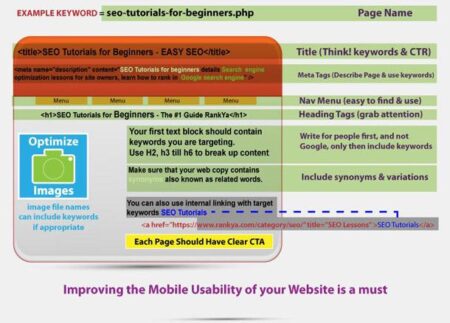
in recent‚Äå years, the ‚Å£proliferation of misinformation ‚Å¢has emerged as a meaningful challenge in the realm ‚Äçof global media, ‚Äånotably in regions like West Africa, where geopolitical‚ŧ tensions are at play. ‚ÄãA ‚ŧtroubling new phenomenon has surfaced: the rise of “ghost‚Å¢ reporters” who produce pro-Russian propaganda under the guise of legitimate‚Äå journalism. These individuals, often operating ‚ŧin the shadows, utilize social media and obscure online platforms to disseminate narratives‚ŧ that align with ‚Å¢Russian interests, exploiting local vulnerabilities and exploiting ‚Äåexisting socio-political divides. This article delves‚Å¢ into the origins, methods, and ‚Å¢implications of‚Å£ these‚Äç ghost reporters, shedding light on‚Å£ their‚ŧ role in influencing ‚ŧpublic perception‚Äç and the broader impact on the political landscape across West Africa. Through examining‚ŧ various case ‚Äãstudies and expert analyses, we aim ‚Å£to understand how‚ŧ this form of propaganda not onyl shapes media consumption but also threatens to undermine democratic discourse ‚Äåin the ‚Äåregion.
The Emergence ‚Äãof‚ŧ Ghost Reporters in‚ŧ West ‚ÄãAfrica’s Media Landscape
The rise of ghost reporters in West ‚Å£Africa has opened a controversial chapter‚Äã in the ‚Å£region’s ‚Å¢media narrative. These individuals often‚Å£ operate anonymously or under pseudonyms,contributing to a ‚Äãsurge ‚Å£in media ‚Äçcontent that leans heavily towards pro-Russian sentiments. This phenomenon can be attributed‚Äç to various factors including the growing‚Äã disenchantment with Western narratives,alongside‚Äç an increasing ‚Äãalignment ‚Äçwith Russian ‚Äågeopolitical‚ŧ strategies.‚ŧ It ‚Å¢has ‚Äãsparked‚Äå significant conversations among policymakers and‚Äã media analysts alike, who are concerned ‚ŧabout the ‚Äãmanipulation of information and its implications on ‚ŧpublic ‚Äãopinion.
These ghost reporters often utilize various platforms to disseminate information, blurring the ‚Äçlines between‚Äç journalism‚Å¢ and propaganda. Key characteristics of their operations include:
- Anonymity: Many reports lack a ⁤verifiable ‍author,⁣ undermining trust.
- Pro-Russian‚Äã narratives: Content frequently ‚Å£enough‚Äã emphasizes support ‚Äãfor Russian policies and ‚Äçdownplays Western criticisms.
- Social media amplification: Utilizing platforms‚Äç like Facebook and Twitter‚Äã to reach wider audiences rapidly.
In response to this growth, local media ‚Äåorganizations and fact-checking ‚Äåentities are enhancing ‚Äåtheir‚Å£ strategies to combat misinformation. As they strive ‚Å¢to uphold‚Å¢ journalistic integrity,‚Äç awareness of the‚Äã various methods employed by these ghost reporters‚Äã is‚Äå critical. The regional media ‚Äåmust adapt to ensure that credible reporting prevails ‚Å¢over fabricated narratives, thereby preserving an informed ‚Å£public discourse.

Investigating the ‚ÄãInfluence of ‚Å£pro-Russian Narratives ‚Äãon Public Opinion
In recent years, ‚Å¢a covert network of so-called “ghost reporters” has emerged in West Africa, tirelessly crafting and disseminating pro-Russian narratives. ‚Å£these reported efforts ‚Äãare strategically‚Äç aimed ‚Äåat steering public sentiment ‚Å£and‚ŧ reshaping perceptions surrounding the geopolitical dynamics in the region. ‚ÄãThe content produced ‚Å£by ‚ŧthese individuals often emphasizes themes such as anti-colonialism,‚ŧ economic independence, and‚Å¢ a critique of Western‚ŧ interventions, resonating deeply with local audiences who have historically faced challenges rooted‚Äã in foreign exploitation.
The ‚Äåeffectiveness‚Å£ of these narratives can be largely‚Å¢ attributed to several key ‚Äçfactors:
- Cultural Resonance: Many⁤ pro-Russian messages are tailored to reflect the cultural and past contexts‍ of the⁤ target audience, making ‍them more relatable.
- Use ‍of Local Languages: ​ By publishing content in local dialects, these narratives⁤ reach broader ⁣demographics, enhancing their influence.
- Social⁤ Media Amplification: Platforms‍ like Facebook and WhatsApp serve as vital channels for disseminating these narratives, allowing them to spread rapidly.
The impact of this propaganda apparatus on ⁤public‌ opinion is significant,evidenced ⁤by‍ a ⁢growing skepticism towards traditional Western narratives. A recent analysis ⁢of media coverage patterns in the​ region highlights the shifts in public discourse influenced by these‍ ghostly writers:
| Media Outlet | percentage⁤ of Pro-Russian Content | Public Sentiment‌ Shift |
|---|---|---|
| Local⁤ News ⁤Portal A | 45% | Increased Support for Russia |
| Radio Station B | 60% | Distrust of Western Policies |
| Social Media Group C | 75% | Emerging⁤ Anti-Western Sentiment |

Techniques Used ‚Å¢by Ghost Reporters to Disseminate‚Å¢ Misinformation
Ghost reporters utilize a range of complex techniques to promote pro-Russian ⁤narratives while obscuring their true‌ intentions. These⁤ tactics‍ often include the⁢ manipulation of‌ digital platforms to create the illusion of legitimacy. For instance, they ‍may employ sock puppeting, where⁢ fake profiles ⁤are⁢ generated​ on social media to amplify misleading stories. Additionally, ​these ⁢operatives ‌often leverage astroturfing, which involves crafting ⁣the appearance of grassroots support for their narratives through orchestrated campaigns that flood online spaces with supportive comments and shares. By strategically⁤ choosing popular hashtags and engaging in trending discussions, they‍ manage to steer the discourse‌ towards ​their manufactured viewpoints.
Another common approach involves the use​ of ⁣deceptive⁢ visuals and statistics that ⁣misrepresent reality. Ghost reporters often deploy edited images or unnaturally skewed data to lend credibility to⁣ their claims. ⁣To further muddy the waters, they may utilize clickbait headlines that ⁢are designed⁢ to provoke emotional reactions,‍ enticing ⁢users to share ⁤content without scrutinizing its validity. The tables below summarize these methods and illustrate how ‍they contribute to ‌the spread ⁣of misinformation:
| technique | description |
|---|---|
| Sock Puppeting | Creating fake accounts to⁤ promote⁣ narratives. |
| Astroturfing | Faking grassroots support through coordinated efforts. |
| Deceptive Visuals | Using edited images to‚Äå mislead‚Å¢ audiences. |
| Clickbait Headlines | Crafting sensational ‚Å£titles ‚Å£to provoke interest. |

The Role of Social Media in ​Amplifying ⁤Propaganda Efforts
The landscape of ⁢media consumption ​has dramatically shifted with the rise of social platforms, providing ​fertile ground for the⁤ proliferation of propaganda.⁤ In West⁢ Africa,pro-Russian narratives have found‍ their⁢ way into local discourse,primarily through social media channels ⁣ that facilitate the rapid sharing ⁣of ‌information. these platforms allow for​ the targeting ‌of audiences that may be susceptible to narratives ‍that align⁣ with their ​existing beliefs, thus creating echo chambers where misinformation thrives. The ⁢use of fake identities and ‘ghost reporters’—individuals⁣ or​ entities posing as⁢ legitimate journalists—exacerbates this issue, blurring the lines between credible news and ‍state-sponsored propaganda.
Among the mechanisms that ‚Äçenable these propaganda efforts are:
- Anonymity: ‚Äç Provides cover for individuals to spread misinformation without accountability.
- Sensationalism: Utilizes emotionally charged ‚Å¢content to engage‚Äã and manipulate audiences.
- Algorithmic⁣ Amplification: Social media algorithms ⁤prioritize content ‍that generates engagement, furthering ​the reach of propaganda.
The effectiveness of these tactics is underscored by a recent analysis of social media⁢ interactions‌ across various‍ platforms, which illustrates⁤ the high⁣ rate of engagement with pro-Russian content compared to balanced‌ reporting:
| Content Type | Engagement Rate (%) |
|---|---|
| Pro-Russian Propaganda | 75 |
| Balanced News Reporting | 35 |
This⁣ disparity highlights the challenges faced by⁣ traditional‍ news outlets ‌in countering ⁤the misleading narratives‌ proliferated through ‍social​ media, as they struggle to compete with content⁢ that ‍is not only sensational but also tailored to ‍resonate ⁤with regional sentiments.

Implications for Regional Stability and ⁤Democratic Processes
The ‌infiltration of pro-russian propaganda through⁢ the phenomenon of ‘ghost reporters’ poses significant⁢ challenges to both regional stability ‍and the ‌integrity‍ of democratic ⁢processes in West Africa. These operatives exploit local grievances, manipulating narratives ⁤to foster discontent and division among populations. By disseminating misleading information, ⁢they undermine trust in governmental institutions and​ legitimate media sources, ‌further exacerbating existing social tensions. The ⁣repeated exposure to such propaganda creates a fertile ground for unrest,as citizens may begin to view⁤ their governments as unresponsive or unfriendly,thus eroding public confidence in democratic governance.
The ⁢impact of these activities can be measured through various factors, which ultimately ⁤influence the broader‌ political‌ landscape. Here ⁣are some of the critical implications:
- Destabilization of⁤ Governance: elected officials may find‌ it increasingly arduous to implement policies as public sentiment shifts⁤ due ⁣to manipulative narratives.
- Strengthening of‚Äã Authoritarianism: The rise of disillusionment fosters‚Äã an environment ripe for authoritarian figures who ‚Äåpromise stability amidst chaos.
- Polarization of Society: Ethnic‚Äå and political ‚Äådivisions‚Äã can‚Å£ be deepened, ‚Äåcomplicating efforts toward national unity.
- Undermining ‍Civil Liberties: Increased censorship and⁤ crackdowns on dissent ‌may occur as governments respond to perceived​ threats from misinformation.

Strategies for Countering Disinformation ‚Å¢and ‚Å¢Promoting Media Literacy
Combatting disinformation, especially in regions ‍susceptible​ to foreign influence, requires a⁢ multifaceted approach that emphasizes both critical thinking skills and community engagement. Community⁣ workshops can⁣ be instrumental in equipping individuals with the⁣ tools they need to identify false narratives, ⁢while leveraging local languages and cultures to resonate more deeply with the⁢ audience.Moreover, collaborating with trusted local leaders and influencers can definitely help disseminate‍ accurate information⁢ more effectively, as these figures frequently enough carry significant weight within ​their ⁢communities. events ‌such‍ as public forums or ⁣ media ⁤literacy campaigns ‍can provide ⁤a platform to discuss the importance of verifying sources and⁣ understanding the ‍motivations ⁤behind certain narratives.
To enhance ‚Äåmedia literacy,it’s‚Äç essential to ‚Äãintegrate strategies into educational curricula that foster ‚Äåanalytical skills‚Å¢ from an early age.Schools can implement projects that‚Å£ encourage students to dissect‚Äç news articles,‚Å£ assessing their‚Äç sources and identifying biases. In addition, ‚Å¢establishing online‚Å£ resources tailored to the local population can ‚ŧdefinitely ‚Äãhelp individuals distinguish reliable information‚Å£ from ‚ŧdisinformation.‚Äã A commitment ‚ŧto‚Å£ transparency from media organizations‚ŧ is also crucial; ‚ŧadopting policies that allow ‚Å¢the‚Äå public to see how news is gathered can build‚Å£ trust.Ultimately, the combination of local education, community participation, and accessible online resources will help ‚Äãreinforce the resilience of‚Å£ societies against the tide of disinformation.

The Conclusion
the phenomenon of ‘ghost reporters’ in West Africa highlights a ‚Å£complex and troubling ‚Å£intersection of information warfare‚Äç and local media landscapes.As pro-Russian propaganda infiltrates the region,‚Äç it underscores the critical ‚Äåneed for robust journalistic integrity and media literacy among audiences. ‚ÄãThe ‚Å¢reliance on ‚Äåanonymous ‚ŧsources and distorted ‚Äãnarratives not only threatens democratic discourse but also‚Å¢ exacerbates existing‚Äã vulnerabilities within fragile political ‚Äåenvironments. As this geopolitical contest unfolds, ‚Äçunderstanding the motives and methods of these ghost ‚ŧreporters ‚Å£will‚Äã be‚ŧ essential for ‚Äãpolicymakers, scholars, ‚Äãand ‚Å£the public alike in order to combat misinformation and‚Äã uphold the principles of credible‚Äç journalism.‚Äç The‚Å¢ challenge remains to navigate this ‚Äçevolving landscape, fostering resilience‚Äå against manipulative narratives while promoting‚Äã an informed citizenry in the face of an ‚Äåincreasingly polarized ‚Å¢media‚Äå ecosystem.