest urban cities, with stunning medieval architecture.
- Chefchaouen: Famous for its blue-washed buildings, reflecting a unique artistic heritage.
- el Jemliya Ancient Site: A remnant of the roman Empire that showcases Morocco’s diverse historical influences.
To encapsulate the grandeur of these landmarks, the following table outlines some key historical sites and their significance:
| Landmark | location | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Kasbah of ait Benhaddou | Ouarzazate | UNESCO World Heritage Site, movie filming location |
| Hassan II Mosque | Casablanca | One of the largest mosques in the world, stunning architecture |
| Medina of marrakech | Marrakech | UNESCO World Heritage Site, ancient market and cultural hub |
Economic Overview: Sectors Driving Growth and Development

Morocco’s economic landscape has experienced robust growth in recent years, largely driven by key sectors that have become the backbone of its development. Among the most significant contributors are agriculture, manufacturing, and the tourism industry. agriculture remains a major employment source, with crops like citrus fruits and olives taking the forefront of exports. Meanwhile,the manufacturing sector has diversified,focusing on textiles,automotive components,and electronics,thereby attracting significant foreign investment. The tourism industry continues to thrive, leveraging Morocco’s rich cultural heritage, stunning landscapes, and historical sites, which draw millions of visitors each year.
This economic dynamism is further supported by the government’s efforts to enhance its infrastructure and promote renewable energy sources. Initiatives such as the Noor Solar Plant demonstrate Morocco’s commitment to sustainable development. Additionally, there are strategic investments in urban development and transport networks, pivotal for facilitating trade and enhancing connectivity. As a result, Morocco is on a trajectory to not only bolster its economy but also improve the quality of life for its citizens, positioning itself as a growing player in the regional and global markets.
Political Landscape: Governance and Key Current Issues

morocco’s political arena is characterized by a blend of constitutional monarchy and parliamentary democracy, with King Mohammed VI holding significant power over the state apparatus. The monarchy has initiated various reforms aimed at enhancing governance, including a new constitution adopted in 2011 that aimed to shift certain powers to the Parliament. However, many political analysts argue that the monarchy still retains substantial influence over crucial government decisions. Key political parties include the Justice and Development Party (PJD), which has held power sence 2011, and the National Rally of Independents (RNI), alongside several other parties partaking in coalition governments.
Currently, Morocco faces a series of pressing issues that call for urgent governance and policy interventions. Among these are:
- Social Inequality: Economic disparities remain a critical challenge,exacerbated by rural-urban divides and unemployment rates,notably among the youth.
- Corruption: Efforts to combat corruption are ongoing, but public trust in governmental institutions is low, affecting citizen engagement.
- Human Rights Concerns: Concerns about freedom of speech, assembly, and the treatment of migrants are increasing, with various NGOs calling for reforms.
| Key Current Issues | Government Response |
|---|---|
| Social Inequality | Economic reforms aimed at job creation and poverty reduction. |
| Corruption | Legal reforms and anti-corruption campaigns launched. |
| Human Rights | Calls for enhancing legal frameworks and protections. |
Social Dynamics: Education, Healthcare and Urbanization Trends

The evolution of the education system in Morocco reflects both historical influences and modern aspirations. Significant investments have been made to enhance access to quality education across the nation,leading to increased enrollment rates in primary and secondary schools. Though, challenges remain in rural areas where infrastructure and resources frequently enough lag behind urban regions. Key highlights include:
- Worldwide Access: Efforts to ensure that all children, regardless of socioeconomic background, can attend school.
- Curriculum Reforms: Introduction of modern educational practices aimed at improving critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
- Teacher Training: Programs designed to equip educators with innovative teaching methodologies and technologies.
Healthcare in morocco has seen substantial improvements, fueled by urbanization and the gradual integration of modern medical practices. The government’s focus on comprehensive healthcare coverage aims to alleviate disparities, particularly in underserved areas. The formation of partnerships with international organizations has bolstered resources, emphasizing preventive care and community health initiatives. Notable trends include:
- Expansion of services: Increased availability of clinics and hospitals in both urban and rural settings.
- Public Health Campaigns: Initiatives targeting common health issues, such as maternal and child health.
- Health Technology Integration: Utilization of telemedicine and health informatics to improve patient access and engagement.
As urbanization continues to shape Morocco’s landscape, the influx of people into cities offers both opportunities and challenges. The rapid growth of urban areas has necessitated the development of effective infrastructures, housing, and public services to accommodate the rising population. This transformation is characterized by:
| Trend | Impact |
|---|---|
| Affordable Housing Projects | Increased availability of homes to combat overcrowding and improve living conditions. |
| Transportation Networks | Enhanced connectivity between urban centers and peri-urban areas, facilitating economic activity. |
| Green Urban Planning | Development of sustainable spaces aimed at promoting health and environmental awareness. |
Tourism Opportunities: Must-Visit Destinations and Travel Tips

Morocco is a treasure trove of diverse landscapes and cultures, offering a plethora of must-visit destinations for any intrepid traveler. From the bustling streets of Marrakech, known for its vibrant souks and the stunning Jardin Majorelle, to the ancient city of Fes, famous for its well-preserved medieval architecture and the world’s oldest university, the options are plentiful. Chefchaouen, with its iconic blue-washed buildings nestled in the Rif Mountains, provides a picturesque escape for photographers and wanderers alike.Don’t miss the Sahara Desert, where guided camel treks and mesmerizing dunes await your discovery.
When planning your journey, consider these essential travel tips to enhance your Moroccan experience:
- Learn Basic Arabic phrases: A few words in Arabic or French can go a long way in establishing rapport with locals.
- Dress Modestly: Especially in rural areas, respecting local customs regarding dress is appreciated.
- Stay Hydrated: The arid climate,particularly in the desert regions,requires travelers to drink plenty of water.
- Bargain Wisely: Haggling is a part of the market culture, so don’t hesitate to negotiate prices in souks.
- Try Local Cuisine: Dishes like tagine and couscous are a culinary must, along with fresh mint tea.
To Wrap It Up
Morocco stands as a vibrant tapestry woven from a rich history, diverse cultures, and stunning landscapes. The nation’s strategic location at the crossroads of Europe and Africa has not only shaped its economic and political dynamics but also contributed to its unique cultural identity. As Morocco navigates the complexities of modern challenges—ranging from economic development to social changes—it continues to honour its heritage and traditions. Whether through its bustling markets, ancient medinas, or breathtaking natural wonders, Morocco offers a compelling narrative that attracts travelers and scholars alike. As the country evolves, it remains firmly rooted in its past while looking forward to a promising future. For further insights and the latest developments,readers are encouraged to explore additional resources that shed light on Morocco’s ongoing journey on the global stage.