Exploring Algeria: ‚ÄćA‚Ā§ Tapestry of Cultures in North Africa‚Äôs‚Äč Heart
Situated‚ÄĆ at the crossroads of ‚Äćnorth Africa, Algeria stands as a vast ‚Äćand ‚Ā§diverse ‚Äćnation‚ĀĘ that encapsulates the ‚Äćrich history‚Ā£ and vibrant ‚Äčcultures of‚Äč the ‚ÄćMediterranean and saharan regions.‚Ā§ As the largest country in Africa, Algeria boasts a complex‚Ā£ tapestry of ‚Ā£landscapes‚ÄĒfrom its ‚ÄĆrugged‚Ā§ coastline ‚Ā§along the Mediterranean‚Ā§ Sea‚Äć to the expansive deserts of ‚Äčthe Sahara that ‚ÄĆdominate ‚Äćits southern territories.This unique geographical‚Äč positioning has not only shaped its natural beauty but‚Ā£ has also ‚ĀĘbeen ‚ÄĆa crucial factor in its ancient‚Äć development, influencing the myriad ‚Ā§of‚ÄĆ ethnicities and traditions that coexist within its‚Äč borders. ‚Ā£In this ‚ĀĘarticle,we‚ÄĆ delve into the multifaceted identity of Algeria,exploring its‚Ā§ historical significance,cultural heritage,and ‚Ā£the contemporary challenges it‚ĀĘ faces‚Äć as a nation ‚Ā§poised at the intersection of ‚Äčtradition and modernity. Join ‚Ā£us on a‚Ā§ journey through Algeria‚Äôs past and present,‚Ā£ as documented in the extensive ‚Ā§insights provided by Britannica.
Exploring Algeria’s ‚ÄćDiverse‚Äč landscapes from ‚Ā£the Mediterranean to‚Ā§ the Sahara
Algeria’s ‚Äčlandscapes offer an ‚Äćamazing tapestry of environments, ‚Äćeach with its own unique charm and ‚Äčbiodiversity. From the azure waters of the‚Ā§ Mediterranean ‚ÄĆcoastline, bustling‚Ā£ with ‚Ā§life and culture,‚Äč to the vast, undulating dunes of the‚Äć Sahara Desert, the country presents a ‚Ā£stunning contrast that captivates the senses.‚Äč Visitors can immerse themselves in vibrant ‚Äćcoastal cities ‚Äčlike Algiers ‚Ā£and‚Äč Oran, known for their‚ĀĘ rich history and striking architecture, or venture into the heart of the Sahara ‚ĀĘin‚Äć places like Ouargla and Timimoun, where ‚Äćthe golden sands stretch endlessly under an expansive sky. These regions not only boast diverse geographical features‚ÄĆ but also host‚ĀĘ a‚ĀĘ myriad of flora and ‚Äćfauna, making‚ĀĘ them essential ‚Äčfor understanding‚Äč Algeria’s ecological tapestry.
The interplay of ‚Äćlandscapes‚ĀĘ showcases ‚ÄčAlgeria’s ‚Ā§environmental diversity, providing habitats ranging from coastal‚Äč wetlands to mountainous terrains. ‚ÄćKey highlights include:
- The Kabylie Mountains: ‚ÄćA rugged region characterized by breathtaking landscapes ‚Ā£and traditional Berber villages.
- The ‚Ā§Saharan ‚ÄĆOases: Picture-perfect ‚Äčsettings that‚Ā§ support ‚ĀĘagriculture and‚ĀĘ are ‚ÄĆhome to ‚Ā§unique species.
- Hoggar ‚Ā§Mountains: An‚Äč impressive ‚Äčrange that‚Äč rises dramatically‚Äć from the surrounding desert, rich in cultural significance and natural beauty.
Through initiatives such‚Ā§ as lasting tourism and conservation efforts, Algeria aims to protect these diverse ecosystems while allowing visitors to ‚Äćappreciate the beauty that ‚ÄĆlies within its borders.‚Ā£ A closer look at these ‚Äčregions highlights the interconnectedness of geography, culture, and ‚ĀĘbiodiversity‚ÄĒmaking algeria a fascinating destination for adventurers ‚ĀĘand ‚ÄĆscholars alike.

Cultural Heritage and Historical ‚ÄĆSignificance‚Ā§ of Algeria’s Major Cities
Algeria’s‚Äć major cities ‚ÄĆare a living‚ÄĆ testament ‚ÄĆto the nation’s rich cultural heritage and‚ÄĆ historical ‚Ā£narratives. From the ‚ÄĆbustling‚Ā§ streets of Algiers, adorned with stunning ‚Ā§Ottoman architecture and French colonial influences, to ‚Ā§the ancient ‚Ā§ruins of Timgad,‚Ā£ these urban centers capture‚Äč the ‚Äćdiverse tapestry of civilizations that have shaped Algeria. Each ‚ĀĘcity boasts ‚ĀĘits own unique identity, reflected ‚Äčin‚ĀĘ its local customs, cuisines,‚ÄĆ and artistic expressions.‚Äč Notable cities include:
- Algiers: The capital city, known for its‚Äć beautiful ‚Ā£coastline and historic Casbah,‚Äč a UNESCO World ‚ÄćHeritage site.
- Oran: ‚Äć Famous for ‚Ā§its vibrant music ‚ĀĘscene and as the birthplace‚ÄĆ of ‚ÄĆRa√Į ‚Ā£music.
- Constantine: ‚Äć Known as the “City of Bridges,” with breathtaking ‚Ā£views and a rich‚Äč Roman history.
- Tlemcen: Renowned for its stunning islamic architecture ‚Äčand cultural festivals.
the importance of these cities‚ĀĘ extends beyond mere ‚Ā§population centers; they‚ĀĘ are basic ‚ĀĘto understanding the‚ÄĆ social ‚ÄĆand political‚ĀĘ evolution of Algeria. For instance,‚ĀĘ the‚ÄĆ historical significance ‚Äčof‚Äč G√©alma in the Saharan region highlights the traditional Berber culture, while cities along the Mediterranean coast illustrate the impact of European colonization. To‚Ā§ further ‚ĀĘillustrate ‚Äčthe major cities and ‚Äčtheir contributions, ‚Äčconsider the following table:
| City | Key Historical Feature | cultural Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Algiers | casbah | Blend of Arab‚Ā£ and‚Ā§ European ‚ÄĆcultures |
| Oran | Music and Festival | Heart ‚ĀĘof Ra√Į‚ĀĘ music movement |
| Constantine | Bridges and Cliffs | Symbol of resilience |
| Tlemcen | medina | Art and Literature Hub |
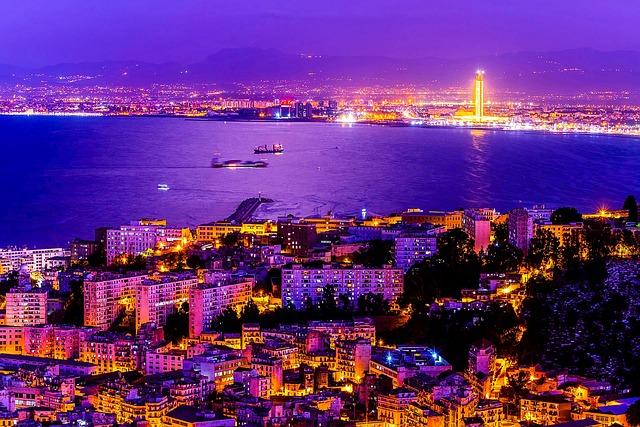

Economic‚Äč Growth ‚ĀĘand Challenges ‚Äčin Algeria’s‚Äć Energy Sector
Algeria’s economic ‚ÄĆgrowth ‚Ā§is inextricably linked to its energy sector, ‚Äćwhich has served as‚ĀĘ a ‚ĀĘcornerstone for national development. The country ‚Ā§is endowed with‚Ā§ ample reserves of‚ĀĘ oil and natural ‚Äćgas, making‚Ā§ it one of ‚ÄĆthe largest‚Äć energy ‚ÄĆproducers in Africa.‚Ā§ The government ‚ÄĆhas prioritized investments‚Ā§ in this sector to enhance production capacity‚ĀĘ and ‚ĀĘattract international‚Ā§ partnerships.‚Äč However,‚Ā§ important challenges persist, including‚Ā£ reliance on ‚Äčhydrocarbons, fluctuating ‚ĀĘglobal oil prices, and ‚Äćthe urgent ‚ĀĘneed to diversify the economy. As Algeria ‚Ā§strives ‚Ā§to solidify ‚Ā§its position as a‚ÄĆ key energy player, it must navigate these issues to foster sustainable economic growth.
To address these challenges and leverage its energy potential, Algeria has initiated several‚Äć strategies aimed at ‚Ā£modernizing its energy‚Ā§ infrastructure and expanding‚Äć renewable energy sources. Notable efforts include:
- Investment in Renewable Energy: ‚Ā§The‚Ā£ government aims‚Äć to ‚Äčgenerate 27% of its ‚Ā§electricity from renewable sources by 2030.
- Foreign Investment Partnerships: ‚ĀĘInitiatives to ‚ÄĆattract foreign companies with technology and expertise in oil ‚ĀĘand‚Äč gas.
- Policy ‚Ā§Reforms: Implementation of new policies to enhance openness and efficiency in the energy sector.
| Energy Source | Current Share (%) | Projected Share by 2030 (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrocarbons | 93 | 73 |
| Renewables | 7 | 27 |

Tourism ‚Ā§Potential‚Ā£ in Algeria: Must-Visit Destinations and Hidden‚Äč Gems
Algeria ‚Ā§boasts a rich ‚Ā§tapestry of history,culture,and natural beauty that positions it‚Äč as ‚Ā§an emerging player in the global tourism market. From the stunning ‚Ā§Mediterranean ‚ÄĆcoastline to the expansive‚Ā£ Saharan landscapes, the country offers‚ĀĘ a diverse range‚Äć of experiences.‚ĀĘ Some must-visit ‚Ā£destinations include:
- Algiers: The ‚Äćcapital city is‚Äć renowned for‚ÄĆ its ottoman architecture and vibrant ‚ÄĆstreet life.
- Tipasa: A ‚ÄĆUNESCO ‚ĀĘWorld Heritage site, this ancient Roman city‚Ā§ has breathtaking‚Äć ruins overlooking‚ĀĘ the sea.
- Tassili ‚ĀĘn’Ajjer: Home‚ĀĘ to unique rock‚Äć formations and prehistoric art, this‚Ā§ national park‚ĀĘ offers ‚Ā§an ‚Ā§otherworldly experience.
- Sahara Desert: Experience ‚Ā£the ‚Äčbeauty‚Äč of sand dunes‚Ā£ and oases, perfect for ‚Ā§trekking and‚Ā§ camel rides.
In addition to well-known attractions,‚Äć Algeria is ‚Ā§also home to several hidden gems waiting to be ‚Äčdiscovered.‚Äć For‚Ā§ those‚Äć looking to venture off the beaten path, ‚ÄĆconsider these‚Äč stunning spots:
- Gharda√Įa: A picturesque town in ‚Äćthe‚Äč M’zab Valley, famous for its unique architecture and rich ‚Ā§Berber culture.
- the Kasbah of algiers: ‚Äć Wander through‚Äć this historic quarter filled with narrow‚Ā£ alleys,bustling ‚Ā§souks,and ancient mosques.
- Ksar ‚ĀĘof Ait Benhaddou: Although situated near the border,this‚Äč medieval fortified village provides a‚Ā£ glimpse into Algeria‚Äôs ‚ÄčSaharan ‚ĀĘarchitecture and history.
- Chrea National Park: A‚Ā§ green oasis in the midst ‚Ā£of mountainous ‚ÄĆterrain, ideal‚ĀĘ for hiking ‚ĀĘand appreciating ‚Ā£local flora and fauna.

Environmental Issues‚Äć and Sustainability ‚ÄĆEfforts in ‚ÄćAlgeria
algeria, with its diverse geography ranging ‚Ā§from the Mediterranean coast to the‚ÄĆ vast expanse of the Sahara, faces a‚Ā§ multitude‚ÄĆ of‚Äč environmental ‚ÄĆchallenges. These include desertification, water‚ĀĘ scarcity, and ‚Äć pollution,‚Ā£ exacerbated by climate change and ‚Äčunsustainable agricultural practices. The country’s rich natural resources‚Äč are ‚ÄĆincreasingly under‚ĀĘ threat, requiring ‚Äćurgent attention to preserve its unique‚ĀĘ ecosystems.To ‚Ā§combat‚Äč these‚ĀĘ issues, Algeria has ‚Äćinitiated various sustainability efforts aimed at fostering a‚Äć balance‚Ā£ between ‚ĀĘeconomic‚ÄĆ development and‚Ā£ environmental protection. Key initiatives include:
- National Action Plan ‚ÄĆon‚Äč Climate Change:‚Äč Aiming‚Ā£ to mitigate the effects of global ‚Äčwarming.
- Afforestation‚Ā§ Projects: Restoring degraded‚Äč lands and enhancing‚ĀĘ biodiversity.
- Promotion‚Äć of Renewable Energy: Investments in solar‚Äć and wind energy to reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
In parallel, algeria’s ‚Äćcommitment to ‚Äčinternational agreements,‚Ā£ such as‚Ā§ the Paris Agreement, demonstrates its proactive‚Äč stance on global ‚Ā£environmental‚Ā§ issues. The country is actively engaging‚Ā£ in collaborations ‚Ā§with various non-governmental organizations‚Äč (NGOs) and international bodies to ensure a more ‚Äčsustainable‚Äć future. ‚Ā£Local communities are also being ‚Äčempowered to ‚Ā£participate ‚ĀĘin‚ĀĘ these ‚Ā§efforts by‚ĀĘ raising awareness about eco-friendly practices and‚Äć the importance of‚Ā§ conserving indigenous biodiversity. ‚Ā§With these integrated approaches, Algeria strives ‚Äčto pave‚Ā§ a greener path ‚Ā£while‚ĀĘ maintaining its cultural and natural‚Ā£ heritage.

The Role ‚Äćof Algeria in Regional Politics and International‚Äč Relations
Algeria’s geographical ‚Ā£positioning‚ÄĆ at ‚Ā£the‚Äč crossroads of North Africa, the mediterranean, and‚Äć the sahara desert bestows ‚Äčupon ‚Äćit a strategic advantage that‚Ā§ significantly ‚Äčinfluences ‚Äćregional politics and international relations. The country is‚Ā£ a pivotal‚Ā£ player in various multilateral organizations, including the African Union and the Arab‚Ā£ League, where‚Ā£ it has championed the cause of African unity, security, and development. Key areas of influence ‚ĀĘ include:
- Mediation in Regional conflicts: ‚ÄčAlgeria has ‚Äćfacilitated‚ÄĆ peace processes in‚Ā§ neighboring countries like Mali and Libya, emphasizing its role as ‚ÄĆa stabilizing force in a ‚Ā£tumultuous ‚ĀĘregion.
- Counterterrorism Efforts: Its commitment to combatting terrorism, especially in the Sahel, showcases Algeria’s proactive ‚Äćstance in ‚Äćsafeguarding ‚Ā§not only its own‚Ā£ interests but also regional stability.
- Economic‚Äč Partnerships: Algeria’s ‚Äčvast natural resources,particularly natural gas,position‚Ā§ it as a key‚ÄĆ energy supplier,influencing‚Ā£ its relationships with both‚ĀĘ African‚Ā§ nations and‚Ā£ international players,especially in Europe.
Moreover,‚Äč Algeria’s‚Äč foreign policy is marked by a non-alignment stance,‚ÄĆ seeking to‚ÄĆ maintain its sovereignty ‚ÄĆwhile engaging with global powers. It ‚ĀĘhas navigated complex‚Äč relationships with countries ‚Ā§such ‚Ā£as the United States, Russia, and‚Äč China, often balancing trade agreements‚Äč and military ‚Äčpartnerships.The country’s leadership‚ĀĘ is motivated by its historical legacy of anti-colonial struggle, driving a foreign policy rooted ‚ÄĆin principles of respect and‚ÄĆ equality, reflected in:
| Country | Type ‚Äčof Relationship | Focus Areas |
|---|---|---|
| United states | Strategic Partnerships | Energy, ‚ĀĘSecurity, ‚ÄčCounterterrorism |
| China | Economic Cooperation | infrastructure‚ĀĘ Development, Trade |
| France | Historical‚ĀĘ Ties | Cultural Exchange,‚ĀĘ Immigration |
In Conclusion
Algeria stands ‚Ā§as a‚Ā£ unique crossroads of diverse cultures, landscapes, and histories within the North African‚ĀĘ region. From its Mediterranean coastline to the expansive Sahara ‚Ā£Desert, the nation embodies ‚ĀĘa rich‚Äč tapestry of geographical and‚Ā£ cultural contrasts. As we have explored in‚Ā£ this article,Algeria’s historical significance,strategic location,and‚Äč vibrant heritage contribute ‚Ā£to its‚Äč importance on both a ‚Ā£regional and global scale. Understanding Algeria‚Ā£ not only deepens our insights into North‚ĀĘ African ‚Ā£dynamics but also ‚Äćhighlights the‚Äć challenges ‚ĀĘand‚Äć opportunities that shape its future. As the country continues to navigate the complexities of modernity while‚Ā£ honoring ‚Ā£its past, Algeria remains a pivotal player ‚ÄĆon‚Ā£ the ‚ÄčMediterranean stage and an‚Äć intriguing subject ‚ÄĆfor ‚Ā£further exploration‚Äć and understanding.