Title: Unraveling Hair Discrimination and Cultural Bias in South Africa’s Education sector
In a nation marked by its rich tapestry of cultures and histories, south Africa’s education sector continues to grapple with deep-seated issues of hair discrimination and cultural bias.Despite constitutional guarantees of equality and the right to education, students of African descent often find themselves subjected to rigid grooming policies that undermine their cultural identity. These policies not only reflect a legacy of racial discrimination but also raise critical questions about equity and inclusivity within academic institutions.This article delves into the pervasive impact of hair-related discrimination on students’ educational experiences, explores the broader implications for cultural identity, and highlights the urgent calls for reform within the system. Through firsthand accounts and expert insights,we aim to shed light on the intersection of race,culture,and education in South Africa,emphasizing the essential need for a more inclusive approach that respects and embraces diversity in all its forms.
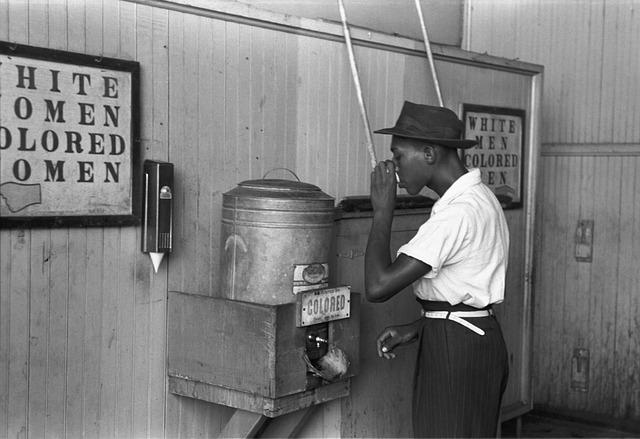
Understanding Hair Discrimination in South Africa’s schools
The issue of hair discrimination in south African schools disproportionately affects learners from Black and mixed-race backgrounds, often enforcing Eurocentric beauty standards that alienate students from their cultural identities. Policies surrounding hairstyles, particularly in public and private educational institutions, have sparked considerable debate over their legitimacy and cultural sensitivity. These rules can manifest as direct bans on specific hair types, styles, or accessories that are recognized as part of African heritage, thus raising critical questions about inclusivity and the true nature of equality in education.
this form of discrimination not only impacts the self-esteem and day-to-day experiences of affected students but can also have long-lasting implications on their educational outcomes and social advancement. Some key factors contributing to this phenomenon include:
- Cultural Ignorance: Lack of education and awareness among educators regarding diverse hair types and their importance.
- Rigid Policies: Institutional policies that do not accommodate cultural expressions of identity.
- Peer Pressure: Societal expectations and the desire to fit in leading to compromised cultural practices.
| Type of Hair Discrimination | Example |
|---|---|
| Ban on Natural Hairstyles | Prohibiting students from wearing afros or braids |
| Styles with Cultural Significance | Restricting hairstyles that are traditionally important |
| Implementation of Eurocentric Standards | favoring straight hair or specific lengths and cuts |

The Impact of Cultural Bias on Students’ Educational Experiences
The intersection of cultural bias and hair discrimination significantly shapes the educational landscape in South Africa. Students with natural African hairstyles often face stigmatization, affecting their self-esteem and academic performance. Such cultural bias can manifest in various forms, including:
- Exclusion from school activities: Students might potentially be sidelined from vital events due to their hairstyles, perpetuating a sense of inadequacy.
- Disciplinary actions: Many schools have rigid grooming policies that disproportionately target students with afro-textured hair, leading to unfair punishments.
- Negative stereotypes: Educators may hold implicit biases that influence their treatment of students based on their appearance, which can hinder academic growth.
These issues not only affect individual students but also create an environment where cultural identity is undermined. Research indicates that schools with inclusive policies tend to have better student outcomes. As an example,a recent study highlighted the importance of culturally responsive teaching methods,which engage students and recognize their backgrounds. The following table summarizes key elements of effective educational practices:
| Key Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Cultural Awareness | Training teachers to understand and respect diverse cultural identities. |
| Adaptable Policies | Implementing inclusive dress and grooming codes that celebrate cultural diversity. |
| Student Engagement | Creating programs that incorporate students’ cultural backgrounds into the curriculum. |

Examining the Psychological Effects of Hair Discrimination
The psychological impact of hair discrimination extends far beyond the immediate conflicts in schools and workplaces. students subjected to negative perceptions based on their hair often experience feelings of alienation and inferiority. This form of discrimination can manifest in several psychological effects, such as:
- Low self-esteem: Constant scrutiny and derogatory comments can lead individuals to feel inadequate, making them question their identity.
- Anxiety and stress: The fear of judgment may cause significant anxiety,which can affect academic performance and social interactions.
- Depression: Prolonged exposure to discrimination can evolve into more severe mental health issues, including depression, leading to withdrawal from social activities.
Moreover, hair discrimination not only impacts studentsŌĆÖ mental health but can also have long-lasting effects on educational outcomes. Many educators remain unaware of the cultural significance of various hairstyles, which can perpetuate biases within the classroom. The table below highlights the potential academic consequences of hair discrimination in educational settings:
| Consequence | Description |
|---|---|
| Reduced Participation | Students may engage less in classroom discussions due to fear of negative attention. |
| Attendance Issues | Discrimination may lead to increased absenteeism as students avoid hostile environments. |
| Decreased Academic Performance | Emotional disturbances from discrimination can hinder concentration and motivation. |

policy Gaps: Addressing Hair Discrimination in Educational Institutions
In South Africa’s education sector, hair discrimination has emerged as a significant issue, reflecting broader societal biases against cultural identity. While policies exist to promote equality, they often fail to address the nuanced experiences of students from diverse backgrounds. Key challenges include a lack of clarity in regulations regarding hairstyles, which may inadvertently uphold Eurocentric beauty standards. Consequently, students face disciplinary action for wearing natural hairstyles, such as afros, braids, or locs, thus stifling their cultural expression.
To bridge these policy gaps, it is crucial to implement extensive training for educators on cultural competence and inclusivity. Educational institutions should embrace a framework that recognizes and celebrates diverse hair types as forms of self-expression. Possible measures include:
- Formulating clear guidelines on acceptable hairstyles that respect cultural heritage.
- Engaging with students and parents to solicit input on hair policies.
- Regularly reviewing policies to ensure they evolve with changing societal norms.
- Introducing educational programs about the significance of natural hairstyles in various cultures.
By fostering an environment that values diversity, educational institutions not only uphold human rights but also promote a sense of belonging among all students. It is imperative that these reforms are not merely cosmetic; they should reflect genuine commitment to dismantling systemic biases and empowering students to embrace their cultural identities.

Empowering Educators: Training Against Cultural Bias
Addressing cultural bias in educational settings is crucial for fostering an inclusive environment. In South Africa,hair discrimination serves as a poignant example of how seemingly innocuous norms can perpetuate systemic inequalities. To combat this, educators must engage in specialized training designed to challenge these biases. Such programs should focus on:
- Understanding Cultural Diversity: Recognizing that hair is an critically important aspect of cultural identity for many students.
- Awareness of Implicit Bias: Training to uncover personal biases that may affect how educators perceive and treat students.
- Practical Strategies for Inclusion: Developing classroom practices that celebrate rather than marginalize studentsŌĆÖ cultural expressions.
Furthermore,educators need a platform to share experiences and strategies for eliminating hair-based discrimination. Implementing collaborative approaches can facilitate meaningful dialog among teachers and students, creating an empowered community. A potential framework could include:
| Training Focus | Implementation Strategy |
|---|---|
| Cultural Competence Workshops | Interactive sessions promoting storytelling and shared experiences. |
| Policy Review Sessions | Collaborative revisiting of school policies related to hair and appearance. |
| Peer Mentorship Programs | Pairing experienced educators with those new to the field to discuss cultural sensitivity. |

Recommendations for Creating Inclusive School Environments
Creating an inclusive school environment is essential in combating hair discrimination and cultural bias. Educators and administrators must prioritize professional development that focuses on cultural competency and social justice. this entails implementing training sessions that address the significance of diverse hair textures and styles in various cultural contexts. Additionally, schools can integrate the following practices:
- Policy Review: Regularly assess school policies regarding hair and appearance to ensure they do not inadvertently promote bias.
- Curriculum Inclusion: Incorporate lessons that celebrate diverse cultures, focusing on the history and significance of various hairstyles.
- support Networks: Establish support groups for students from marginalized backgrounds to foster a sense of community and belonging.
Moreover, engaging parents and the wider community is critical. Schools should host workshops and forums that invite parents to share their experiences and perspectives. These interactions can lead to greater understanding and support for diversity within the educational setting. Below is a simple table highlighting inclusive strategies that can be adopted:
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Awareness Campaigns | Initiatives to promote understanding of different cultures and hair types. |
| Flexible Dress Codes | Policies allowing various hairstyles that reflect students’ cultural identities. |
| Diverse Role Models | Highlighting professionals from various backgrounds to inspire students. |
Closing Remarks
the issue of hair discrimination and cultural bias within South Africa’s education sector highlights the urgent need for systemic change to ensure equity and inclusivity for all students. As this article has explored,the enforcement of strict hair policies frequently enough disproportionately affects learners from marginalized backgrounds,exacerbating existing inequalities and undermining the very essence of a fair education system.
It is indeed imperative that educators, policymakers, and communities come together to challenge these discriminatory practices and advocate for regulations that respect and celebrate the diverse identities within the student population.By fostering an environment that values cultural heritage and expression, South Africa can take meaningful strides toward a more just educational landscape. Emphasizing inclusivity in schools not only uplifts individual learners but enriches the collective experience of the entire educational community, paving the way for a brighter, more equitable future.