In a remarkable turn of events, ornithologists and bird enthusiasts alike have been captivated by the unexpected reappearance of a rare avian species in madagascar, a sighting that has eluded researchers for an astounding 24 years. The elusive bird, known scientifically for its unique characteristics and limited habitat, was last documented nearly a quarter of a century ago, leading too fears that it may have disappeared from the island nation forever. This recent sighting not only ignites hope for conservationists but also highlights the importance of protecting Madagascar’s rich biodiversity, which is home to a plethora of endemic species. As scientists race to gather more data on this rediscovered avian treasure, the event underscores both the challenges and triumphs of wildlife conservation in one of the world’s most ecologically unique regions.
Resurgence of the Rare Bird Sparks Conservation Interest in Madagascar
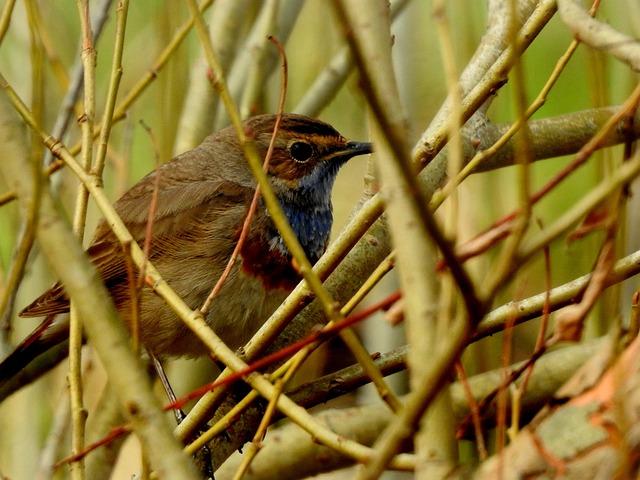

The unexpected reappearance of a previously lost avian species in Madagascar has reignited interest in conservation efforts across the island. For years, this rare bird, once thoght to be extinct, had eluded researchers and birdwatchers alike, making its resurgence a significant event for conservationists. The news has spurred various wildlife organizations and local communities to recognize the importance of safeguarding Madagascar’s unique biodiversity, which includes numerous endemic species that face threats from habitat destruction and climate change. To effectively respond to this development, many have taken to implementing strategic conservation initiatives, focusing on enduring land-use practices and habitat restoration.
Considering this event, key stakeholders have come together to discuss the most effective methods for preserving the ecosystem that supports not just this rare bird but also many other species at risk. Their collaborative dialog highlights several focal points:
- Community Involvement: Engaging local populations in conservation efforts to foster a sense of ownership.
- Research Funding: Increasing financial support for studies focused on vulnerable species in Madagascar.
- Awareness Campaigns: Launching educational programs about the importance of biodiversity and conservation.
| Conservation Strategy | Description | Status |
|---|---|---|
| Habitat Protection | Establishing protected areas to safeguard critical habitats. | Ongoing |
| Species Monitoring | Regular assessments of bird population and health. | Planned |
| Community Programs | Building local capacity for conservation through education. | In Progress |
Biologists analyze the Implications of the Rare Bird’s Appearance

researchers are buzzing with excitement as they delve into the significance of the rare bird spotted in Madagascar after its long disappearance. This nicknamed “ghost of the forest,” which has eluded scientists since its last confirmed sighting in 1999, is prompting a reevaluation of its habitat and conservation status. Experts are focusing on the following critical implications:
- Ecological Role: The bird’s potential contribution to the ecosystem may provide insights into the health of Madagascar’s unique biodiversity.
- Genetic Diversity: The re-emergence of this rare species may indicate a broader spectrum of genetic variation that could benefit future conservation efforts.
- Tourism Potential: Its return could bolster local tourism, highlighting the need for sustainable measures to protect its habitat.
Furthermore, studies are being initiated to assess the factors that may have contributed to the bird’s reappearance.Researchers are particularly interested in environmental changes, including deforestation and climate shifts, that could have impacted the species’ survival over the years. The following data is particularly compelling:
| Year | Sighting Status | Estimated population |
|---|---|---|
| 1999 | Last Sighting | Unknown |
| 2023 | Confirmed Sighting | Approx. 50 |
As biologists continue to investigate the ramifications of this rediscovery, there is optimism that it may drive renewed conservation initiatives in Madagascar. The reappearance could serve as a crucial reminder of the delicate balance of ecosystems and the ongoing journey to protect the rich and diverse life forms that inhabit our planet.
Tracking Techniques: How Modern Science Aids in Bird Conservation

The resurgence of a rare bird species in Madagascar is a testament to the amazing advancements in avian tracking techniques that have revolutionized bird conservation efforts. Modern science employs a variety of methods to monitor bird populations, allowing researchers to gather critical data about migratory patterns, breeding habits, and habitat preferences. Some of the most effective techniques include:
- GPS Tracking: Utilizing GPS devices, researchers can collect real-time location data, helping to understand migratory routes and seasonal behaviors.
- Radio Telemetry: This method involves attaching a lightweight transmitter to the bird, enabling scientists to track their movements over large distances.
- Camera Traps: Placed strategically within habitats, these devices capture images or videos of birds, providing insights into their activities without human interference.
- citizen Science Initiatives: Engaging the public in data collection allows for a broader reach and stimulates community interest in conservation efforts.
Furthermore, the integration of data analytics and machine learning is enhancing the way researchers interpret the vast amounts of information collected. For example, by analyzing spatial data, scientists can identify critical habitats that require preservation or restoration.The following table illustrates some key metrics associated with contemporary bird conservation strategies:
| Technique | Data Collected | impact on Conservation |
|---|---|---|
| GPS tracking | Migration paths, stopover points | Identifies critical migratory zones |
| Radio Telemetry | Movement behavior, habitat use | Informs habitat management strategies |
| Camera Traps | Behavioral patterns, species interaction | Supports biodiversity monitoring |
| Citizen Science | Population sightings, nesting data | Enhances community engagement |
Challenges Ahead: preserving the Habitat of the Resurfaced Species

The rediscovery of the rare bird in Madagascar marks a significant moment,but it also highlights the pressing challenges that lie ahead in conserving the unique habitats that support its survival. As the environmental conditions continue to shift, a multitude of factors threaten the delicate ecosystems where this species resides. Key challenges include:
- Deforestation: Rapid land clearing for agriculture and urban development disrupts the natural habitats required for the bird’s sustenance and breeding.
- Climate Change: Altered weather patterns can lead to changes in food availability and nesting conditions.
- Invasive Species: Non-native plants and animals can outcompete indigenous species, degrading the ecosystem.
- Pollution: Increased use of pesticides and chemicals in agriculture affects the health of local flora and fauna.
Efforts to mitigate these threats must be multifaceted, involving local communities, conservation organizations, and governmental bodies. Solutions should prioritize sustainable practices that protect the habitat while supporting the livelihoods of those who inhabit these regions. Critical steps toward this goal could include:
| Action | Description |
|---|---|
| Reforestation | Planting native trees to restore lost habitats and improve biodiversity. |
| Community Education | Raising awareness about the importance of conserving endemic species and their habitats. |
| Policy Development | Implementing regulations to curb land development that threatens wildlife habitats. |
Community Involvement: Engaging Locals in wildlife Protection Efforts

Engaging local communities in wildlife protection efforts has become increasingly essential, particularly in areas where endangered species, like the recently rediscovered bird in madagascar, reside. Local residents possess invaluable knowledge about the ecosystems and the challenges they face. By fostering partnerships between conservation organizations and community members, we can create a sustainable approach to wildlife preservation. Some strategies include:
- Organizing community workshops to raise awareness about the importance of biodiversity.
- Providing training for locals in eco-tourism, creating economic incentives to protect rather than exploit natural resources.
- Implementing community-based monitoring programs to keep track of wildlife populations and habitats.
Moreover, when locals are actively involved in conservation initiatives, they become stakeholders in the success of wildlife protection. This leads to a sense of ownership and pride in their natural heritage. Key benefits of community involvement include:
- Enhanced reporting of illegal wildlife activities, supported by local knowledge.
- Stronger advocacy for environmental policies that reflect community values.
- Promotion of cultural practices that align with conservation goals, ensuring that wildlife preservation is integrated into daily life.
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Improved Monitoring | Communities can provide continuous observation of local wildlife. |
| Economic Incentives | More jobs in eco-tourism lead to less reliance on harmful practices. |
| cultural Integration | Using local traditions to promote conservation enhances community bonds. |
Future Research Directions: What We Can Learn from the Rediscovery

The recent rediscovery of a rare bird species in Madagascar serves as a poignant reminder of the gaps in our knowledge regarding biodiversity and conservation. This unexpected resurgence opens avenues for further research that can deepen our understanding of the species’ ecological requirements, breeding habits, and habitat needs. Potential future research directions include:
- Population Dynamics: Investigating the factors that contribute to population fluctuations and survival rates.
- Habitat Preferences: Assessing the types of environments that support thriving populations.
- predation and Competition: Exploring interactions with other species that might impact its survival.
- Climate Adaptation: Studying how environmental changes traditionally affect this species and similar avian dwellers.
A collaborative approach involving local communities, conservationists, and international researchers can maximize the impact of these studies. Insights gained from fieldwork and observation can inform conservation strategies and policy-making at various levels.The table below illustrates potential research methodologies and their expected outcomes:
| Research Methodology | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|
| Field Surveys | Data on population size and distribution |
| Genetic Analysis | Understanding genetic diversity and health |
| Remote Sensing | Identifying habitat viability and changes over time |
| Community Engagement | Enhancing local stewardship and protection efforts |
Final Thoughts
the remarkable reappearance of the elusive Madagascar ibis, a bird untraceable for nearly a quarter of a century, offers a glimmer of hope for conservationists and ornithologists alike. This unexpected resurgence underscores the importance of protecting Madagascar’s unique ecosystems, which are home to numerous endemic species facing existential threats. As researchers continue to study this rare avian marvel, efforts to conserve its habitat and ensure its long-term survival are more crucial than ever. the rediscovery serves as a reminder of nature’s resilience and the ongoing need for vigilance in wildlife conservation. The world watches with bated breath as the story of the Madagascar ibis unfolds, hoping it marks the beginning of a new chapter for this remarkable species.