As of October 31, ‚ĀĘ2024, West and ‚Ā§Central Africa find themselves grappling with a pressing humanitarian crisis caused‚Ā§ by widespread flooding, exacerbated by heavy rainfall‚Äč and ‚Äćclimatic variability.‚Ā§ This comprehensive overview delves into the scale and impact of the flooding across the region,assessing its toll on ‚Äćcommunities,infrastructure,and agricultural livelihoods. Since ‚Ā§the onset ‚Ā£of the ‚Äčrainy season, affected countries have faced severe ‚Ā§disruptions, prompting urgent ‚ÄĆresponses from governments, non-governmental organizations,‚Ā£ and international agencies. This ‚Äćarticle will highlight key statistics, ongoing relief efforts, and the challenges ahead, providing a detailed snapshot ‚ĀĘof a ‚Äčsituation that ‚ÄĆcontinues to evolve as weather patterns change and recovery efforts intensify. ‚Ā£Thru this analysis,‚Ā§ we aim to shed light on the resilience of the affected populations and the vital need for ‚Ā£sustained ‚Ā£support in‚Ā£ the‚ÄĆ wake‚Äć of multiple disasters.
Impact‚ÄĆ of Recent Flooding Events on Local Communities
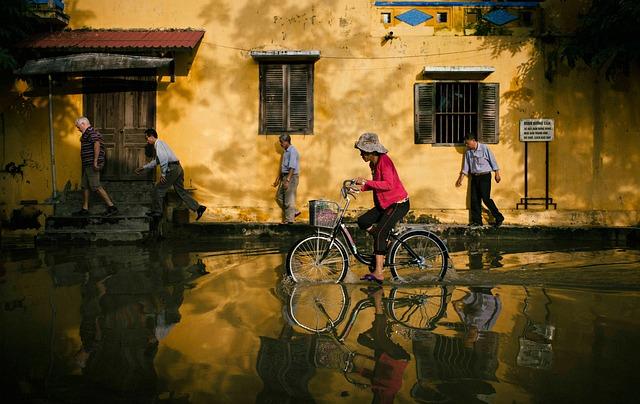
Recent ‚Ā§flooding events in West and‚ĀĘ central Africa have profoundly affected‚ÄĆ local communities, displacing‚Äč thousands and‚ĀĘ disrupting daily life.In‚Ā§ manny areas, the floods‚Äč have ‚ÄĆled to devastating consequences such as:
- loss of homes: Many residents have been forced ‚Ā§to evacuate‚Ā£ and seek refuge in temporary shelters, leading‚ĀĘ to a humanitarian crisis.
- Agricultural Devastation: Farmlands‚Ā§ have‚Äć been submerged, jeopardizing‚Ā§ food security and economic stability.
- Health Risks: Stagnant water has increased the likelihood of waterborne‚ĀĘ diseases, posing‚Äć a meaningful threat to community health.
The response to ‚Äćthese incidents has been challenging, as local governments and NGOs work tirelessly to provide necessary assistance. Though, the scale of destruction has overwhelmed existing resources, highlighting the urgent need for support‚Äć in the following areas:
- Emergency Relief Aid: Immediate supplies,‚Äč including food, clean water, and medical assistance, are crucial ‚Äčfor affected ‚Ā£populations.
- Infrastructure Repair: Restoration of damaged roads and ‚Ā§bridges‚Ā£ is vital to facilitate access to remote areas and expedite ‚Äčrecovery efforts.
- Long-term Resilience Strategies: Investing ‚Ā§in flood defenses and community training programs can ‚Ā§mitigate future risks ‚ĀĘand promote lasting recovery.
| Community Impact | Immediate Needs |
|---|---|
| Displaced Families | Temporary Housing |
| Food Shortages | Emergency Food Supplies |
| health Risks | Medical‚Ā£ Support |
| School Closures | Educational ‚ÄćResources |
Current Humanitarian ‚ÄćResponse Efforts and Gaps

The ongoing flooding crisis across West and Central Africa ‚Ā§has mobilized various humanitarian response efforts‚Äć aimed at‚Ā£ alleviating the ‚Äčsuffering ‚ĀĘof affected populations. Organizations such as the‚Äč United Nations Office‚ĀĘ for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (OCHA),‚Äč the International Federation of red Cross ‚Äčand ‚Ā§Red Crescent Societies ‚Äč(IFRC), and local ngos are actively providing essential services, including emergency shelter, food‚ĀĘ distribution, and healthcare. Key ‚Äčareas of‚ÄĆ focus in this response include:
- Emergency relief distribution – Providing food, clean water, and hygiene‚ÄĆ kits to displaced communities.
- Health services – Setting up ‚Äćmobile clinics to ‚Ā£combat waterborne diseases and providing mental health support.
- Restoration of livelihoods – Implementing income-generating programs aimed ‚Äčat‚Ā§ helping families recover.
Despite these efforts,‚Ā§ significant gaps remain in fully addressing the needs of affected‚Äć populations. Challenges include‚Äć limited access to remote areas due to ‚ĀĘdamaged ‚ĀĘinfrastructure and ongoing security concerns. Furthermore, funding shortfalls hinder the ability ‚ÄĆof organizations ‚ĀĘto scale up their response adequately. A recent assessment identified‚Äć crucial areas requiring immediate attention:
| Areas Needing attention | Current Status | Funding Requirement |
|---|---|---|
| water, sanitation, and Hygiene (WASH) | Insufficient clean water‚ĀĘ supply | $5 million |
| Health Services | Limited‚Ā§ access‚Äć to medical ‚Äćcare | $3 million |
| Food Security | Increased malnutrition rates | $7 ‚ÄĆmillion |
Assessment of Infrastructure Damage and Recovery Needs

As ‚Äćof late October 2024, ‚ÄĆthe‚Ā£ severe flooding in West‚ĀĘ and Central ‚ĀĘAfrica has resulted in considerable infrastructure damage‚Ā§ across ‚Äćseveral ‚ĀĘcountries. the impact ‚Ā§on essential services‚ÄĒincluding transportation,healthcare,and ‚Äčeducation‚ÄĒhas been profound,exacerbating the challenges faced by vulnerable communities. Key areas affected include:
- Road networks: Major highways and local‚ÄĆ roads have been rendered impassable, isolating communities and complicating relief efforts.
- Healthcare facilities: ‚Äć Numerous clinics and hospitals have suffered water‚Ā£ damage, disrupting services and jeopardizing patient care.
- Schools: Educational institutions are‚Äć temporarily closed, affecting children’s access to‚Äć learning and social support.
Recovery efforts must prioritize rehabilitating this critical infrastructure to restore normalcy and ‚Ā§improve‚ÄĆ resilience against future disasters. Stakeholders are urged to conduct comprehensive assessments‚ĀĘ to quantify the scale of ‚Äćdestruction and determine recovery needs. A preliminary evaluation indicates the following priorities:
| Priority Area | Estimated Needs (in USD) | Action Required |
|---|---|---|
| Road Restoration | 10 million | Immediate repairs and upgrades |
| Healthcare Facility Repairs | 5 million | Infrastructure rehabilitation and medical supplies |
| School ‚ÄćReconstruction | 7 million | Rebuild classrooms‚Äč and provide educational materials |
Public Health Risks Arising from Flood Conditions

Flood ‚ÄĆconditions in West and Central Africa exacerbate numerous public health risks, considerably impacting‚Äć vulnerable ‚Äćpopulations. ‚ÄĆStanding ‚Äćwater creates ‚Äčoptimal breeding grounds‚Äć for disease vectors, such as mosquitoes, increasing ‚Ā§the incidence of malaria, dengue fever, and other vector-borne‚Ā£ diseases. ‚ÄćAdditionally, the contamination of water‚ĀĘ supplies can lead to outbreaks of‚Ā§ waterborne‚ÄĆ diseases, including cholera and typhoid fever, as communities struggle‚Äć to access clean drinking‚ÄĆ water. This is particularly alarming in urban areas where sanitation systems‚ÄĆ may be overwhelmed, amplifying the risk of disease transmission.
Moreover, psychological impacts cannot be overlooked in the face of flooding. The stress,‚ÄĆ trauma, and loss experienced by affected individuals can ‚ĀĘlead to ‚Äčlong-term mental health challenges, including depression and anxiety.Access to healthcare services is frequently enough‚ĀĘ disrupted, leaving communities without adequate‚ÄĆ medical‚Ā£ support. the following factors are critical in understanding‚Ā§ the public health ‚ĀĘimplications of ‚ĀĘflooding conditions:
- Increased disease transmission ‚Ā§due to stagnant water and poor sanitation.
- Overburdened health systems, struggling to meet the ‚Äčrising demand for treatment.
- Psychosocial ‚ĀĘchallenges arising from ‚ÄĆdisplacement and loss ‚Äčof livelihoods.
Long-term Mitigation Strategies for Future Flooding Incidents
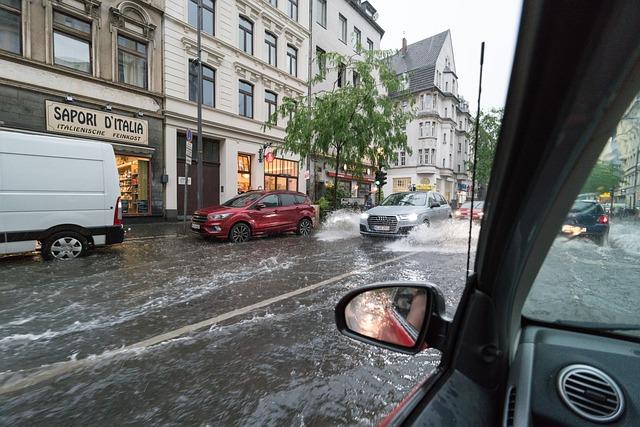

The‚Ā£ persistent threat of flooding in‚Äč West and Central Africa necessitates the development of comprehensive‚Ā£ long-term mitigation strategies. Key measures include:
- Enhancing Infrastructure Resilience: Investing in flood-resistant infrastructure such as levees,drainage systems,and water retention basins ‚Äčcan significantly reduce ‚ĀĘthe ‚ĀĘimpact of flooding.
- Implementing Ecosystem-Based Solutions: Protecting and restoring wetlands,‚Äć mangroves, and riverbanks can serve as natural buffers, absorbing excess ‚ÄĆrainwater and mitigating flood risks.
- Adopting Sustainable Land Use Practices: Encouraging sustainable agriculture and forestry management practices minimizes soil degradation and enhances the land’s ability to absorb rainfall.
- Investing ‚Äćin Early Warning Systems: developing ‚Äčrobust meteorological and hydrological monitoring systems improves response times and allows communities to‚ÄĆ prepare ‚Ā£for impending floods.
Moreover, collaboration among governments, ‚Ā£NGOs, and ‚ÄĆlocal communities is essential for effective flood management. Regular training and ‚Ā£awareness programs can empower communities to implement these‚Ā§ strategies. A collective approach might‚Ā§ include:
- Establishing Local Flood Management Committees: Involving community members‚Äč in decision-making can ensure that local knowledge‚Äč and‚Ā£ needs are incorporated‚ÄĆ into flood strategy planning.
- Facilitating Knowledge Exchange: Sharing best practices and experiences‚ÄĆ from regions less prone‚ĀĘ to flooding can provide ‚Ā§valuable insights into‚Ā§ effective adaptation techniques.
| Strategy | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|
| Infrastructure Investment | Reduced flood damage ‚ĀĘand improved recovery times |
| Ecosystem‚ÄĆ Restoration | Enhanced biodiversity and natural‚ÄĆ flood control |
| Early‚ÄĆ Warning‚Äć Systems | Increased ‚Ā§preparedness among communities |
Recommendations for International Aid‚Äć and Support ‚ÄćInitiatives

In light‚ÄĆ of the ongoing ‚Äčflooding‚Ā£ crisis in West ‚Äčand Central Africa, it‚Äć is ‚Ā§imperative for international aid organizations and local governments to collaborate on effective support initiatives. frist and foremost,‚Äć establishing ‚ÄĆa rapid response‚Äč mechanism is ‚ÄĆcrucial ‚Ā£to ensure timely delivery ‚ÄĆof resources. Aid should prioritize communities most ‚ÄĆaffected‚ÄĆ by the flooding, focusing on‚Ā£ the provision of essential supplies such as:
- Clean ‚Äćdrinking water to prevent waterborne diseases;
- Food security‚Ā£ interventions to support ‚ĀĘboth immediate needs and ‚Ā§long-term recovery;
- Medical assistance to treat injuries and illnesses ‚ÄĆcaused ‚Ā§by the flooding;
- Temporary shelter‚ÄĆ solutions ‚ÄĆ to protect displaced populations.
Additionally, strengthening local resilience should be at the forefront of international ‚Äčaid strategies.‚Ā£ This can be ‚ÄĆachieved ‚Ā£through community training programs focused on disaster preparedness and response. Key initiatives could include:
- Educational‚Ā£ workshops on climate adaptation‚Ā§ techniques;
- Investment in infrastructure to‚Äć improve drainage systems and flood‚Ā£ defenses;
- Partnerships with local NGOs to leverage community networks for more effective outreach and recovery efforts.
It is indeed ‚Äčessential to monitor the‚Äć effectiveness of these initiatives through regular assessments that allow for adaptive management of resources.By prioritizing both immediate relief and long-term sustainability, international aid ‚Äčcan ‚Äćsignificantly bolster the resilience of affected communities.
In Summary
As we draw this overview to a close, the flooding ‚ÄĆsituation in West and ‚ÄćCentral Africa remains a critical concern,‚Äč with extensive humanitarian implications.As of October ‚Ā£31, 2024, the ongoing impacts‚Ā£ of seasonal rains have exacerbated vulnerabilities across affected regions, displacing communities, damaging ‚Äčinfrastructure, ‚Äćand challenging existing relief efforts.
In light ‚ÄĆof these ongoing crises, it ‚ÄĆis indeed imperative for stakeholders‚ÄĒgovernments, international‚Äć organizations, ‚ĀĘand NGOs‚ÄĒto enhance their ‚ÄĆcollaborative response‚Ā£ strategies.‚Ā£ Continued monitoring and timely dissemination of‚Ā£ information will be vital in addressing the immediate needs of‚Ā§ those affected while also working‚Ā§ towards long-term resilience and ‚Äčrecovery ‚Äćsolutions.
The situation underscores‚ÄĆ the ‚Äćurgent need for ‚Äćcomprehensive disaster preparedness planning and climate adaptation strategies to mitigate the effects of future flooding. As we‚ĀĘ continue ‚Äćto follow this evolving scenario, the commitment to solidarity and support from the global community‚Äč will ‚Äćbe crucial in helping the affected populations rebuild their lives and regain‚Ā§ stability.‚ĀĘ For up-to-date reports and information, ‚ĀĘReliefWeb‚Ā§ remains a key resource ‚Ā£for stakeholders and the general public alike.







