In the heart of Central Africa, the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) is once again thrust into the global spotlight as conflict resurfaces in its eastern regions, particularly following the fall of key urban centers Goma and Bukavu. The March 23 Movement, or M23, has re-emerged as a critically important military force, raising concerns not only about regional stability but also about the broader humanitarian crisis affecting millions. This article delves into the current trajectory of the M23 conflict,examining the political,social,and economic ramifications of recent events. As peace remains elusive, the international community and local stakeholders face pressing questions: What are the implications of M23’s resurgence for the DRC and its neighbors? And how can lasting solutions be forged amidst a complex web of ethnic tensions, security challenges, and humanitarian needs? Join us as we explore the evolving landscape of the DRCŌĆÖs conflict and its potential paths forward.
The Impacts of Goma and BukavuŌĆÖs Fall on regional Stability

The recent takeover of Goma and Bukavu by the M23 rebel group has sent shockwaves throughout the region, raising significant concerns regarding stability in Eastern Democratic republic of Congo (DRC). With the strategic positions of these cities, their fall is likely to trigger a ripple affect, exacerbating tensions between various local militias, national forces, and foreign powers. The already fragile social fabric in the region may face severe strains, as communities grapple with issues of displacement and resource control. Key impacts include:
- Escalation of Ethnic Conflicts: the power vacuum created by the fall of Goma and Bukavu could reignite old animosities among various ethnic groups, leading to violent clashes.
- Displacement Crisis: The influx of refugees fleeing violence poses a humanitarian challenge, stretching resources and support systems in neighboring countries.
- International Intervention: Increased military and diplomatic interest from regional neighbors and international organizations may complicate the geopolitical landscape.
- Empowerment of Other Rebel Groups: The success of M23 may embolden other factions, potentially leading to a fragmented and more volatile security situation.
As the situation unfolds, understanding the local and international dynamics at play becomes critical. A recent analysis highlights the resulting shifts in alliances and the need for diplomatic solutions:
| Entity | Position | Potential Action |
|---|---|---|
| M23 | Increased territorial control | Possibly seek formal recognition |
| Congolese Government | Heightened military response | Engage in negotiations |
| Regional Governments | Strategic intervention | Support for rival groups |
| International Community | Humanitarian assistance | Promote peace talks |
The actions taken by these various entities will significantly influence the trajectory of conflict in the region, underscoring the precarious balance between military power and diplomatic engagement. The implications of Goma and BukavuŌĆÖs fall extend far beyond the immediate conflict, marking a pivotal moment for the broader East african region.
Understanding the Motivations Behind M23ŌĆÖs Resurgence

The resurgence of M23 can be attributed to a complex interplay of regional dynamics, internal strife, and geopolitical factors. Analysts suggest that the groupŌĆÖs resurgence stems from several key motivations, including:
- Resource Control: The eastern regions of the DRC are rich in minerals like coltan and gold, providing a lucrative incentive for armed groups.
- Political Influence: M23 aims to establish itself as a political force, seeking recognition and legitimacy amidst the fractured governance landscape in the DRC.
- Local Discontent: Ethnic tensions and local grievances against the government offer fertile ground for M23 to gain support and recruit members.
Moreover, external influences cannot be overlooked. Regional players frequently enough exploit instability in the DRC for their strategic interests, fueling the conflict. To understand the broader implications of M23ŌĆÖs resurgence, it is indeed essential to examine the role of neighboring countries, particularly in terms of:
| Neighboring Country | Influence on M23 |
|---|---|
| rwanda | Accusations of support for M23 as a means to exert control over DRC resources. |
| Uganda | Alleged involvement in facilitating arms supplies and tactical support. |
| Burundi | Potential for harboring M23 members and affecting regional security dynamics. |
Humanitarian Crisis Escalates: The Plight of Displaced Civilians
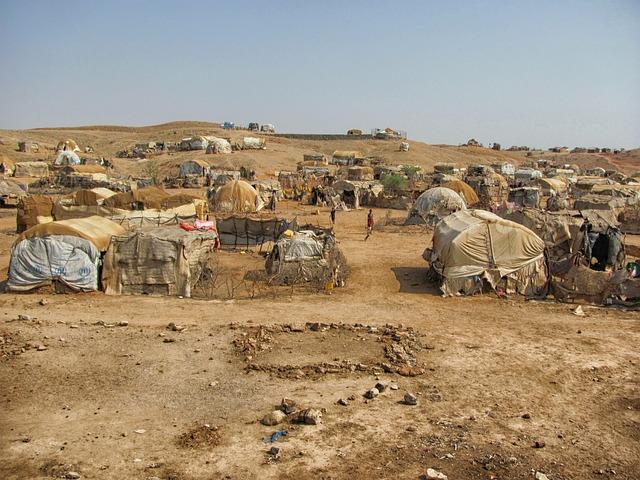

The ongoing conflict in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) has resulted in a staggering increase in the number of displaced civilians.As rival factions vie for control in regions like Goma and Bukavu, the humanitarian situation deteriorates, prompting urgent calls for assistance. The conflict has not only led to immediate threats of violence but has also created a humanitarian landscape riddled with acute food insecurity, lack of medical care, and psychological trauma among those uprooted from their homes. Many civilians have found refuge in overcrowded camps, facing precarious living conditions and limited access to basic services.
The recent escalation in hostilities has forced thousands to flee towards neighboring countries, frequently enough enduring perilous journeys in search of safety. The international community has a crucial role to play in addressing these urgent needs. Key areas of concern include:
- Emergency shelter and protection for vulnerable populations
- Immediate access to food, water, and healthcare
- Psychosocial support for trauma-affected civilians
| Displacement Statistics | 2023 Estimates |
|---|---|
| Total Displaced Persons | Over 5 million |
| Children Affected | 2 million |
| New Displacements in 2023 | 1.5 million |
International Response: Reevaluating Diplomatic Engagement in the Region
The recent escalation of conflict in the eastern Democratic Republic of the congo (DRC), following the seizure of Goma and Bukavu by the M23 rebel group, has profound implications for international diplomatic strategies in the region. As global actors reassess their involvement, a few pivotal considerations emerge:
- Engagement versus Isolation: many nations are reconsidering the effectiveness of previous diplomatic efforts, weighing sanctions against the necessity for dialog.
- Regional Coordination: Countries neighboring the DRC, along with international organizations, must unite to formulate a cohesive strategy to stabilize the area.
- Humanitarian Concerns: The urgent need for humanitarian aid is a priority that could drive diplomatic discussions,making it necessary to include various stakeholders,including local NGOs and community leaders.
Moreover, the potential for peace agreements hinges on the delicate balance between military intervention and diplomatic negotiations. Historical precedents suggest that sustainable solutions require not just immediate responses but long-term commitments to rebuilding trust and governance. Key factors include:
| Factor | Importance |
|---|---|
| Inclusive Dialogue | Involves all factions to ensure lasting peace. |
| International Monitoring | To oversee ceasefires and agreements. |
| Growth Aid | To stabilize and rebuild communities affected by conflict. |
Paths to Peace: Recommendations for Sustainable Conflict Resolution

In the wake of ongoing violence and instability in the eastern regions of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC),particularly following the upheavals in Goma and Bukavu,a complete approach to sustainable conflict resolution becomes imperative. It is essential for local, national, and international stakeholders to engage in meaningful dialogue that addresses the core grievances of affected communities. Key recommendations include:
- Inclusive Dialogue: Establish platforms for dialogue among all conflict parties,including marginalized groups,to foster understanding and build trust.
- Strengthening Governance: Invest in enhancing the legitimacy of local governance structures to ensure that they represent the interests of all ethnic communities.
- Community-Based Initiatives: Encourage grassroots peacebuilding initiatives that empower communities to develop their own strategies for conflict resolution.
- Regional Cooperation: Promote collaboration among neighboring countries to address cross-border issues exacerbating the conflict, such as resource exploitation and illegal arms trade.
Moreover, addressing underlying socioeconomic disparities is vital for establishing lasting peace. The DRCŌĆÖs staggering levels of poverty and unemployment contribute to ongoing unrest, making economic development a priority in peace discussions. Initiatives such as microfinance programs and vocational training can help uplift communities and reduce the appeal of armed groups.A collaborative framework could look like this:
| Initiative | Objective | stakeholders |
|---|---|---|
| Job Creation Programs | Reduce unemployment | Government, NGOs |
| Community Dialogues | Build trust | Local leaders, civil society |
| Cross-border Forums | Enhance cooperation | Regional governments, international bodies |
The Role of Neighboring Countries in Shaping the Future of Eastern Congo

The dynamics of Eastern Congo are heavily influenced by the geopolitical landscape created by its neighboring countries. These nations, each with their own strategic interests, play a critical role in either stoking or mitigating the ongoing conflict involving the M23 rebel group. Key players include:
- Rwanda: Accused of providing support to M23, fostering tensions with the Congolese government.
- Uganda: Historically involved in Eastern Congo, UgandaŌĆÖs involvement can either exacerbate or ease the conflict, depending on its political agenda.
- Burundi: While primarily focused on its internal issues, any stability or instability in Burundi can have ripple effects across the region.
In this context, diplomatic engagements, regional summits, and international pressure play a crucial role in shaping future strategies. A potential solution could be a coordinated effort among these nations to address shared security concerns and economic interests. The following table summarizes recent initiatives aimed at fostering regional cooperation:
| Initiative | Objective | Status |
|---|---|---|
| Regional Security Forum | To address cross-border insurgency and enhance cooperation. | Ongoing |
| Joint Military Exercises | Strengthen military ties and operational readiness. | Planned |
| Resource Sharing Agreements | Improve economic interdependence and reduce conflict incentives. | proposed |
Insights and Conclusions
As the situation in the Democratic Republic of the Congo continues to evolve following the fall of Goma and Bukavu, the future trajectory of the M23 rebellion remains uncertain. The ongoing conflict, marked by complexities of regional dynamics, internal political strife, and humanitarian crises, poses significant challenges not only to the Congolese government but also to international stakeholders advocating for stability and peace.
With the DRCŌĆÖs rich resources caught in the crossfire and civilians bearing the brunt of the violence, the international community must prioritize diplomatic efforts and humanitarian assistance to address the immediate needs of displaced populations while also seeking long-term solutions to the underlying issues fueling the conflict.
As we await developments in this volatile region, it is critical for observers and policymakers alike to stay informed and focused on the realities on the ground. the fate of millions hangs in the balance, as the DRC navigates a precarious path towards peace amidst the shadows of ongoing conflict. The coming months will be crucial in defining the future of the M23 and the broader implications for stability in Central Africa.