in recent years, France’s military presence in Africa has come under increasing scrutiny, as a wave of anti-French sentiment and a shifting geopolitical landscape push the nation to reassess its role on the continent. driven by a complex interplay of local nationalism, allegations of neocolonialism, and the rise of new partnerships with global powers like Russia and China, several African nations have begun to sever military ties with France. this trend reflects a broader transformation in Africa’s security dynamics and a growing desire among countries to assert their sovereignty. The Associated Press examines the factors contributing to France’s military withdrawal from various African nations, highlighting the implications for regional stability and the future of international relations in a rapidly changing world.
France’s Military Presence in Africa: A Historical Overview
France’s military involvement in Africa traces back to colonial times,when the French Empire sought to establish and maintain control over vast territories across the continent. Post World War II, as decolonization swept through Africa, France managed to retain its influence through a series of military agreements and interventions. This strategy was particularly evident in West and Central Africa, where France deployed forces under the guise of protecting its interests and ensuring stability. Key operations included interventions in Chad, Mali, and the Central African Republic, showcasing a dual objective: countering threats like terrorism while safeguarding French economic interests, especially in resource-rich regions.
However, the tides have changed in recent years. Increasing anti-french sentiment in several former colonies has led to a pushback against French military presence. Factors driving this shift include rising nationalism,disillusionment with the perceived neocolonial patronage,and growing aspirations for self-determination among African nations. Additionally, other global powers, such as Russia and China, have begun to step into the void left by France, offering option partnerships that appeal to many african nations. Consequently, the landscape of military alliances in africa is rapidly evolving, reflecting a meaningful shift away from traditional western dominance.
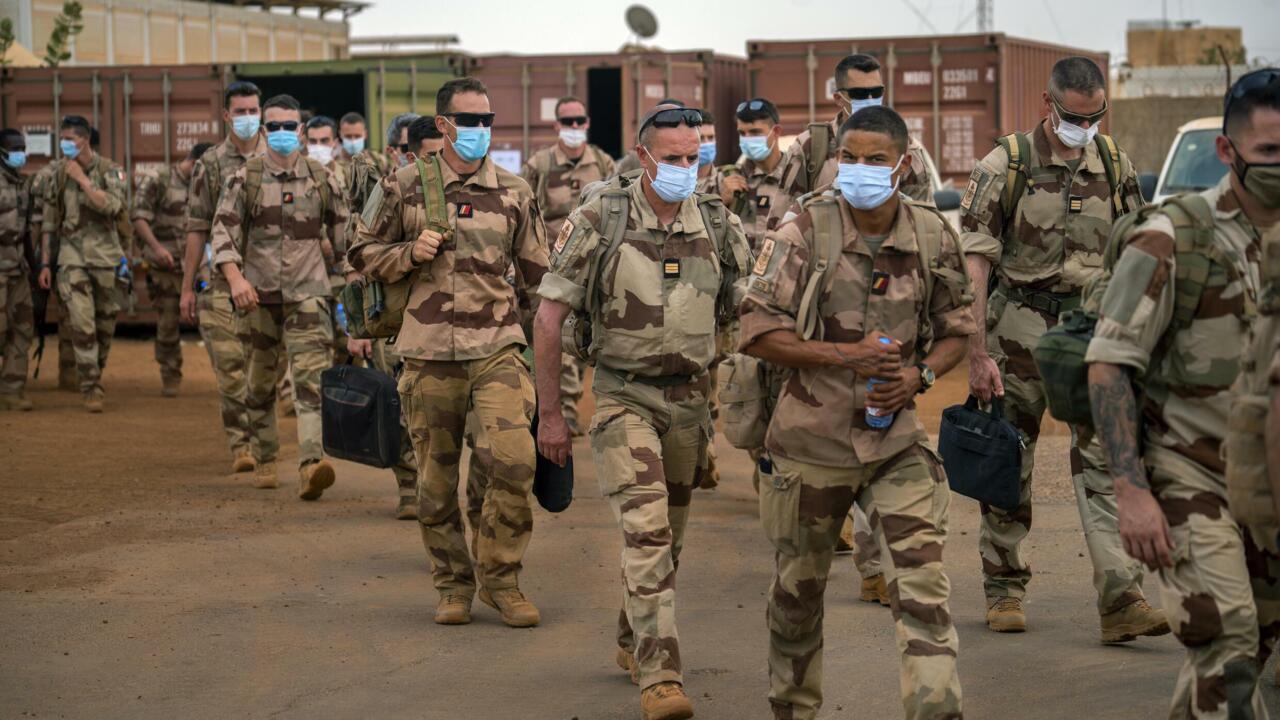
shifts in African Sentiment: Rising Nationalism and Anti-Colonial Sentiments
Across the African continent, national sentiment is undergoing a significant transformation, marked by a surge of pride in local identities and a fervent rejection of foreign military presence. This growing nationalism is fueled by a combination of factors, including historical grievances from colonial rule and a desire for self-determination. Many African nations are increasingly asserting their sovereignty and redefining their relationships with former colonial powers. Consequently, this has led to heightened public support for local governance and military forces, which are often viewed as more in tune with the aspirations of the people.
As feelings of nationalism rise, so to do anti-colonial sentiments. Citizens are voicing their frustrations through protests, policy demands, and social media campaigns, calling for an end to what they perceive as neo-colonial practices. Countries like Mali and Burkina Faso have exemplified this trend by actively seeking the withdrawal of French troops, emphasizing their autonomy in addressing security issues. This shift in perspective can be seen as part of a wider movement towards resurgence in local governance and as an prospect to re-evaluate alliances that have, for too long, prioritized foreign interests over the needs of African nations.

Geopolitical Rivalries: The Role of Russia and China in Africa
The shifting dynamics in Africa have created a fertile ground for both Russia and China to expand their influence as France’s military presence wanes. With a growing sense of nationalism and a desire for self-determination,many African countries are increasingly rejecting the post-colonial military support historically provided by France. In contrast, Russia and China are stepping in to fill the void, leveraging economic partnerships, military support, and soft diplomacy.Their approach frequently enough aligns with a broader strategy aimed at countering Western dominance in the region, prioritizing access to natural resources and securing lucrative contracts.
Russia’s presence is marked by an increased number of private military contractors and a series of arms deals that bolster local militaries. Meanwhile,China’s engagement is characterized by significant investments in infrastructure and technology,with projects ranging from highways to telecommunications,all packaged with political goodwill. The impact of these geopolitical rivalries is profound, as African nations navigate a complex terrain of self-identity and sovereignty while balancing between former colonial powers and emerging superpowers. This new alignment has implications for stability and governance in the region, as countries work to attract foreign investments while safeguarding their political autonomy.

The Impact of Troop Withdrawals on Regional Stability
The recent trend of troop withdrawals from African nations by France has led to a significant reevaluation of power dynamics within the region. As French forces withdraw, several factors come into play that could perhaps destabilize long-established security frameworks. Regional powers and local militias may seize the opportunity to fill the void left by a diminished French presence. This has raised concerns over the resurgence of extremism, as groups previously kept at bay by foreign troops may exploit the ensuing power vacuum. The shift also poses risks to established agreements and partnerships that had relied on French military support, potentially leading to a breakdown of previously stable relationships.
Furthermore, the geopolitical landscape in Africa is becoming increasingly polarized, as nations may seek alliances with non-Western powers in the absence of French support. The withdrawal could accelerate this trend, creating a new breed of rivalry among global players like Russia and China in the region. It is critical for local governments to step up their internal security measures to prevent chaos and maintain peace. Key implications may include:
- Increased extremism: As local insurgent groups feel emboldened.
- Shifts in alliances: Countries may pivot towards rival global powers.
- Impact on humanitarian efforts: aid deliveries may become more arduous.
In light of these developments, it might potentially be crucial for regional leaders and international organizations to reassess their strategies in order to foster cooperation and stability. Preparing for potential unrest and establishing frameworks for security cooperation among African nations will be vital to mitigating the potential negative consequences of troop withdrawals.

Strategies for Future Engagement: Building Partnerships without Military Presence
As the dynamics of international relations evolve,it is imperative for countries to explore innovative strategies for collaboration that do not rely on military presence. One effective method is fostering economic partnerships through investment in local infrastructure and sustainable progress projects. By providing support in areas such as education,health,and technology,nations can build trust and long-lasting relationships. This approach not only empowers local communities but also creates a stable environment conducive to mutual growth. Engaging local stakeholders, such as community leaders and businesses, ensures that initiatives are aligned with the needs and desires of the population.
Additionally, cultural diplomacy serves as a powerful tool to strengthen ties without military involvement. By promoting cultural exchanges, art exhibitions, and academic collaborations, countries can enhance their soft power and foster a sense of camaraderie. Initiatives such as youth programs and language training reinforce interpersonal connections and promote a shared understanding. Establishing a framework for dialog and cooperation can facilitate discussions on critical issues like climate change, public health, and regional security, ultimately leading to a more engaged and cooperative relationship.

Recommendations for france: Adapting Foreign Policy to New Realities in Africa
France’s strategic shift in Africa necessitates a reevaluation of its foreign policy framework. To reestablish trust and enhance cooperation with African nations, the French government should consider the following approaches:
- Fostering economic partnerships: Transition from a military-centric presence to establishing robust economic ties that empower local economies and foster sustainable development.
- Supporting local governance: Prioritize assistance to strengthen democratic institutions and encourage political stability through transparent electoral processes.
- Enhancing cultural diplomacy: Promote cultural exchanges and educational initiatives that celebrate African heritage and French ties, improving mutual understanding.
- Engaging in multilateralism: Collaborate with regional organizations such as the African Union to address shared challenges collectively, reinforcing France’s commitment to African sovereignty.
Moreover, revising the narrative surrounding military intervention is crucial for France’s long-term interests in Africa. It is essential to transition towards:
- Counterterrorism assistance: Focus on intelligence-sharing and training local forces to combat extremist threats without direct military involvement.
- Sustainable development goals: Invest in infrastructure and health initiatives that address the root causes of instability and extremism.
- Public diplomatic outreach: Develop a dialogue strategy that openly addresses past operations while highlighting positive contributions to African nationsŌĆÖ development.

In Retrospect
France’s gradual withdrawal from various African countries marks a significant shift in its historical military presence on the continent. This reconfiguration of military engagement arises from a complex interplay of local political dynamics, rising anti-colonial sentiments, and the evolving landscape of global alliances. As African nations seek greater autonomy in their security affairs, the implications of this transition will resonate far beyond the immediate geopolitical realm. Understanding these changes is crucial, as they not only reflect the transformations within Africa but also indicate the broader challenges Western powers face in maintaining influence in a rapidly changing world. The future of Franco-African relations will depend on how both sides navigate this landscape, while ensuring stability and fostering mutual respect.







