In the face of escalating climate change challenges, small island nations like Mauritius are increasingly vulnerable to a range of environmental threats.As global temperatures rise and weather patterns become more erratic, understanding and mitigating these risks is essential for sustainable progress and resilience. Amid this pressing need, the Stimson Center has launched the CORVI initiative—a comprehensive framework designed to assess and prioritize climate risks in Mauritius. This article delves into the CORVI methodology,its implications for policy-making,and how it aims to empower local communities in navigating the complexities of climate adaptation. By highlighting the importance of data-driven insights and collaborative approaches, CORVI stands as a pivotal effort in safeguarding the future of Mauritius against the backdrop of a changing climate.
Understanding the CORVI Framework and Its Relevance to Mauritius
The CORVI Framework, short for Climate Outcomes and Risk Vulnerability Index, serves as a critical tool for assessing and prioritizing climate risks across various regions, including Mauritius. Designed to provide a comprehensive view of vulnerability and resilience, the framework integrates both quantitative and qualitative data to inform policymakers and stakeholders. For a nation like Mauritius, which faces pressing climate challenges such as rising sea levels, increased cyclonic activity, and biodiversity loss, the CORVI Framework is particularly relevant. It allows for a nuanced understanding of risk factors that are specific to the local context, enabling targeted actions to enhance climate resilience. The framework categorizes risks into several domains:
- Environmental Impact: Evaluation of how climate change affects local ecosystems and resources.
- Socio-Economic Factors: Analysis of the implications of climate risks on livelihoods, health, and local economies.
- Governance and Policy: Assessment of existing policies and institutional capacities to respond to climate challenges.
As mauritius continues to strategize its response to climate change, leveraging the insights provided by the CORVI Framework can considerably improve its adaptive capacity. The framework facilitates the prioritization of actions by comparing different climate risks and vulnerabilities, ensuring that the most pressing issues receive the attention they need. A sample evaluation of risks may look as follows:
| Risk Category | Impact Level | Urgency |
|---|---|---|
| Sea Level Rise | High | Immediate |
| Cyclonic Events | Medium | Short-term |
| Biodiversity Loss | Medium | Medium-term |
Key Climate Risks identified Through the CORVI Assessment
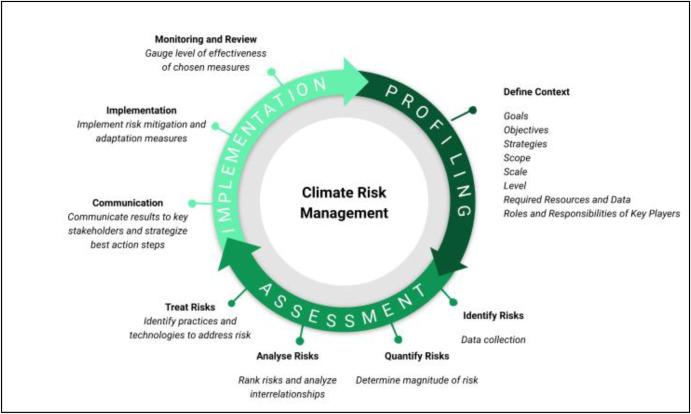
The CORVI assessment has spotlighted a range of critical climate risks that Mauritius faces, each bearing significant implications for the island’s communities and ecosystems. These risks encompass both direct impacts, such as increased frequency of extreme weather events, and secondary consequences affecting food security and human health. Some of the key risks identified include:
- Coastal Erosion: Rising sea levels threaten coastal infrastructure, leading to displacement and loss of arable land.
- Water Scarcity: Altered precipitation patterns are likely to decrease freshwater availability,impacting agriculture and drinking water supplies.
- Food Security: Increased temperatures and erratic rainfall jeopardize crop yields, challenging the food supply and farmer livelihoods.
- Public Health Risks: Climate change may exacerbate health issues, as rising temperatures facilitate the spread of vector-borne diseases.
The assessment also underscored vulnerabilities within key economic sectors, particularly tourism and fisheries. With the potential for decreased biodiversity and shifting marine ecosystems, the fishing industry may confront unsustainable yields. To better illustrate the interconnectedness of these risks, the following table summarizes the sectors most affected and their corresponding climate risks:
| Sector | Associated Risks |
|---|---|
| Tourism | Extreme weather events, loss of biodiversity, shoreline degradation |
| Agriculture | Water scarcity, increasing pest populations, reduced crop yields |
| Fisheries | Marine ecosystem shifts, declining fish stocks, overfishing |
impacts of climate Change on mauritius’ Ecosystems and Economy

Climate change poses a significant threat to Mauritius’ rich ecosystems, which are already under pressure from human activities and invasive species. The alteration of weather patterns has led to increased frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, including cyclones and heavy rainfall. These changes jeopardize biodiversity, particularly in fragile environments such as coral reefs and coastal mangroves. Some key impacts include:
- Coral bleaching: Rising sea temperatures threaten coral reefs that support marine life and local fisheries.
- Coastal erosion: Increased storm surges and sea-level rise endanger coastal habitats and communities.
- Endangered species: Flora and fauna unique to Mauritius face habitat loss and changing climates that affect their survival.
Beyond ecological consequences, the economy of Mauritius is also at risk, as many industries depend on stable environmental conditions. Tourism, a crucial sector that attracts visitors with its natural beauty, could suffer dramatically due to deteriorating ecosystems. Economic repercussions are seen across various sectors, including:
| sector | Impact |
|---|---|
| Tourism | Decline in visitor numbers due to damaged natural attractions. |
| Agriculture | Reduced crop yields from changing rainfall patterns and droughts. |
| Fisheries | Decreased fish stocks caused by ecosystem degradation and temperature shifts. |
Strategies for Mitigating Climate Risks in Vulnerable Communities

To effectively manage climate risks in vulnerable communities, it is indeed essential to adopt a multifaceted approach that encompasses the local socioeconomic dynamics and environmental factors. Community engagement is a cornerstone of successful risk mitigation strategies.By involving local populations in the planning and implementation processes,authorities can ensure that their strategies are culturally relevant and tailored to the specific needs of the community. This can be achieved through:
- Conducting regular workshops and training sessions to enhance local knowledge and awareness about climate risks.
- Creating platforms for community members to share their experiences and insights regarding climate adaptation.
- Establishing partnerships with local NGOs and academic institutions to leverage their expertise in developing practical solutions.
In addition to grassroots engagement, integrating data-driven approaches can significantly enhance resilience. Utilizing technology and data analysis can provide a clearer understanding of climate risks and inform evidence-based decision-making. Establishing a climate monitoring system can facilitate the identification of at-risk areas and allow for timely interventions. Key strategies include:
- Implementing predictive modeling to foresee extreme weather events and their potential impacts.
- Developing early warning systems that disseminate critical information to communities promptly.
- Investing in green infrastructure projects that not only mitigate risks but also provide sustainable economic benefits.
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Community Workshops | Engage residents in understanding and addressing local climate threats. |
| Climate Monitoring | utilize data systems to identify and predict climate-related risks. |
| Green Infrastructure | Implement eco-friendly projects to enhance both resilience and community wellbeing. |
Recommendations for policy Makers: Building Resilience in Mauritius

To enhance resilience against climate risks in Mauritius, policy makers should prioritize a comprehensive and inclusive approach that integrates climate adaptation strategies into all sectors of the economy. Investment in climate infrastructure,such as flood defenses and sustainable drainage systems,is crucial. Additionally, promoting sustainable agriculture practices can safeguard food security while reducing environmental impacts. Stakeholders at all levels should engage in community-led initiatives that empower local populations to take proactive measures in climate resilience.
Moreover, fostering partnerships between government agencies, civil society, and the private sector can lead to innovative solutions tailored to the unique challenges faced by communities in Mauritius. Key strategies to consider include:
- Strengthening Early Warning Systems: Enhance the capabilities for timely information dissemination during climate-related events.
- Implementing Education and Training Programs: Equip citizens with knowledge about climate risks and adaptive measures.
- Encouraging Research and Investment in Green Technologies: Promote initiatives that focus on renewable energy and sustainable practices.
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Community workshops | Facilitate sessions for knowledge sharing on climate adaptation strategies. |
| Policy Incentives | Provide financial incentives for sustainable practices in agriculture and industry. |
| Research Collaboration | Encourage partnerships with research institutions for evidence-based policy making. |
Future Directions for Climate Risk Management in the Indian Ocean Region
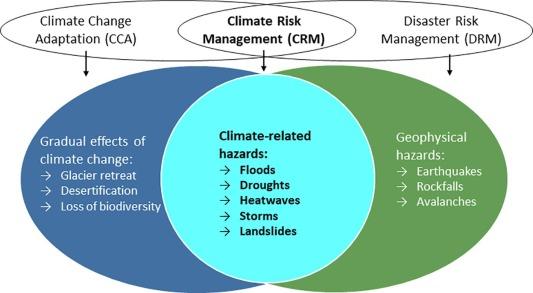
As the impacts of climate change intensify across the Indian Ocean region, the necessity for proactive climate risk management strategies becomes paramount. Regional collaboration will be essential in addressing shared vulnerabilities and ensuring adaptive capacities are strengthened. Key pathways include:
- Enhancing Regional Cooperation: Fostering collaboration between Indian Ocean nations to develop joint monitoring systems and response frameworks.
- Investing in Infrastructure Resilience: Upgrading essential infrastructure such as roads, ports, and utilities to withstand extreme weather events.
- Promoting Indigenous Knowledge: Leveraging local communities’ conventional practices and insights in formulating effective climate adaptation strategies.
Furthermore, advancing research initiatives and data-sharing platforms can yield significant benefits in understanding and mitigating climate risks. Initiatives to focus on include:
- Creating Comprehensive Climate risk Databases: Establishing platforms where stakeholders can access climate data and scientific research for informed decision-making.
- Integrating Climate Education: Implementing educational programs that equip communities with the knowledge and skills to adapt to climate changes.
- Encouraging Sustainable Practices: Supporting investments in renewable energy and sustainable agriculture to reduce vulnerability and enhance ecosystem resilience.
The Conclusion
As Mauritius navigates the increasingly complex challenges posed by climate change,the importance of robust risk assessments can hardly be overstated. The recent initiative by the Stimson Center, outlined in “CORVI: Assessing Priority Climate Risks in Mauritius,” highlights a proactive step toward identifying and strategizing against potential climate threats. By leveraging comprehensive data and engaging local stakeholders, this assessment not only helps to illuminate the most pressing risks facing the island nation but also serves as a foundation for resilience-building efforts.
The findings of the CORVI project underscore the critical need for aligned action among policymakers, community leaders, and residents in Mauritius.As the nation prepares to face the impacts of climate change, this collaborative approach promises a pathway to mitigating risks and safeguarding both the environment and the livelihoods of its people.
Moving forward, the recommendations derived from this assessment will play a pivotal role in informing strategic planning, resource allocation, and the implementation of effective climate adaptation measures. The ongoing efforts to address these findings will require sustained commitment and innovation, positioning Mauritius not only to respond effectively to emergencies but also to thrive in a rapidly changing world.
As we reflect on the implications of this crucial work,it becomes clear that ongoing dialog,research,and action will be essential in shaping a sustainable future for Mauritius in the face of an uncertain climate.