In an era characterized by increasing global trade tensions, the impact of trade policies enacted by major economies reverberates far beyond their borders. This is particularly evident in the case of Lesotho, South Africa, Nigeria, and Kenya, which find themselves navigating the complex repercussions of tariffs imposed by the Trump governance. As thes nations strive to maintain economic stability and foster growth, they face important challenges stemming from elevated trade barriers that threaten their export sectors. This article explores how the tariffs affect the economies of these four African countries, examining the broader implications for regional trade dynamics, employment, and investment. Through a closer look at the intricate relationship between U.S. trade policy and African economies, we uncover the vulnerabilities and resilience of nations caught in the crossfire of international economic rivalry.
Impact of Trump’s Tariffs on Lesotho’s Textile industry
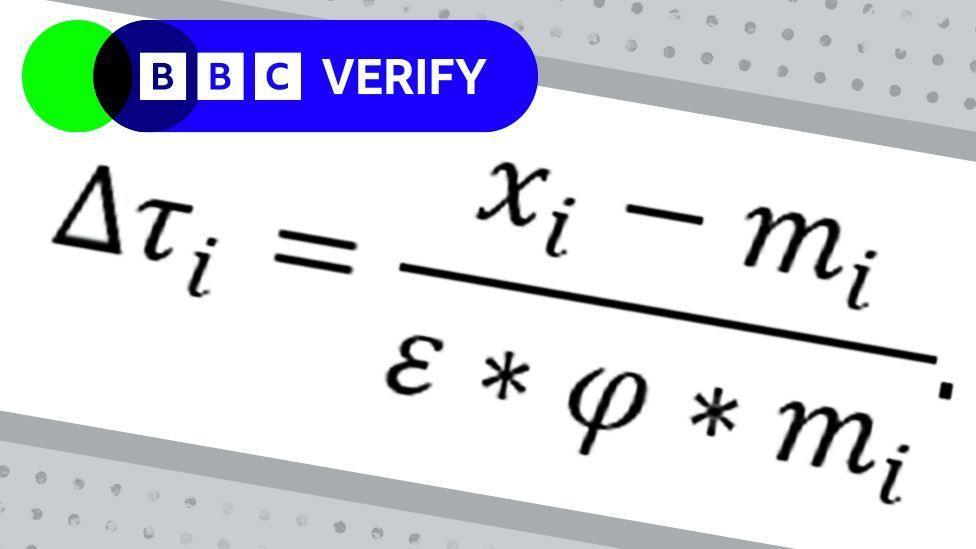
The imposition of tariffs by the Trump administration has had significant repercussions for Lesotho’s textile sector, which has long been a lifeline for the country’s economy and its workforce. As a member of the African Growth and Prospect Act (AGOA), Lesotho benefited from duty-free access to the U.S. market, allowing its garment manufacturers to thrive. However, the rise of tariffs has altered the competitive landscape, squeezing margins and escalating production costs. Factories that relied heavily on exports to the U.S. market have been confronted with diminished demand as retailers strive to avoid the added expenses associated with tariffs.
Moreover, the economic ripple affect on Lesotho’s economy has proven profound. The textiles industry is intertwined with local employment,with thousands of workers depending on these factories for their livelihoods. The fallout from reduced orders has lead to job cuts, factory closures, and the decline of local suppliers. As a countermeasure, many companies have sought to diversify their markets, pivoting towards Europe and other regions, but the challenges remain formidable. With the looming threat of tariffs creating uncertainty, investment in the textile sector has stalled, leading to a growing concern about the long-term sustainability of Lesotho‚Äôs economic fabric.
Economic Ramifications for South African Manufacturing Sectors

The imposition of tariffs by the U.S. government has reverberated through the South African manufacturing sectors,causing significant economic strain. Key industries, including textiles, automotive, and machinery, have faced enhanced costs and reduced competitiveness in international markets. Consequently, many manufacturers are experiencing a downturn in demand for their exports. This shift not only threatens job security for thousands but also challenges the long-term viability of several sectors, which rely heavily on the export market for growth and innovation.
Trade relationships are increasingly fragile,with South African manufacturers struggling to adapt to the new tariff landscape. Some of the notable impacts include:
- Increased Production Costs: Sourcing raw materials has become more expensive, leading to higher prices for end consumers.
- Investment Slowdown: Companies are hesitant to make new investments in capacity expansion amid uncertainty about future tariff policies.
- Job Losses: As demand shrinks, companies may resort to layoffs or hiring freezes, exacerbating unemployment in the sector.
| Sector | Impact of Tariffs |
|---|---|
| Textiles | Higher import costs leading to decreased exports and potential closures. |
| Automotive | Reduced access to U.S. markets, affecting production plans and workforce. |
| Machinery | Increased manufacturing costs,impacting competitiveness against foreign firms. |
Nigerian Agricultural Exports at Risk: Analyzing Vulnerabilities

The impact of Donald Trump’s tariffs on agricultural exports has significant implications for nigeria, where the economy is heavily reliant on agricultural trade. Tariffs have hampered the competitiveness of Nigerian goods in international markets, particularly in sectors like cocoa, sesame seeds, and yams. The uncertainties introduced by these tariffs not only affect pricing but also disrupt established supply chains, with farmers struggling to meet international demand. This situation could lead to job losses, reduced income, and a destabilization of the agricultural sector, which remains a critical component of Nigeria’s economy.
Moreover, the vulnerabilities within Nigeria’s agricultural export framework are exacerbated by a lack of infrastructure and technological advancement. Many farmers still face challenges in reaching local and international markets due to poor transportation networks and insufficient storage facilities, resulting in post-harvest losses. The table below outlines crucial agricultural products that are facing difficulties due to tariff-related constraints:
| Product | impact of Tariffs |
|---|---|
| cocoa | Reduced global competitiveness, lower prices |
| Sesame seeds | Increased export costs, loss of market share |
| Yams | Decreased demand, potential job losses |
Kenya’s Trade Balance: navigating New Challenges in a Global Market
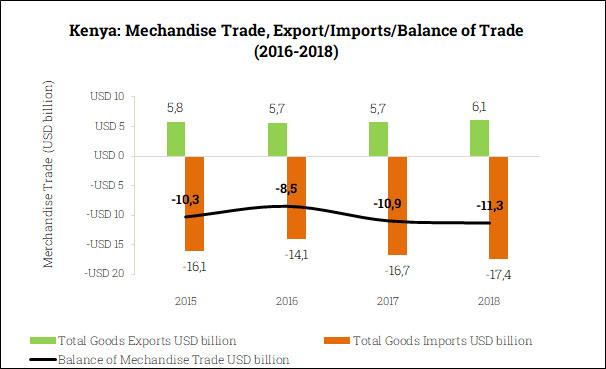
kenya’s trade balance is experiencing significant pressures as the global market evolves and nations grapple with the implications of protective trade policies. The imposition of tariffs by the United States under the Trump administration has sent ripples through the economies of multiple African nations, including Kenya.Key industries such as agriculture and textiles,which have traditionally relied on exports to the U.S., are facing heightened competition and reduced market access. This situation is exacerbated by rising costs of raw materials and logistic challenges, prompting the government to explore new trade partnerships and strategies to stabilize the economy.
In light of these challenges, Kenya is adopting several measures to enhance its trade resilience. The government is focusing on diversifying its export markets and products by leveraging trade agreements with neighboring countries and seeking new ties with emerging markets. Additionally, there is an emphasis on boosting local production to reduce dependency on imports and minimize trade deficits. Some key strategies include:
- Investing in infrastructure: Upgrading ports and transport networks to facilitate smoother trade.
- Enhancing local industries: Supporting small and medium-sized enterprises to scale and compete internationally.
- promoting innovation: Encouraging technology adoption in agricultural practices to improve output and quality.
As these initiatives develop, the importance of robust economic policies and active engagement in international trade discussions remains paramount for Kenya to navigate the complexities of today’s global market.
Recommendations for Mitigating Tariff Impacts on African Economies

To effectively address the challenges posed by tariffs, African nations can adopt several strategic measures aimed at bolstering their economies. Firstly, countries like Lesotho and Kenya should focus on diversifying their export markets. By expanding trade relationships beyond conventional partners, these nations can reduce dependency on U.S. markets and mitigate the impacts of tariffs. Additionally, fostering regional trade agreements within the African continent could enhance intra-African trade and strengthen economic ties among neighboring countries. This collaborative approach can be pivotal in creating a more resilient trade framework.
Moreover, investment in local industries and innovation is essential for long-term sustainability. Governments in South Africa and Nigeria could prioritize funding for sectors such as agriculture and manufacturing to stimulate domestic production capabilities, thereby reducing reliance on imported goods. This focus not only fortifies local economies but also enhances job creation. Governments should also consider establishing safety nets for adversely affected workers,including retraining programs and support for small enterprises,to cushion the workforce during transitions caused by tariff discrepancies.
Strategic Responses: Strengthening trade Alliances and Diversification Efforts
The recent introduction of tariffs by the Trump administration has prompted several African nations, including Lesotho, South Africa, Nigeria, and Kenya, to reassess their trade strategies. In response to these economic pressures, countries are increasingly focusing on strengthening trade alliances with one another and with other global partners. By forming regional trade agreements, they can enhance market access, reduce dependency on traditional trading partners, and mitigate the impacts of unilateral tariff policies. African nations are also seeking to leverage platforms such as the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA) to bolster intra-African trade and promote a more resilient economic landscape.
Moreover, diversification efforts are becoming crucial for these nations as a means to offset reliance on a limited range of export markets. Countries are initiating programs aimed at expanding their economic base and developing industries that can withstand external shocks. Strategies include:
- Encouraging local manufacturing and agricultural production to reduce import dependency.
- Investing in technology and innovation to improve product quality and competitiveness.
- exploring non-traditional markets in Asia and Latin America to open new avenues for trade.
This move towards diversification not only aims to cushion economies from tariff impacts but also strives to create sustainable growth pathways that enhance resilience and self-sufficiency.
wrapping Up
the imposition of tariffs by the Trump administration has had significant repercussions for countries such as Lesotho, South Africa, Nigeria, and Kenya. These nations, which have traditionally relied on trade with the United States to bolster their economies and create job opportunities, now face a challenging landscape marked by uncertainty and potential economic downturns. As these countries grapple with the fallout, the broader implications for trade relations and economic stability in the region cannot be overlooked.Stakeholders must navigate this complex habitat with strategic measures to mitigate the adverse effects of tariffs while seeking new avenues for growth.Understanding the nuances of these economic shifts will be crucial for policymakers and businesses alike as they adjust to an evolving global trade framework.







