In a remarkable archaeological discovery, Egyptian authorities have unveiled a series of ancient stone blocks believed to have originated from the temple of the illustrious 18th dynasty queen, Hatshepsut. This notable find, reported by Reuters, underscores the ongoing efforts to unearth the rich history of Ancient Egypt and shed light on one of its most powerful female pharaohs. Hatshepsut, who reigned over 3,500 years ago, is celebrated for her ambitious building projects and innovative reign, which challenged the traditional gender roles of her time. The recent excavation, which adds to the growing body of evidence about her influence and legacy, offers new insights into the architectural and cultural achievements of a civilization that continues to captivate historians and enthusiasts alike. as archaeologists meticulously analyze the site, the implications of this discovery may reveal further intricacies about Hatshepsut’s life and the remarkable era she represented in Egyptian history.
Egyptian Archaeologists Discover 18th Dynasty Blocks from Hatshepsut Temple
In a remarkable development, Egyptian archaeologists have unveiled a treasure trove of ancient blocks believed to be remnants of the temple dedicated to the powerful female pharaoh Hatshepsut, dating back to the 18th Dynasty. The discovery was made near the Valley of the Kings,a site already rich in archaeological meaning. The blocks, characterized by their finely scripted hieroglyphics and intricate carvings, provide invaluable insight into the religious and cultural practices that flourished during Hatshepsut’s reign. Excavations revealed that these blocks were likely part of a grand architectural scheme, showcasing the artistic talents of the era.
The temple of Hatshepsut, one of the few female pharaohs of ancient Egypt, is known for its majestic design and has long fascinated historians and archaeologists alike. The newly discovered blocks are expected to contribute to a deeper understanding of her rule, which is frequently enough celebrated for its significant contributions to art, trade, and architecture. Preliminary analyses suggest that these blocks may have originally formed part of a larger wall or structure within the temple complex. The significance of this find aligns with Egypt’s ongoing efforts to promote its archaeological heritage,attracting both scholarship and tourism to its ancient sites. Key details of the discovery include:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Date Discovered | October 2023 |
| Location | Near the Valley of the Kings |
| Era | 18th Dynasty |
| Significance | Insights into Hatshepsut’s reign |
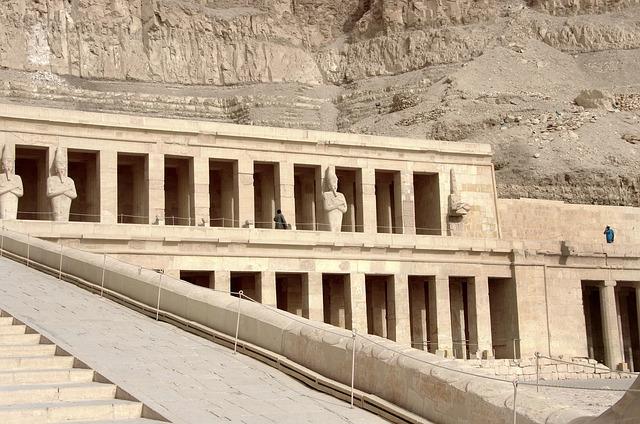

Significance of Hatshepsut’s Legacy in Ancient Egyptian History
Hatshepsut’s reign marked a pivotal point in the history of ancient Egypt, as she broke from tradition to become one of the few female pharaohs. Her era was distinguished by significant building projects, notably her mortuary temple at Deir el-Bahari, which stands as an architectural marvel highlighting her prowess as a leader. During her reign, Hatshepsut fostered trade expeditions, notably to Punt, which not only enriched Egypt’s economy but also expanded its cultural horizons. This diversification of Egypt’s wealth under her governance exemplifies her ability to elevate the nation during a time when female leaders were often marginalized.
The discovery of blocks from Hatshepsut’s temple reinforces her enduring legacy,showcasing the importance of her contributions to Egyptian society. beyond her ambitious construction projects, she was revered for her diplomatic skills and ability to navigate the complexities of power. her portrayal in art and inscriptions often emphasized her divine right to rule, melding femininity with authority in a traditionally patriarchal society. The significance of her legacy can be captured through the following key points:
- Empowerment: Hatshepsut paved the way for future female leadership.
- cultural Exchange: Her trade initiatives heightened Egypt’s influence and access to foreign goods.
- Architectural Innovation: Her temple remains a testament to ancient Egyptian engineering prowess.

The Uncovering Process: techniques and Technologies Used by Archaeologists
The uncovering process in archaeology relies on a combination of traditional techniques and cutting-edge technologies. Archaeologists often start their work by employing manual excavation, which allows for careful removal of soil and debris in a stratified manner. this meticulous technique minimizes damage to historical artifacts and structures. In addition, tools such as trowels, brushes, and shovels are indispensable for detailing fine features and ensuring the preservation of delicate materials. Supplementing these tools are modern technologies that enhance their ability to locate and excavate buried relics:
- Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) – This non-invasive method uses radar pulses to image subsurface structures and detect anomalies.
- 3D Scanning – Utilized for detailed documentation of finds, allowing for precise reconstruction of excavation sites.
- GIS Mapping – Geographic Data Systems enable archaeologists to plot artifacts and features spatially, revealing patterns and relationships.
In addition to these methods, dendrochronology and radiocarbon dating are crucial for establishing the chronology of discovered items, helping researchers piece together historical timelines. As archaeologists and scientists collaborate, the integration of techniques allows for multidisciplinary insight, enhancing our understanding of ancient civilizations like that of Queen Hatshepsut. For instance,advanced excavation methods supported by stratigraphic analysis are crucial in ensuring a holistic interpretation of the context surrounding each find. This is particularly valuable when assessing the significance of monumental structures and the societal implications thay hold:
| Technique | Description |
|---|---|
| Manual Excavation | Careful removal of soil by hand to find artifacts. |
| Ground Penetrating Radar | uses radar to visualize underground features without excavation. |
| 3D Scanning | Creates digital records of artifacts for analysis and preservation. |
| GIS Mapping | Spatial analysis to visualize artifact distribution and context. |

Implications for Future Excavations in Luxor and Beyond
The recent discovery of blocks from the 18th dynasty Queen hatshepsut temple not only enriches our understanding of ancient Egyptian architecture but also sets an exciting precedent for future archaeological endeavors in Luxor and surrounding areas.As researchers delve into this site, they may uncover additional artifacts and structural elements that provide insight into this remarkable period of Egyptian history. The implications of this discovery extend beyond a single site, suggesting a broader network of temples and monuments that await exploration. Future excavations could focus on:
- Interconnectedness of Sites: Investigating how temples were linked, revealing cultural exchanges and the religio-political landscape.
- Architectural innovations: Analyzing construction techniques and materials used during the 18th dynasty, possibly influencing modern archaeological practices.
- Artifact Recovery: A comprehensive strategy to recover and preserve artifacts that could provide invaluable historical context.
This discovery also emphasizes the need for interdisciplinary collaboration among archaeologists, historians, and conservationists. By pooling their expertise, they can maximize the impact of findings and ensure that significant sites like those linked to Hatshepsut are meticulously documented and preserved for future generations. Alongside traditional excavation methods, innovative technologies such as ground-penetrating radar and 3D imaging could play a crucial role in revealing hidden treasures beneath the sands of Luxor. The potential findings from future excavations could lead to:
| Potential Findings | Significance |
|---|---|
| New Artifacts | Enhanced understanding of daily life in ancient Egypt. |
| additional Monuments | Insights into the scale and influence of Hatshepsut’s reign. |
| Burial Sites | Mapping royal lineage and cultural practices. |

Cultural Heritage Preservation: Recommendations for Maintaining Newly Discovered Artifacts
The recent discovery of the blocks from the 18th dynasty queen Hatshepsut temple highlights the importance of effective management strategies for newly uncovered artifacts. Preserving these historical treasures requires a multifaceted approach that includes scientific analysis, conservation techniques, and community engagement. Key recommendations for maintaining these artifacts include:
- Thorough Documentation: Record the context of each artifact, including its location and condition at the time of discovery.
- Environmental Controls: Implement humidity and temperature monitoring to mitigate deterioration risks from environmental factors.
- Restoration Protocols: Develop systematic methods for restoring artifacts while ensuring the integrity of the original materials is preserved.
- Education and Training: Provide training for local conservators and archaeologists to foster expertise in preservation techniques.
Furthermore, collaboration with local communities can amplify awareness and support for heritage preservation.by involving residents in the narrative of their cultural legacy, authorities can ensure a deeper commitment to safeguarding these treasures.Establishing community outreach programs and initiatives that focus on:
- Workshops: Invite community members to learn about artifact care and cultural significance.
- Volunteer Programs: Engage local volunteers in preservation activities to strengthen community ties and historical pride.
- Exhibitions: Create opportunities for the public to interact with artifacts through exhibitions, showcasing the importance and beauty of their heritage.

Engaging the Public: How Discoveries Can Enhance Tourism and Education in Egypt
Recent archaeological discoveries at the temple of Queen Hatshepsut have reignited interest in Egypt’s ancient civilization, presenting a unique opportunity to integrate these findings into both tourism and education. By showcasing new artifacts and historical context, visitors can engage deeply with Egypt’s rich heritage. The incorporation of interactive exhibits and guided tours that reflect the latest discoveries can substantially enhance the tourist experience,leading to increased visitor numbers,thereby stimulating the local economy and promoting cultural preservation.
Moreover, educational programs designed around these discoveries can be instrumental in schools and universities. by utilizing multimedia resources and immersive workshops based on recent archaeological findings, students can grasp the importance of Egypt’s ancient history in a modern context. Such initiatives can include:
- Hands-on workshops with replica artifacts
- Virtual reality experiences of the temple
- Collaborative projects with local museums
| Aspect | Impact |
|---|---|
| Tourism Growth | Increased visitors and revenue |
| Education | Enhanced learning experiences |
| Cultural Awareness | Greater understanding of history |
Concluding Remarks
the recent discovery of large blocks from the temple of Queen Hatshepsut marks a significant archaeological find, shedding light on the grandeur of one of Egypt’s most remarkable pharaohs. This 18th Dynasty structure, dedicated to Hatshepsut, stands as a testament to her reign and the architectural advancements of ancient Egypt. As excavations continue, researchers hope to uncover more artifacts that could further illuminate the historical narrative surrounding Hatshepsut’s legacy and the broader cultural context of her time. This uncovering not only adds depth to our understanding of Egyptian history but also highlights the ongoing significance of archaeological efforts in revealing the past. As Egypt opens new chapters in its ancient history, the efforts to preserve and investigate these ruins will undoubtedly enrich our gratitude of this remarkable civilization.