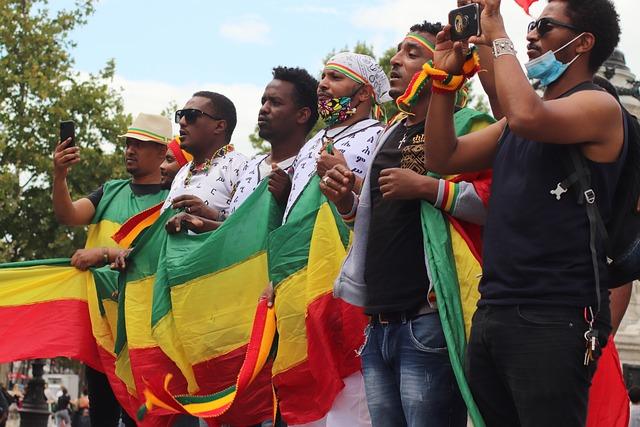
In a notable advancement amidst ongoing regional tensions, Ethiopia and Eritrea have made a joint commitment to avert warfare, signaling a cautious step towards stability in the Horn of Africa. However, despite this pledge, neither nation has outlined a clear framework for lasting peace, raising concerns among analysts and citizens alike. As historical grievances linger and border disputes persist, the promise to avoid conflict presents both hope and uncertainty for a region long plagued by rivalry and strife. This article delves into the implications of this agreement, examining the complex dynamics at play and the potential hurdles that could undermine the fragile peace.
Ethiopia and Eritrea’s Commitment to Peaceful Coexistence Amid Tensions
The commitment between Ethiopia and Eritrea to foster peaceful coexistence is crucial in the context of their historically tumultuous relationship.Leaders from both nations have openly declared their intention to avert conflict, focusing on diplomatic dialog as a primary means of addressing disputes. However, the absence of concrete peace guarantees raises concerns among observers and citizens alike. Key initiatives aimed at promoting stability include:
- Enhanced diplomatic engagement to resolve outstanding issues related to border disputes.
- Community-building efforts that encourage cross-border cultural exchange and economic collaboration.
- Joint security arrangements designed to address mutual threats while fostering trust.
Despite these positive steps, skepticism remains, fueled by the volatility of past conflicts and ongoing regional disputes. to provide a clearer picture of the current situation, the following table summarizes the principal areas requiring attention:
| Area of Concern | Current Status | Next Steps |
|---|---|---|
| Border Security | Tensions remain high; sporadic skirmishes reported. | Initiate joint patrols and monitoring mechanisms. |
| Economic Cooperation | Limited trade agreements in effect. | Explore opportunities for joint ventures and investments. |
| humanitarian Issues | Inadequate support for displaced populations. | Collaborate with international organizations for aid distribution. |

Historical Context of the Ethiopia-Eritrea Conflict and Its Aftermath
The conflict between Ethiopia and Eritrea has deep historical roots that date back to the late 19th century when Eritrea was colonized by Italy. Following World War II, Eritrea was federated with ethiopia, creating tensions as nationalist movements emerged. The situation escalated in the 1960s, leading to the Eritrean War of Independence, which lasted until 1991 when the Eritrean Peopel’s Liberation Front (EPLF) successfully ousted the ethiopian government. This victory, however, did not lead to lasting peace. Instead, political disputes and territorial claims cultivated animosity, culminating in a brutal conflict from 1998 to 2000 over border demarcations, which resulted in tens of thousands of casualties and deep scars on both sides.
Despite a peace agreement signed in 2000, the aftermath has been characterized by a tense standoff, military confrontations, and deep-seated mistrust. Both nations have grappled with the economic and social impacts of the conflict, leading to a prolonged period of isolation and military build-up. In 2018, a critically important thawing of relations occurred when Ethiopia’s Prime Minister Abiy Ahmed announced an end to hostilities, paving the way for renewed diplomatic engagement. Though, as recent developments indicate, efforts to guarantee peace are still fragile, raising concerns over a potential resurgence of conflict. Key elements contributing to the ongoing volatility include:
- Territorial disputes: Persistent disagreements over contested border regions.
- National identity: Competing narratives of nationalism that fuel the enmity.
- Military readiness: Both nations maintaining large military forces, which can be easily mobilized.
- Regional dynamics: Influence of neighboring countries and international actors complicating negotiations.

Challenges to Sustained Peace: Political and Social Dynamics in the Region
The fragile promise made by Ethiopia and Eritrea to avoid war reinforces the complex political and social dynamics at play in the region.Both nations have a historical backdrop of conflict that continues to cast a long shadow over their current interactions. numerous factors complicate the pursuit of lasting peace,including:
- Ethnic tensions: A multitude of ethnic groups demands representation and autonomy,leading to potential unrest.
- Border disputes: Ongoing disagreements over territorial claims create flashpoints for renewed conflicts.
- Political leadership: The stability of both governments is precarious, with leaders facing pressure from both internal and external actors.
Moreover, social dynamics also play a crucial role in maintaining a tenuous peace. The narratives shaped by media and education can inflame public sentiment or foster reconciliation. In such a context, the importance of community dialogue becomes paramount. Regions affected by past conflicts often exhibit a desire for:
- Community engagement: Initiatives aimed at fostering understanding and cooperation among diverse groups.
- Economic cooperation: Joint ventures that promote mutual prosperity can help bridge divides.
- International mediation: Diplomatic efforts from third parties may be essential in guiding both nations toward a stable peace.

International Community’s Role in Supporting Stability and Dialogue
The role of the international community in fostering stability and dialogue in conflict-prone regions such as the Horn of Africa is crucial. Nations and organizations can serve as mediators,facilitating conversations between Ethiopia and eritrea to prevent misunderstandings and promote peaceful coexistence. By leveraging diplomatic avenues,they can encourage both governments to commit to tangible agreements that address underlying issues,such as border disputes and resource allocation,thereby enhancing regional security. Key strategies include:
- Mediation Initiatives: Encouraging third-party mediators to facilitate discussions and negotiations.
- Monitoring Mechanisms: Establishing self-reliant observation teams to ensure compliance with ceasefire agreements.
- Economic Incentives: Offering economic cooperation programs that promote trade and investment between the nations.
Furthermore, the establishment of multilateral partnerships can enhance the sustainability of peace efforts. By pooling resources and expertise, international organizations can provide assistance that not only focuses on immediate tensions but also addresses long-term developmental challenges. The following table illustrates potential areas of collaboration that the international community might explore:
| Area of collaboration | Description |
|---|---|
| Humanitarian Assistance | Support for displaced communities and address urgent basic needs. |
| Capacity Building | Training programs for conflict resolution and governance. |
| Security Cooperation | Joint security initiatives focusing on border control and trafficking. |

recommendations for Building Trust and Fostering Long-Term Cooperation
to build trust and foster long-term cooperation between Ethiopia and Eritrea, it is essential to implement strategic measures that prioritize open dialogue and mutual understanding. Both nations should engage in regular diplomatic discussions to address unresolved issues and enhance transparency. This can include:
- Establishing Joint Committees: Creating panels composed of representatives from both countries to facilitate negotiations on shared concerns, such as border disputes and resource management.
- promoting Cultural Exchange: Encouraging programs that celebrate cultural heritage and history can enhance mutual respect and understanding among citizens.
- Strengthening Economic Ties: developing trade agreements and joint economic projects to financially interlink both nations, creating a vested interest in maintaining peace.
In addition to these initiatives, both governments must commit to cultivating a spirit of accountability and obligation within their leadership and institutions. transparency in governance and shared responsibilities can mitigate suspicion and enhance security. The following actions can bolster credibility:
| Action | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|
| Regular Dialogue Forums | Improved interaction and reduced misunderstandings. |
| Peace Education Programs | Enhanced public support for peace initiatives. |
| Joint Security Operations | Increased confidence in mutual protection efforts. |

Looking Ahead: the Path to Lasting Peace Between Ethiopia and eritrea
The relationship between Ethiopia and Eritrea has a long and tumultuous history,marked by periods of conflict and fragile truce.As both nations pledge to avoid war, it is crucial to recognize that merely promising peace is insufficient without concrete actions to build trust and foster cooperation.To achieve a lasting peace, both governments must focus on several key areas:
- Dialogue and Diplomacy: Opening channels of communication and engaging in regular discussions can pave the way for mutual understanding.
- economic Collaboration: Joint ventures in trade and infrastructure development can create interdependency that discourages conflict.
- Addressing Human Rights Concerns: Ensuring the protection of human rights and addressing grievances can alleviate long-standing tensions.
- Cultural Exchange Initiatives: Promoting people-to-people connections through cultural and educational programs can help bridge gaps.
Moreover,external support from the international community can play a pivotal role in sustaining these efforts. A collaborative framework involving regional stakeholders and international organizations could facilitate peacebuilding activities. The following table illustrates potential areas of cooperation:
| Area of cooperation | Expected Outcomes |
|---|---|
| Security and stability | Reduction in border tensions and mutual security agreements. |
| Trade Agreements | Increased economic ties leading to prosperity for both nations. |
| Joint Humanitarian efforts | Improved living conditions and support for affected populations. |
| Environmental Initiatives | Collaborative projects for sustainable resource management. |
Understanding that peace is a journey, not a destination, both Ethiopia and Eritrea must be committed to this path, recognizing that the choices made today will shape their relationship for generations to come.
Closing Remarks
while the leaders of Ethiopia and Eritrea have publicly committed to avoiding conflict, the absence of specific guarantees for lasting peace raises concerns among observers and regional stakeholders. The historic complexities and lingering tensions between the two nations underscore the challenges ahead. As both countries navigate their relationship, fostering dialogue and mutual understanding will be essential to transforming promises into a sustainable peace. Analysts will be watching closely to see how these pledges manifest in policy and practice, as the people of both nations hope for a stable future free from the shadows of war. The path to reconciliation is fraught with obstacles, but it is indeed a necessary journey that must be undertaken for the benefit of future generations.