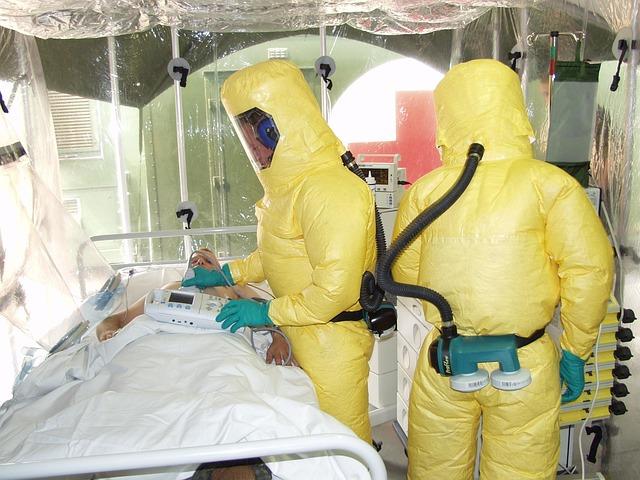
In a concerning development,health authorities in Uganda have reported a new cluster of Ebola cases,raising alarms among health officials and the international community. The African Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (Africa CDC) confirmed the emergence of this outbreak, which underscores the ongoing threat posed by the virus in the region. As efforts to contain the spread intensify, experts emphasize the need for swift intervention and public awareness to mitigate the impact of this deadly disease. Wiht UgandaS history of previous outbreaks, this latest incident serves as a stark reminder of the challenges faced in managing infectious diseases and the imperative for coordinated responses to safeguard public health. This article delves into the specifics of the outbreak, the response measures being enacted, and the implications for both local and global health security.
New Outbreak of Ebola Confirmed in Uganda Prompting Urgent Response

Health authorities in Uganda are scrambling to contain a newly identified outbreak of Ebola, with early reports indicating several confirmed cases in regions previously affected by the virus. The Africa Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (Africa CDC) has expressed concern regarding the rapid spread of this highly infectious disease. As frontline workers mobilize to respond, measures are being implemented to ensure public safety and reduce transmission risks among communities.
In response to the outbreak,the Ugandan government is coordinating with international health organizations to bolster it’s response efforts. The following actions are currently underway:
- Establishment of isolation units to treat infected individuals.
- contact tracing to identify and monitor individuals who may have been exposed.
- Community education campaigns to raise awareness about symptoms and prevention methods.
- vaccination plans to protect healthcare workers and vulnerable populations.
| Action | Description |
|---|---|
| Isolation Units | Designated facilities for treatment of confirmed cases |
| Contact Tracing | Tracking individuals who came into contact with infected persons |
| Community Education | Informing the public about symptoms and preventive measures |
| Vaccination Campaigns | Protecting at-risk populations through vaccination |
Health Authorities Mobilize Resources to Contain Ebola Threat

In response to the recent detection of a new Ebola cluster in Uganda, health authorities are rapidly mobilizing a variety of resources to mitigate the threat. Key interventions include:
- Surveillance Efforts: Enhanced monitoring in high-risk regions to quickly identify and isolate new cases.
- Healthcare Support: Deployment of additional medical personnel and equipment to treat affected individuals.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Informing communities about symptoms, transmission methods, and preventive measures through local media and outreach programs.
Additionally, regional and international organizations, such as the Africa CDC, are collaborating with local health ministries to ensure a coordinated response. A comprehensive strategy is being outlined, encompassing:
- Vaccination Strategies: Exploration of vaccine rollouts for frontline workers in at-risk areas.
- research Initiatives: Increased funding for research into treatments and effective response strategies.
- Resource Allocation: Financial and material support directed towards affected communities to bolster their healthcare infrastructure.
Impact on Public Health Infrastructure and Community Preparedness

The recent outbreak of Ebola in Uganda serves as a stark reminder of the vulnerabilities in public health infrastructure across Africa.Countries grappling with limited resources frequently enough face challenges in effectively responding to outbreaks. This situation underscores the importance of investing in health systems that not only enhance diagnosis and treatment but also facilitate rapid communication and coordination among local, national, and international health authorities. A robust system enables timely access to vaccines and essential medical supplies, which are critical in mitigating the spread of the virus.
Additionally, community preparedness plays a pivotal role in combating infectious diseases.Grassroots initiatives that focus on education and awareness can empower individuals to take proactive measures to protect themselves and their families. Key strategies include:
- Training healthcare workers: Ensuring that local personnel are equipped with the necessary skills to handle outbreaks.
- Engaging community leaders: Utilizing influencers to disseminate information and mobilize resources effectively.
- Conducting regular drills: Simulating outbreak scenarios to improve response times and community confidence.
| Essential Components | Impact on Preparedness |
|---|---|
| Surveillance Systems | Early detection of outbreaks |
| emergency Response Plans | Rapid mobilization of resources |
| Public Health Education | Informed communities |
Global Health Experts Assess Risks and Recommend Surveillance Measures

Considering the recent Ebola outbreak detected in Uganda,global health experts are raising alarms over the potential risks associated with the spread of the virus. The Africa CDC highlights that rapid mobilization and coordinated efforts will be vital in managing this emerging health crisis. Experts stress the importance of timely interventions, including:
- Enhanced surveillance: Monitoring and tracking the virus through genomic sequencing and contact tracing.
- Public health communication: Educating communities about symptoms and prevention methods to mitigate fear and misinformation.
- Resource allocation: Ensuring adequate supplies of vaccines and treatment for healthcare facilities within affected regions.
the Africa CDC also underscores the necessity for countries to collaborate and share valuable data. Establishing a regional response framework can be beneficial in controlling outbreaks before thay escalate. As part of these recommendations, specialists encourage building robust healthcare infrastructures. The following table outlines key recommended measures:
| Measure | description |
|---|---|
| Vaccination campaigns | Prompt deployment of vaccines in at-risk populations. |
| Health worker training | Training medical staff on Ebola symptom identification and management. |
| Community engagement | Involving local leaders to promote health practices. |
| Travel restrictions | Implementing cautious travel protocols to prevent the virus’ spread. |
vaccination Strategies and treatment Options Under Review
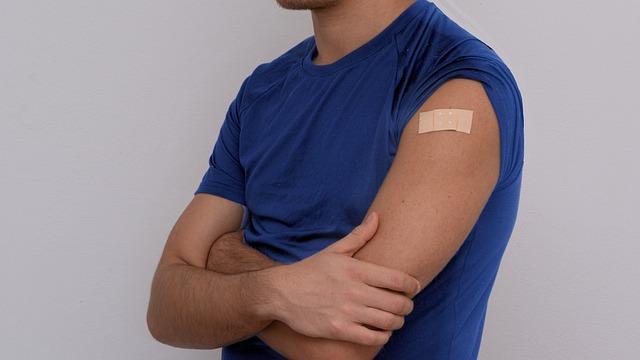
As health authorities grapple with the resurgence of Ebola in Uganda, several vaccination strategies are being considered to curb the outbreak’s spread. Key among these is the use of the rVSV-ZEBOV vaccine,which has demonstrated efficacy in previous outbreaks. In addition to this, choice candidates such as the Ad26.ZEBOV/MVA-BN-Filo vaccine regimen are currently under review, offering hope for adaptive vaccination approaches tailored to the evolving virus. Distribution logistics and community education will be crucial in ensuring these vaccines reach vulnerable populations effectively.
On the treatment front, investigational therapies are being evaluated for their ability to improve survival rates among infected patients. Prominent candidates include monoclonal antibodies like Inmazeb and Ebanga, which have shown promise in clinical trials. Other innovative treatments,such as antiviral medications and supportive care protocols,are also under consideration. The following table summarizes the current status of key treatment options:
| Treatment Option | Status | Efficacy |
|---|---|---|
| rVSV-ZEBOV Vaccine | Proven Efficacy | Up to 100% |
| Ad26.ZEBOV/MVA-BN-Filo | In Review | Pending Results |
| Inmazeb | Approved | Abbreviated Data |
| Ebanga | In Use | Encouraging |
community Engagement and Education Critical for Containment efforts

In the wake of the newly detected Ebola cluster in Uganda, the importance of community engagement has never been more paramount. Local populations are often the first line of defense against outbreaks, and their involvement in containment efforts is critical. This can be achieved through targeted awareness campaigns that focus on:
- Understanding Transmission: Educating communities on how Ebola spreads can help reduce stigma and promote safer practices.
- Recognizing Symptoms: Early identification of symptoms encourages timely medical intervention, which is crucial for controlling the virus.
- Promoting Hygiene Practices: Simple measures like handwashing and safe burial practices can considerably limit the spread of the virus.
Educational initiatives must also empower communities with relevant knowledge about the virus. Engaging local leaders to disseminate information fosters trust and drives community participation. This approach can be supplemented by establishing monitoring systems to assess health status and track potential outbreaks. The table below illustrates the key components for effective community involvement:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Awareness Campaigns | Dissemination of information regarding prevention and treatment. |
| Training Sessions | Workshops for health workers and community members on response strategies. |
| Feedback Mechanisms | Channels for community input to improve local response efforts. |
In Conclusion
the recent identification of a new Ebola cluster in Uganda underscores the persistent threat posed by this dangerous virus, despite past containment efforts.As health authorities mobilize resources and initiate rigorous contact tracing, the situation demands vigilant monitoring and swift action. The Africa CDC’s timely intervention highlights the importance of regional collaboration in managing outbreaks and protecting public health. As the world remains watchful, it is imperative that communities stay informed and adhere to health guidelines to mitigate the spread of the virus. Continued support for research and preparedness efforts will be crucial as Uganda navigates this latest challenge in the fight against Ebola.